Abstract
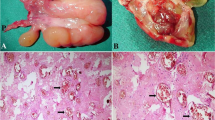
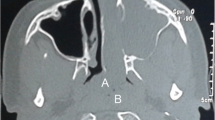
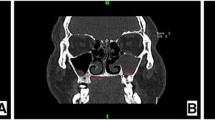
Antrochoanal polyps are the most common type of choanal polyp. Angiomatous polyp is a rare subtype of Antrochoanal polyp that might be misdiagnosed as malignant lesion due to its clinical features. A retrospective observational study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital in patients who were diagnosed with Angiomatous Antrochonal polyp that underwent functional endoscopic sinus surgery from 2017 to 2020. We analyzed the clinical symptoms, radiological findings, and pathological features of all patients diagnosed with Angiomatous Antrochonal polyp. Unilateral nasal obstruction, rhinorrhea, and epistaxis were the common symptoms. Antrochoanal polyps all originated from maxillary sinus and extended to nasal cavity with or without involving the nasopharynx. Expansile mass with surrounding bony destruction are typical on computed tomography imaging but specific for Angiomatous Antrochoanal polyp. The magnetic resonance revealed high signal intensity on T1-weighted images and hypo-intense rim on T2-weighted images. Computed tomography and magnetic resonance together might give rise to more accurate diagnosis of Angiomatous Antrochoanal polyp. Incisional biopsy does help if the clinician suspects a malignant lesion. Complete removal is treatment of choice for Angiomatous Antrochoanal polyp.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
De Vuysere S, Hermans R, Marchal G (2001) Sinochoanal polyp and its variant, the angiomatous polyp: MRI findings. Eur Radiol 11(1):55–58
Batsakis JG, Sneige N (1992) Choanal and angiomatous polyps of the sinonasal tract. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 101(7):623–625
Sheahan P, Crotty PL, Hamilton S, Colreavy M, McShane D (2005) Infarcted angiomatous nasal polyps. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262(3):225–230
Wang YZ, Yang BT, Wang ZC, Song L, Xian JF (2012) MR evaluation of sinonasal angiomatous polyp. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33(4):767–772
Zhou J, Man F, Deng K, Zheng Y, Hao D, Xu W (2014) CT and MR imaging findings of sinonasal angiomatous polyps. Eur J Radiol 3(3):545–551
Huang CC, Lee TJ, Chang PH, Huang CC (2010) Radiology quiz case 1.Infarcted angiomatous polyps of the maxillary sinus. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136(7):740, 742.
Yfantis HG, Drachenberg CB, Gray W, Papadimitriou JC (2000) Angiectatic nasal polyps that clinically simulate a malignant process: report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Arch Pathol Lab Med 124(3):406–410
Ceylan A, Asal K, Celenk F, Uslu S (2007) An angiomatous nasal polyp: a very rare variant of sinochoanal nasal polyps. B-ENT 3(3):145–147
Dai LB, Zhou SH, Ruan LX, Zheng ZJ (2012) Correlation of computed tomography with pathological features in angiomatous nasal polyps. PLoS ONE 7(12):e53306
Park CS, Noh H, Bae SC et al (2006) Antrochonal polyp’s varient, the angiomatous nasal polyp: A case report. Korean J Otolaryngo Head and Neck Surg 49(4):443–446
Sayed RH, Abu-Dief EE (2007) Does antrochoanal polyp present with epistaxis? B-ENT 3(3):145–147
Verma N, Kumar N, Azad R et al (2011) Angiomatous nasal polyp: A condition difficult to diagnose. Otolaryngology Clinics: An Internatinal J 3(2):93–97
Cummings CW, Fredrickson JM, Harker LA, et al. (1999) eds. Otolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery. 3rd ed. St. Louis 7: Mosby; 679–702.
Patrocınio JA, Patrocınio LG, Carrijo Borba BH, Bonatti BDS, Guimaraes AH (2005) Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma in an elderly woman. Am J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Med Surg 26:198–200
Som P, Cohen B, Sacher M (1982) The angiomatous polyp and the angiofibroma: Two different lesions. Radiology 144:329–334
S Jayaram, N Svecova, T C Biggs, J Theaker, R J Salib (2013) Angiectatic nasal polyp—the great Imitator. Internet J Otorhinolaryngol Volume 15 Number 1.
Yoon TM, Kim JH, Cho YB (2006) Three cases of organized hematoma of the maxillary sinus. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263:823–826
Lee HK, Smoker WR, Lee BJ et al (2007) Organized hematoma of the maxillary sinus: CT findings. Am J Roentgenol 188:370–373
Lee BJ, Park HJ, Heo SC (2003) Organized hematoma of the maxillary sinus. Acta Otolaryngol 123:869–872
Song HM, Jang YJ, Chung YS et al (2007) Organizing hematoma of the maxillary sinus. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136:616–620
Unlu HH, Mutlu C, Ayhan S et al (2001) Organized hematoma of the maxillary sinus mimicking tumor. Auris Nasus Larynx 28:253–255
Yagisawa M, Ishitoya J, Tsukuda M (2006) Hematoma-like mass of the maxillary sinus. Acta Otolaryngol 126:277–281
Ding C, Wang Q, Guo Q, Wang Z, Lu X, Zhang J (2015) Sinonasal angiomatous polyp: evaluation with 2-phase helical computed tomography. Medicine (Baltimore) 94(29):e1196
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interests.
Ethical Approval
Permission taken from the institutional ethical committee for doing this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jagadeeswaran, V.U., Vallur, S. & Shivanand, J.S. Management of Angiomatous Antrochoanal Polyp: Our Experience. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 2), 1082–1087 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02148-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-02148-6