Abstract
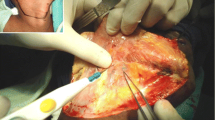
In the current scenario, the management of N0 neck in early-stage oral cancer is debatable, whether or not they should undergo elective neck dissection. Most of the time these patients are either over-treated or under-treated. Sentinel lymph node (SLN) biopsy is a good option to identify occult LN in this cohort of patients for guiding neck dissection. With a focus on SLN biopsy using methylene blue dye, this study aims to evaluate its feasibility and accuracy in node-negative oral squamous cell carcinoma. A prospective observational study was conducted involving operable squamous cell carcinoma patients with clinically and radiologically node-negative neck. Methylene blue was injected in the peritumoral area and after that SLN was identified and then neck dissection was completed. Of 47 patients, SLN was identified in 82.98%, with 53.85% having more than two SLN. Common locations were in levels IB, IA and IIA. Occult metastasis was observed in 12.82% of cases, predominantly in T2 patients. Sensitivity, specificity and NPV were 50%, 100% and 88.89% respectively. The study affirms the feasibility and accuracy of methylene blue-assisted SLN biopsy in oral cancer. Despite a high detection rate, methylene blue dye alone should not be used for SLN identification in oral cavity cancer. However, it can be used as an adjunct of lymphoscintigraphy to increase the yield of the procedure. Multi-institutional trials with larger cohorts may provide valuable insights and more information for comprehensively addressing the limitations of this technique and its broader applicability in decision-making, particularly in resource-constrained countries like India where lymphoscintigraphy is not readily accessible.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin MB, Greene FL, Edge SB, Compton CC, Gershenwald JE, Brookland RK et al (2017) The eighth edition AJCC cancer staging manual: continuing to build a bridge from a population-based to a more “personalized” approach to cancer staging. CA Cancer J Clin 67(2):93–99
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71(3):209–249
Shah JP, Candela FC, Poddar AK (1990) The patterns of cervical lymph node metastases from squamous carcinoma of the oral cavity. Cancer 66(1):109–113
Shah JP, Andersen PE (1994) The impact of patterns of nodal metastasis on modifications of neck dissection. Ann Surg Oncol 1(6):521–532
Civantos FJ, Zitsch RP, Schuller DE, Agrawal A, Smith RB, Nason R et al (2010) Sentinel lymph node biopsy accurately stages the regional lymph nodes for T1–T2 oral squamous cell carcinomas: results of a prospective multi-institutional trial. J Clin Oncol 28(8):1395–1400
Alkureishi LWT, Ross GL, Shoaib T, Soutar DS, Robertson AG, Thompson R et al (2010) Sentinel node biopsy in head and neck squamous cell cancer: 5-year follow-up of a European multicenter trial. Ann Surg Oncol 17(9):2459–2464
Govers TM, Hannink G, Merkx MAW, Takes RP, Rovers MM (2013) Sentinel node biopsy for squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity and oropharynx: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Oral Oncol 49(8):726–732
Pezier T, Nixon IJ, Gurney B, Schilling C, Hussain K, Lyons AJ et al (2012) Sentinel lymph node biopsy for T1/T2 oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma—a prospective case series. Ann Surg Oncol 19(11):3528–3533
Broglie MA, Haerle SK, Huber GF, Haile SR, Stoeckli SJ (2013) Occult metastases detected by sentinel node biopsy in patients with early oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas: impact on survival. Head Neck 35(5):660–666
Sollamo EMJ, Ilmonen SK, Virolainen MS, Suominen SHH (2016) Sentinel lymph node biopsy in cN0 squamous cell carcinoma of the lip: a retrospective study. Head Neck 38(Suppl 1):E1375-1380
Thompson CF, St John MA, Lawson G, Grogan T, Elashoff D, Mendelsohn AH (2013) Diagnostic value of sentinel lymph node biopsy in head and neck cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 270(7):2115–2122
Schilling C, Stoeckli SJ, Haerle SK, Broglie MA, Huber GF, Sorensen JA et al (2015) Sentinel European node trial (SENT): 3-year results of sentinel node biopsy in oral cancer. Eur J Cancer Oxf Engl 1990 51(18):2777–2784
Ramamurthy R, Kottayasamy Seenivasagam R, Shanmugam S, Palanivelu K (2014) A prospective study on sentinel lymph node biopsy in early oral cancers using methylene blue dye alone. Indian J Surg Oncol 5(3):178–183
National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Guidelines head and neck cancers (Version 1.2024). https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/head-and-neck.pdf. Accessed 27 Oct 2023
Somashekhar SP, Zaveri Shabber S, Udupa Venkatesh K, Venkatachala K, Parameshwaran, Vasan Thirumalai MM (2008) Sentinel lymphnode biopsy in early breast cancer using methylene blue dye and radioactive sulphur colloid—a single institution Indian experience. Indian J Surg 70(3):111–119
Mathelin C, Croce S, Brasse D, Gairard B, Gharbi M, Andriamisandratsoa N et al (2009) Methylene blue dye, an accurate dye for sentinel lymph node identification in early breast cancer. Anticancer Res 29(10):4119–4125
Varghese P, Abdel-Rahman AT, Akberali S, Mostafa A, Gattuso JM, Carpenter R (2008) Methylene blue dye–a safe and effective alternative for sentinel lymph node localization. Breast J 14(1):61–67
Report of the Hospital Based Cancer Registries (2021) [Internet]. [cited 2023 Nov 12]. https://ncdirindia.org/All_Reports/HBCR_2021/
DeVita, Hellman, and Rosenberg’s Cancer: Principles & Practice of Oncology [Internet]. [Cited 2023 Nov 12]. Available from: https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/know/cancer-principles-and-practice-of-oncology
Chhetri DK, Rawnsley JD, Calcaterra TC (2000) Carcinoma of the buccal mucosa. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 123(5):566–571
Extent of lymph node dissection in T3/T4 cancer of the alveolo‐buccal complex | Semantic Scholar [Internet]. [cited 2023 Nov 12]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Extent-of-lymph-node-dissection-in-T3-T4-cancer-of-Rao-Deshmane/393e103d01826230a2eb062ce19952e29f8a308f
Lim YC, Song MH, Kim SC, Kim KM, Choi EC (2004) Preserving level IIb lymph nodes in elective supraomohyoid neck dissection for oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130(9):1088–1091
Shah JP, Andersen PE (1995) Evolving role of modifications in neck dissection for oral squamous carcinoma. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 33(1):3–8
van den Brekel MW, van der Waal I, Meijer CJ, Freeman JL, Castelijns JA, Snow GB (1996) The incidence of micrometastases in neck dissection specimens obtained from elective neck dissections. Laryngoscope 106(8):987–991
Vaish R, Gupta S, D’Cruz AK (2015) Elective versus therapeutic neck dissection in oral cancer. N Engl J Med 373(25):2477
Ding Z, Xiao T, Huang J, Yuan Y, Ye Q, Xuan M et al (2019) Elective neck dissection versus observation in squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity with clinically N0 neck: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 77(1):184–194
Kuntz AL, Weymuller EA (1999) Impact of neck dissection on quality of life. Laryngoscope 109(8):1334–1338
Payakachat N, Ounpraseuth S, Suen JY (2013) Late complications and long-term quality of life for survivors (>5 years) with history of head and neck cancer. Head Neck 35(6):819–825
Garrel R, Makeieff M, Alovisetti C, Costes V, Comte F, Crampette L et al. Sentinel lymph nodes in oropharyngeal and oral carcinomas. In 2005 [cited 2023 Nov 12]. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Sentinel-lymph-nodes-in-oropharyngeal-and-oral-Garrel-Makeieff/3fa9f973cd1c3fdb14ebf234d3be5deb0f522dfb
Stoeckli SJ, Pfaltz M, Ross GL, Steinert HC, MacDonald DG, Wittekind C et al (2005) The second international conference on sentinel node biopsy in mucosal head and neck cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 12(11):919–924
Alkureishi LWT, Ross GL, MacDonald DG, Shoaib T, Gray H, Robertson G et al (2007) Sentinel node in head and neck cancer: use of size criterion to upstage the no neck in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 29(2):95–103
Calabrese L, Bruschini R, Ansarin M, Giugliano G, De Cicco C, Ionna F, Paganelli G, Maffini F, Werner JA, Soutar D (2006) Role of sentinel lymph node biopsy in oral cancer. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 26(6):345–349
Vishnoi JR, Kumar V, Gupta S, Chaturvedi A, Misra S, Akhtar N et al (2019) Outcome of sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity with methylene blue dye alone: a prospective validation study. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 57(8):755–759
Shivakumar K, Vipin G, Suraj M, Rajaram BV, Rakesh R, Anuradha A et al (2016) Sentinel lymph node biopsy in N0 neck for squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity: a prospective study. Indian J Surg Oncol 7(4):375–379
Rakheja M, Radhakrishnan R, Solomon M (2014) Sentinel lymph node biopsy in oral squamous cell carcinoma—ensuing from elective to selective. J Res Med Dent Sci 1(2):5
Chone CT, Aniteli MB, Magalhães RS, Freitas LL, Altemani A, Ramos CD et al (2013) Impact of immunohistochemistry in sentinel lymph node biopsy in head and neck cancer. Eur Arch Oto-Rhino-Laryngol 270(1):313–317
List of Nuclear Medicine Facilities Licensed by AERB. Atomic Energy Regulatory Board. Government of India. https://www.aerb.gov.in/english/nuclear-medicine
Blessing WD, Stolier AJ, Teng SC, Bolton JS, Fuhrman GM (2002) A comparison of methylene blue and lymphazurin in breast cancer sentinel node mapping. Am J Surg 184(4):341–345
Simmons RM, Smith SM, Osborne MP (2001) Methylene blue dye as an alternative to isosulfan blue dye for sentinel lymph node localization. Breast J 7(3):181–183
Eldrageely K, Vargas MP, Khalkhali I, Venegas R, Burla M, Gonzalez KD, Vargas HI (2004) Sentinel lymph node mapping of breast cancer: a case-control study of methylene blue tracer compared to isosulfan blue. Am Surg 70(10):872–875
Shoaib T, Soutar DS, Prosser JE, Dunaway DJ, Gray HW, McCurrach GM et al (1999) A suggested method for sentinel node biopsy in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Head Neck 21(8):728–733
Singh S, Gaud U, Shukla R, Shukla M, Kumar M, Pandey M et al (2011) Sentinel lymph node biopsy using blue dye technique in carcinoma of the buccal mucosa. World J Surg Med Radiat Oncol 1(1):1–8
Ross GL, Shoaib T, Soutar DS, MacDonald DG, Camilleri IG, Bessent RG et al (2002) The first international conference on sentinel node biopsy in mucosal head and neck cancer and adoption of a multicenter trial protocol. Ann Surg Oncol 9(4):406–410
Hassan O, Taha MS, El Mehairy H (2015) Sentinel lymph node biopsy versus elective neck dissection in evaluation of cN0 neck in patients with oral and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Systematic review and meta-analysis study. Egypt J Ear Nose Throat Allied Sci 16(1):25–34
Woolgar JA (1999) Pathology of the N0 neck. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37(3):205–209
Byers RM, El-Naggar AK, Lee YY, Rao B, Fornage B, Terry NH et al (1998) Can we detect or predict the presence of occult nodal metastases in patients with squamous carcinoma of the oral tongue? Head Neck 20(2):138–144
Paleri V, Rees G, Arullendran P, Shoaib T, Krishman S (2005) Sentinel node biopsy in squamous cell cancer of the oral cavity and oral pharynx: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Head Neck 27(9):739–747
Pantvaidya GH, Pal P, Vaidya AD, Pai PS, D’Cruz AK (2014) Prospective study of 583 neck dissections in oral cancers: implications for clinical practice. Head Neck 36(10):1503–1507
Manola M, Aversa C, Moscillo L, Villano S, Pavone E, Cavallo C et al (2011) Status of level IIb lymph nodes of the neck in squamous cell carcinoma of the oral tongue in patients who underwent modified radical neck dissection and lymph node sentinel biopsy. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital 31(3):130–134
Funding
No funding was obtained from the private or public sector for conducting this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Ethical Approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of University (Swami Rama Himalayan University) (Date.16.09.2022./No.—SRHU/HIMS/ETHICS/2022/316).
Informed Consent of the Participants
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, C., Arora, A., Nandi, S. et al. A Prospective Cohort Study on Neck Lymph Node Mapping in Oral Cancers Using Methylene Blue Dye. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04682-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04682-z