Abstract
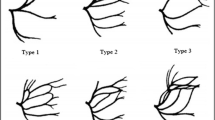
Facial nerve is responsible for the facial expressions and its preservation during parotidectomy is an important aspect for the operating surgeon. The nerve has a long course and the terminal part traverses through the parotid gland. The branching pattern of the nerve within the gland is highly complex and variable, making parotidectomy a challenging surgery. A cross-sectional record based study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital of a medical college in north India between November 2020 and December 2021 with an aim to describe the branching pattern of the facial nerve within the parotid gland. Patients of all age groups and both genders who underwent superficial parotidectomy for benign parotid gland tumors were taken into consideration. The branching pattern of the nerve was observed and recorded. Twenty patients were included in the study. In seventy percent cases the nerve divided into two main branches whereas in the rest, three branches emerged. In sixty five percent cases, the upper division (temporofacial) further divided into two branches whereas in rest it divided into three. The lower division (cervicofacial) divided into two subdivisions in majority of the cases. Multiple communications were found in the branches given off from the upper division and buccal branch had the most variable origin. A knowledge of branching pattern and the communications between the branches of facial nerve helps in avoiding an iatrogenic injury during parotidectomy and preserving the nerve function.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saha S, Pal S, Sengupta M, Chowdhury K, Saha VP, Mondal L (2014) Identification of facial nerve during parotidectomy: a combined anatomical & surgical study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 66(1):63–68
Park IY, Lee ME (1977) A morphological study of the parotid gland and the peripheral branches of the facial nerve in Koreans. Yonsei Med J 18(1):45–51
Davis RA, Anson BJ, Budinger JM, Kurth LR (1956) Surgical anatomy of the facial nerve and parotid gland based upon a study of 350 cervicofacial halves. Surg Gynecol Obstet 102(4):385–412
Katz AD, Catalano P (1987) The clinical significance of the various anastomotic branches of the facial nerve. Report of 100 patients. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113(9):959–962
Proctor B (1984) The extratemporal facial nerve. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 92(5):537–545
Anbusudar K, Arumugam B (2013) Anatomical study on intra parotid course of facial nerve and its terminal braches. J evol Medical and Dental Sciences 2(12):1828–1839
Kopuz C, Turgut S, Yavuz S, Ilgi S (1994) Distribution of facial nerve in parotid gland: analysis of 50 cases. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn 70(6):295–299
Heeneman H (1975) Identification of the facial nerve in parotid surgery. Can J Otolaryngol 4(1):145–151
Kwak HH, Park HD, Youn KH et al (2004) Branching patterns of the facial nerve and its communication with the auriculotemporal nerve. Surg Radiol Anat 26(6):494–500
Baker DC, Conley J (1979) Avoiding facial nerve injuries in rhytidectomy. Anatomical variations and pitfalls. Plast Reconstr Surg 64(6):781–795
Tsai SC, Hsu HT (2002) Parotid neoplasms: diagnosis, treatment and intraparotid facial nerve anatomy. J Laryngol Otol 116(5):359–362
Saki N, Nikahlagh S, Mashali L, Fazeli S (2015) Pattern of distribution in facial nerve in the Benign parotid gland tumors. Biomed Pharmacol J 8:47–50
Khaliq BA, Nisar J, Yousuf A, Maqbool T, Ahmad R (2017) Facial nerve branching pattern as seen in parotidectomy in Kashmiri population: our experience. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg 3(1):95–97
Myint K, Azian AL, Khairul FA (1992) The clinical significance of the branching pattern of the facial nerve in malaysian subjects. Med J Malaysia 47(2):114–121
Ekinci N (1999) A study on the branching pattern of the facial nerve of children. Kaibogaku Zasshi 74(4):447–450
Kim YS, Suh YJ, Kim W (2002) Branching pattern of the facial nerve in the parotid gland. J Korean Surg Soc 62:453–455
Kilic C, Kirici Y, Kocaoglu M (2010) Double facial nerve trunk emerged from the stylomastoid foramen and petrotympanic fissure: a case report. J Korean Med Sci 25(8):1228–1230
Chummy S (1999) Last’s anatomy: Regional and applied, 11th edn. Elsevier, London
Standring S (2008) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice, 40th edn. Elsevier, London
Hollinshead WH (1962) Textbook of anatomy, 5th edn. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, London
Al-Hayani A (2007) Anatomical localization of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve. Folia Morphol 66(4):307–313
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ashish Chandra Agarwal was involved in conceptualization of the study, data collection and revision of the manuscript; Anitya Srivastava was involved in data collection, analysis and drafting; Tejaswi Gupta was involved in data collection and drafting the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they do not have any competing interests.
Ethical Standards
The authors assert that all procedures contributing to this work comply with the relevant national and institutional guidelines on human experimentation and with the Helsinki declaration of 1975, as revised in 2008.
Financial support
This research received no specific grant from any funding agency, commercial or not- for ? profit sectors.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Agarwal, A.C., Srivastava, A., Gupta, T. et al. Intra-parotid Course and Variations in the Branching Pattern of Facial Nerve: Our Experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 75, 1806–1812 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03750-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-023-03750-0