Abstract
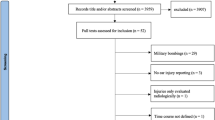
The frequency of injuries secondary to terrorist attack explosion is globally increasing. Like any other country, our country experienced multiple suicide bombings in recent years. Otologic injuries may be observed after these kinds of attacks. Considering otologic complaints are well known medical results of explosion attacks, routine otologic evaluation in the first examining hospital—even in case of no relevant complaint- is crucial for establishing causal relation in following forensic medicine evaluation. In this study, 33 cases from 6 suicide bomber attacks in 4 different incidents that happened in Turkey were evaluated for otologic injuries. Two out of three patients were not evaluated for otologic injuries in their first hospital visit. It was considered that 8 cases had a loss of hearing and 9 cases had tympanic membrane rupture secondary to the explosion. Complaints such as hearing loss and tinnitus very often after a bomb attack, we saw that 22 of 33 included patients did not have an ear nose, and throat examination at the time of the incident. In this kind of attack, there can be various life-threatening injuries and therefore relatively less important evaluations such as ENT examination can often be overlooked.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mathews ZR, Koyfman A (2015) Blast injuries. J Emerg Med 49:573–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.03.013
Wolf SJ, Bebarta VS, Bonnett CJ et al (2009) Blast injuries. Lancet 374:405–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60257-9
Golan R, Soffer D, Givon A, Peleg K (2014) The ins and outs of terrorist bus explosions: Injury profiles of on-board explosions versus explosions occurring adjacent to a bus. Injury 45:39–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2013.02.004
Cave KM, Cornish EM, Chandler DW (2007) Blast injury of the ear: clinical update from the global war on terror. Mil Med 172:726–730. https://doi.org/10.7205/milmed.172.7.726
Joseph AR, Shaw JL, Clouser MC et al (2018) Impact of blast injury on hearing in a screened male military population. Am J Epidemiol 187:7–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwx199
Macgregor AJ, Zouris JM, Watrous JR, et al (2020) Multimorbidity and quality of life after blast-related injury among US military personnel: a cluster analysis of retrospective data. 1–9
Mizutari K (2019) Blast-induced hearing loss. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 20:111–115. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1700051
Van Haesendonck G, Van Rompaey V, Gilles A et al (2018) Otologic outcomes after blast injury: The Brussels bombing experience. Otol Neurotol 39:1250–1255. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002012
Qureshi TA, Awan MS, Hassan NH et al (2017) Effects of bomb blast injury on the ears: The aga khan university hospital experience. J Pak Med Assoc 67:1313–1317
10/10/2015 Tren Garı
Merasim Sokak
1415521 @ www.aa.com.tr
Vodafone Arena
CDC (2017) Disability and health overview. Cdc 725–728
Perez R, Gatt N, Cohen D (2000) Audiometric configurations following exposure to explosions. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:1249–1252. https://doi.org/10.1001/archotol.126.10.1249
Esquivel CR, Parker M, Curtis K et al (2018) Aural blast injury/acoustic trauma and hearing loss. Mil Med 183:78–82. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usy167
De Régloix SB, Crambert A, Maurin O et al (2017) Blast injury of the ear by massive explosion: a review of 41 cases. J R Army Med Corps 163:333–338. https://doi.org/10.1136/jramc-2016-000733
Helling ER (2004) Otologic blast injuries due to the kenya embassy bombing. Mil Med 169:872–876. https://doi.org/10.7205/milmed.169.11.872
Aslier M, Yuksel Aslier NG (2017) Analysis of Otologic injuries due to blast trauma by handmade explosives. Turk Otolarengoloji Arsivi Turkish Arch Otolaryngol 55:64–68. https://doi.org/10.5152/tao.2017.2328
Klamkam P, Jaruchinda P, Nivatwongs S et al (2013) Otologic manifestations from blast injuries among military personnel in Thailand. Am J Otolaryngol Head Neck Med Surg 34:287–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjoto.2012.12.007
Shah A, Ayala M, Capra G et al (2014) Otologic assessment of blast and nonblast injury in returning middle east-deployed service members. Laryngoscope 124:272–277. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.24169
Tungsinmunkong S, Chongkolwatana C, Piyawongvisal W et al (2007) Blast injury of the ears: the experience from Yala Hospital, Southern Thailand. J Med Assoc Thail 90:2662–2668
Turégano-Fuentes F, Caba-Doussoux P, Jover-Navalón JM et al (2008) Injury patterns from major urban terrorist bombings in trains: the Madrid experience. World J Surg 32:1168–1175. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-008-9557-1
Salazar JW, Meisel K, Smith ER et al (2019) Depression in patients with tinnitus: a systematic review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg USA 161:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0194599819835178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Demiray, E., Aydogan, H.C., Cavlak, M. et al. Otologic Injuries Secondary to Explosive Attack. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 1), 569–574 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02384-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-021-02384-4