Abstract
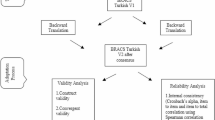
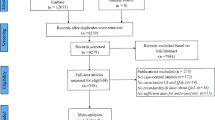
To develop and validate a simple questionnaire for the diagnosis of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) and also to accurately predict the involved side in BPPV. Patients (N = 148) who presented with dizziness to the ENT department were asked to fill out a questionnaire which was formulated to diagnose BPPV and the affected side. Five questions were part of the questionnaire. The fifth question was set to ascertain the affected side in BPPV. All the patients underwent a detailed neuro-otological examination and the findings were noted. The findings of the examination were correlated with the questionnaire findings. The mean age of the patient group was 54.72 years of age. The sensitivity of the questionnaire in detecting BPPV was 94.5%, though in 12.79% (n = 11) the side was not predicted correctly. The specificity of the questionnaire was 91.22%. The positive predictive value of the questionnaire in detecting BPPV was assessed at 94.5%.The questionnaire can be effectively used in predicting BPPV amongst patients presenting with dizziness and thus helps in avoiding unnecessary imaging and referrals to higher centres in view of suspicion of central causes of dizziness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya N, Gubbels SP, Schwartz SR, Edlow JA, El-Kashlan H, Fife T, Holmberg JM, Mahoney K, Hollingsworth DB, Roberts R, Seidman MD, Steiner RW, Do BT, Voelker CC, Waguespack RW, Corrigan MD (2017) Clinical practice guideline: benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 156(3_suppl):S1–S47. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599816689667
von Brevern M, Radtke A, Lezius F et al (2007) Epidemiology of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo: a population based study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:710–715
Li L, Liu JG, Wang ZW, Qi XK (2017) Formulation and evaluation of diagnostic questionnaire for benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 97(14):1061–1064. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.0376-2491.2017.14.007. (in Chinese)
Higashi-Shingai K, Imai T, Kitahara T, Uno A, Ohta Y, Horii A, Nishiike S, Kawashima T, Hasegawa T, Inohara H (2011) Diagnosis of the subtype and affected ear of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo using a questionnaire. Acta Otolaryngol 131(12):1264–1269
van Dam VS, Maas BDPJ, Schermer TR, van Benthem PG, Bruintjes TD (2021) Two symptoms strongly suggest benign paroxysmal positional vertigo in a dizzy patient. Front Neurol 11:625776. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2020.625776
Bi JT, Liu B, Zhang Y, Duan JP, Zhou Q (2019) Rapid screening questionnaire based on clinical symptoms of patients with benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi 33(3):209–212. https://doi.org/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.03.006. (in Chinese)
Soto-Varela A, Santos-Perez S, Rossi-Izquierdo M, Sanchez-Sellero I (2013) Are the three canals equally susceptible to benign paroxysmal positional vertigo? Audiol Neurootol 18(5):327–334. https://doi.org/10.1159/000354649. (Epub 2013 Sep 28 PMID: 24080713)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: Dr. Aishwarya M. Methodology: Dr. Aishwarya M. Formal analysis and investigation: Dr. Pooja S. Writing—original draft preparation: Dr. Aishwarya M Writing—review and editing: Dr. Yogeshwar C. Supervision: Dr. Niveditha J.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
We further confirm that any aspect of the work covered in this manuscript that has involved human patients has been conducted with the ethical approval of all relevant bodies and that such approvals are acknowledged within the manuscript. We confirm that the manuscript has been read and approved by all named authors. We confirm that the order of authors listed in the manuscript has been approved by all named authors.
Informed Consent
Institutional Ethics Committee clearance was taken and informed consent was taken from all patients prior to involving them in the study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Muraleedharan, A., Somnath, P., Chandrashekar, Y. et al. Diagnosis of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Using a Questionnaire in a Hospital Based Rural Setting in India. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04646-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04646-3