Abstract
Aims
In this study, we attempt to compare the pure tone audiometry findings with ossicular chain status intraoperatively in patients of chronic otitis media.
Materials and methods
102 patients who presented with COM during a period of one year and met the inclusion criteria were included in the study. All patients underwent preoperative pure tone Audiometry and findings were tabulated. All patients were evaluated intraoperatively by the same surgeon and observations were made regarding ossicular chain integrity.
Results
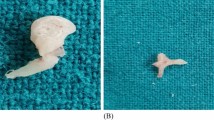
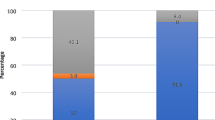
Small central perforation was noted in 10%, medium central perforation in 38.57%, large central perforation in 27.14% and subtotal perforation in 24.28%. 71.56% patients had an intact ossicular chain, of which 94.5% was mucosal disease and 5.5% were squamous disease. 29 cases showed eroded/absent ossicles, out of which, 28 had squamous type and 1 case had central perforation. Ossicular status was classified based on Austin Classification. Conductive hearing loss was found to be maximum where all 3 ossicles were eroded/absent, with a mean AB gap of 45.33 and mean air conduction threshold of 60.33.
Conclusion
There is a good correlation between the hearing threshold of the patient and the status of ossicular chain. Preoperative knowledge of the degree of hearing loss and status of ossicular chain would allow the surgeon to plan proper ossicular reconstruction and give the patient a better advice regarding prognosis of hearing improvement after surgery.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olsen JM, Ribeiro F, de AQ, Yasui MMM, dos Santos ITR (2015) Hearing loss assessment in primary and secondary acquired cholesteatoma. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 81(6):653–657
Albera R, Canale A, Piumetto E, Lacilla M, Dagna F (2012) Ossicular chain lesions in cholesteatoma. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital Organo Uff Della Soc Ital Otorinolaringol E Chir Cerv-facc 32(5):309–313
Martins O, Victor J, Selesnick S (2012) The relationship between individual ossicular status and conductive hearing loss in cholesteatoma. Otol Neurotol off Publ Am Otol Soc Am Neurotol Soc Eur Acad Otol Neurotol 33(3):387–392
Carrillo RJC, Yang NW, Abes GT (2006) Relationship of pure Tone Audiometry and Ossicular Discontinuity in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Philipp J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 21(1–2):5–10
Baig M, Ajmal M, Fatima S (2011) Prevalence of Cholesteatoma and its complications in patients of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. J Rawalpindi Med Coll 15:16–17
Alireza KY, Babak S, Mojtaba F, Hamidreza S (2011) Association between audiometric profile and intraoperative findings in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 23(2):37–42
Devashri U, Patil S, Kulkarni K, Burse S, Chavan Correlation of the puretone audiometry findings with intraoperative findings in patients with chronic suppurative otitis media. Int J Dev Res IJDR [Internet]. 2017 Oct 10 [cited 2023 Nov 26];7. Available from: https://www.journalijdr.com/correlation-puretone-audiometry-findings-intraoperative-findings-patients-chronic-suppurative-otitis
Gupta S, Harshvardhan R, Samdani S (2019) To study the Association of the size and site of tympanic membrane perforation with the degree of hearing loss. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg off Publ Assoc Otolaryngol India 71(Suppl 2):1047–1052
Dornelles C, Costa SS da, Meurer L, Schweiger C (2005) Some considerations about acquired adult and pediatric cholesteatomas. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 71(4):536–545
Hossain MD, Ahamed MNU, Sumon MMAK, Shoyeb BA (2015) Status of Ossicles in Cholesteatoma. Bangladesh J Otorhinolaryngol 21(2):97–101
Mohammadi G, Naderpour M, Mousaviagdas M (2012) Ossicular erosion in patients requiring surgery for cholesteatoma. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 24(68):125–128
Sade J, Berco E, Buyanover D, Brown M (1981) Ossicular damage in chronic middle ear inflammation. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 92(3–4):273–283
Varshney S, Nangia A, Bist SS, Singh RK, Gupta N, Bhagat S (2010) Ossicular Chain Status in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media in adults. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 62(4):421–426
Hassan Haidar R, Sheikh A, Larem A, Elsaadi H, Abdulkarim S, Ashkanani, Abdulsalm Alqahtani (2015). Ossicular Chain Erosion in Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media. Otolaryngol Open Access [Internet]. Jul 31 [cited 2023 Nov 27];5(4). Available from: https://www.omicsonline.org/open-access/ossicular-chain-erosion-in-chronic-suppurative-otitis-media-2161-119X-1000203.php?aid=57342
KADAMBOTT S, KUMAR GURE P, GHATAK S, DUTTA M, SETH C (2023) How does preoperative pure tone Audiometry relate to the findings at surgery to explain the hearing status in Chronic Otitis Media? Medeni Med J 38(1):16–23
Shinta N, Purnami N, Ahadiah TH (2018) Study report: association between pure tone average and ossicular status in chronic suppurative otitis media. J Phys Conf Ser 1075:012062
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The author(s) declare none.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the ethical standards of the relevant national and institutional guidelines on human experimentation (please name) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Maran, R., Meena, K. & George, S.P. Correlation Between Pure Tone Audiometry Values and Middle Ear Ossicular Chain Status in Chronic Otitis Media: Study in a Tertiary Health Care Centre. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04557-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-024-04557-3