Abstract
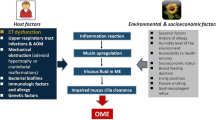
Eosinophilic otitis media (EOM) is an inflammatory chronic disease of the middle ear, characterized by the presence of a particularly viscous effusion with a high content of protein toxins of eosinophilic origin in the middle ear cavity. The pathology has relationship with bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps. EOM is characterized by a sluggish course, a tendency to relapse, which can lead to a gradual hearing decrease up to complete deafness. In this paper, we reviewed the international literature with special attention to pathogenesis and treatment management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Koch H (1947) Allergical investigations of chronic otitis. Acta Otolaryngol 62(Suppl.):1–201
Tomioka S, Yuasa R, lino Y (1994) Intractable otitis media in cases with bronchial asthma. Recent advances in otitis media with effusion. In: Proceedings of the second extraordinary international symposium on recent advances on otitis media. Kugler Publications, Inc., Amsterdam, pp 183–186
Suzuki H, Matsutani S, Kawase T, Iino Y, Kawauchi H, Gyo K et al (2004) Epidemiologic surveillance of ‘‘eosinophilic otitis media’’ in Japan. Otol Jpn 14:112–117 (In Japanese)
Grossman J (1997) One airway, one disease. Chest 111(2 Suppl):11S–16S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.111.2_supplement.11s
Azadarmaki R, Westra W, Prasad S (2015) Eosinophilic Mucin otomastoiditis and otopolyposis: a progressive form of eosinophilic otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 124(9):752–756. https://doi.org/10.1177/0003489415577988
Neff BA, Voss SG, Carlson ML, O’Brien EK, Butterfield JH (2017) Treatment of eosinophilic otitis media with pegylated interferonalpha 2a and 2b. Laryngoscope 127:1208–1216
Lara-Sánchez H, Vallejo L (2017) Eosinophilic otitis media. N Engl J Med 376(7):e10. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMicm1510852
Chow K, Cosetti M (2020) Use of IL-5 inhibitor benralizumab as a novel therapy for eosinophilic otitis media. Otol Neurotol 41(2):e238–e240. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002493
Iino Y, Tomioka-Matsutani S, Matsubara A, Nakagawa T, Nonaka M (2011) Diagnostic criteria of eosinophilic otitis media, a newly recognized middle ear disease. Auris Nasus Larynx 38:456–461
Omori M, Ziegler S (2007) Induction of IL-4 expression in CD4(+) T cells by thymic stromal lymphopoietin. J Immunol 178(3):1396–1404. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.178.3.1396
Simson L, Foster PS (2000) Chemokine and cytokine cooperativity: eosinophil migration in the asthmatic response. Immunol Cell Biol 78(4):415–422. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1711.2000.00922.x
Yao T, Kojima Y, Koyanagi A et al (2009) Eotaxin-1, -2, and -3 immunoreactivity and protein concentration in the nasal polyps of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis patients. Laryngoscope 119(6):1053–1059. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.20191
Ueki S, Konno Y, Takeda M, Moritoki Y, Hirokawa M, Matsuwaki Y, Honda K, Ohta N, Yamamoto S, Takagi Y, Wada A, Weller PF (2016) Eosinophil extracellular trap cell death-derived DNA traps: their presence in secretions and functional attributes. J Allergy Clin Immunol 137(1):258–267. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2015.04.041Epub 2015 Jun 9
IinoY Kakizaki K, Saruya S, Katano H, Komiya T, Kodera K et al (2006) Eustachian tube function in patients with eosinophilic otitis media associated with bronchial asthma evaluated by sonotubometry. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 132:1109–1114
Kanazawa H, Yoshida N, Hara M, Hasegawa M, Matsuzawa S, Shinnabe A et al (2013) Risk factors for eosinophilic otitis media in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis. Int Adv Otol 9:353–358
Iino Y (2010) Role of IgE in eosinophilic otitis media. Allergol Int 59:233–238. https://doi.org/10.2332/allergolint.10-RAI-0223
Ohta N, Ueki S, Konno Y, Hirokawa M, Kubota T, Tomioka-Matsutani S, Suzuki T, Ishida Y, Kawano T, Miyasaka T, Takahashi T, Suzuki T, Ohno I, Kakehata S, Fujieda S (2018) ETosis-derived DNA trap production in middle ear effusion is a common feature of eosinophilic otitis media. Allergol Int 67(3):414–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2017.11.007
Ueki S, Ohta N, Takeda M, Konno Y, Hirokawa M (2017) Eosinophilic otitis media: the aftermath of eosinophil extracellular trap cell death. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 17(5):33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11882-017-0702-5
Papayannopoulos V, Metzler KD, Hakkim A, Zychlinsky A (2010) Neutrophil elastase and myeloperoxidase regulate the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps. J Cell Biol 191(3):677–691. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201006052
Uchimizu H, Matsuwaki Y, Kato M, Otori N, Kojima H (2015) Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin, elastase, and cytokine profile in effusion from eosinophilic otitis media. Allergol Int 64(Suppl):S18–S23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.alit.2015.03.007Epub 2015 Apr 25
Miura T, Matsubara A, Kudo N, Hara R, Takahata J, Sasaki A (2018) The expression of thymic stromal lymphopoietin in patients and animal models with eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 138(5):447–451. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2017.1416170
Nonaka M, Fukumoto A, Ozu C, Mokuno E, Baba S, Pawankar R et al (2003) IL-5 and eotaxin levels in middle ear effusion and blood from asthmatics with otitis media with effusion. Acta Otolaryngol 123:383–387
Iino Y, Kakizaki K, Katano H, Saigusa H, Kanegasaki S (2005) Eosinophil chemoattractant in middle ear patients with eosinophilic otitis media. Clin Exp Allergy 35:1370–1376
Iino Y, Nagamine H, Yabe T, Matsutani S (2001) Eosinophils are activated in middle ear mucosa and middle ear effusion of patients with intractable otitis media associated with bronchial asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 31:1135–1143
Matsubara A, Nishizawa H, Kurose A, Nakagawa T, Takahata J, Sasaki A (2014) An experimental study of inner ear injury in an animal model of eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 134(3):227–232. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.859395(Epub 2013 Dec 23)
Kudo N, Matsubara A, Nishizawa H, Miura T (2017) Immunohistological analysis of eotaxin and RANTES in the model animal of eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 137(5):476–481. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2016.1266508(Epub 2016 Dec 16)
Takayama G, Arima K, Kanaji T, Toda S, Tanaka H, Shoji S et al (2006) Periostin: a novel component of subepithelial fibrosis of bronchial asthma downstream of IL-4 and IL-13-signals. J Allergy Clin Immunol 118:98–104
Okamoto M, Hoshino T, Kitasato Y, Sakazaki Y, Kawayama T, Fujimoto K et al (2011) Periostin, a matrix protein, is a novel biomarker for idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Eur Respir J 5:1119–1127
Nishizawa H, Matsubara A, Nakagawa T, Ohta N, Izuhara K, Shirasaki T, Abe T, Takeda I, Shinkawa H (2012) The role of periostin in eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 132(8):838–844. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2012.668708Epub 2012 Jun 5
Iino Y (2008) Eosinophilic otitis media: a new middle ear disease entity. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 8(6):525–530
Kanazawa H, Yoshida N, Yamamoto H, Hara M, Hasegawa M, Matsuzawa S, Shinnabe A, Iino Y (2014) Risk factors associated with severity of eosinophilic otitis media. Auris Nasus Larynx 41(6):513–517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2014.08.003
Tanaka Yukako, Nonaka Manabu, Yamamura Yukie, Tagaya Etsuko, Pawankar Ruby, Yoshihara Toshio (2013) Improvement of eosinophilic otitis media by optimized asthma treatment. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res 5(3):175–178
Seo Yukako, Nonaka Manabu, Yamamura Yukie (2018) Optimal control of asthma improved eosinophilic otitis media. Asia Pacific Allergy 8(1):e5
Chung WJ, Lee JH, Lim HK, Yoon TH, Cho KJ, Baek JH (2012) Eosinophilic otitis media: CT and MRI findings and literature review. Korean J Radiol 13(3):363–367. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.3.363
Saliba I, Alzahrani M, Weng X, Bestavros A (2017) Eosinophilic otitis media diagnosis using flow cytometric immunophenotyping. Acta Oto-Laryngol. https://doi.org/10.1080/00016489.2017.1385845
Masi AT, Hunder GG, Lie JT, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Arend WP et al (1990) The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Churg-Strauss syndrome (allergic granulomatosis and angiitis). Arthritis Rheum 33:1094–1100
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Andrassy K, Bacon PA, Churg J, Gross WL et al (1994) Nomenclature of systemic vasculitides. Proposal of an international consensus conference. Arthritis Rheum 37:187–192
Harabuchi Yasuaki, Kishibe Kan, Tateyama Kaori, Morita Yuka, Yoshida Naohiro, Kunimoto Yasuomi, Matsui Takamichi, Sakaguchi Hiroshi, Okada Masahiro, Watanabe Takeshi, Inagaki Akira, Kobayashi Shigeto, Iino Yukiko, Murakami Shingo, Takahashi Haruo, Tono Tetsuya (2017) Clinical features and treatment outcomes of otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (OMAAV): a retrospective analysis of 235 patients from a nationwide survey in Japan. Mod Rheumatol 27(1):87–94. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2016.1177926
Ishiyama A, Canalis RF (2001) Otological manifestations of Churg–Strauss syndrome. Laryngoscope 111(9):1619–1624. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-200109000-00024
Martinez Del Pero M, Moffat D, Sudhoff H (2008) Unusual presentation of temporal bone involvement in Churg–Strauss syndrome. J Laryngol Otol 122:425–427
Seccia V, Fortunato S, Cristofani-Mencacci L et al (2016) Focus on audiologic impairment in eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Laryngoscope 126(12):2792–2797. https://doi.org/10.1002/lary.25964
Ovadia S, Dror I, Zubkov T, Tanay A, Levy D, Zandman-Goddard G (2009) Churg–Strauss syndrome: a rare presentation with otological and pericardial manifestations: case report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 28(Suppl. 1):S35–S38
Groh M, Pagnoux C, Baldini C et al (2015) Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg–Strauss) (EGPA) Consensus Task Force recommendations for evaluation and management. Eur J Intern Med 26:545–553
Fukuda A, Morita S, Nakamaru Y, Hoshino K, Fujiwara K, Homma A (2019) Differentiation between eosinophilic otitis media and otitis media associated with eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis. Otol Neurotol 40(8):e796–e802. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000002295
Chusid MJ, Dale DC, West BC, Wolff SM (1975) The hypereosinophilic syndrome: analysis of fourteen cases with review of the literature. Medicine 54(1):1–27. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-197501000-00001
Takayama K, Yadohisa O, Furuno T, Hashimoto S, Nakanishi Y, Abe M et al (1995) Case report: the first report of idiopathic hypereosinophilic syndrome involved with lung and middle ear. Am J Med Sci 309:282–284
Reiter A, Gotlib J (2017) Myeloid neoplasms with eosinophilia. Blood 129(6):704–714. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2016-10-695973
Longmore M, Wilkinson I, Turmezei T, Cheung CK (2007). Oxford handbook of clinical medicine. Oxford. p 316. ISBN:978-0-19-856837-7
Iino Y, Nagamine H, Kakizaki K, Komiya T, Katano H, Saruya S et al (2006) Effectiveness of instillation of triamcinolone acetonide into the middle ear for eosinophilic otitis mediaassociated with bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 97:761–766
Iino Y, Nagamine H, Kakizaki K et al (2006) Effectiveness of instillation of triamcinolone acetonide into the middle ear for eosinophilic otitis media associated with bronchial asthma. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 97(6):761–766. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60967-2
Matsubara A, Kuroda R, Usami S, Takahata J, Shinkawa H (2001) The effect of topical administration of heparin to the eosinophilic otitis media. In: Takasaka T, Yuasa R, Hozawa K (eds) Recent advances in otitis media. Bologna: Monduzzi Editore, pp 403–406
Esu Y, Iino Y, Masuda M, Kanazawa H, Yoshida N (2018) Proposal of a treatment strategy for eosinophilic otitis media based on middle ear condition. Otol Neurotol 39(8):e671–e678. https://doi.org/10.1097/MAO.0000000000001912
Okude A, Tagaya E, Kondo M, Nonaka M, Tamaoki J (2012) A case of severe asthma with eosinophilic otitis media successfully treated with anti-IgE monoclonal antibody omalizumab. Case Rep Pulmonol 2012:340525
Smith KA, Pulsipher A, Gabrielsen DA, Alt JA (2018) Biologics in chronic rhinosinusitis: an update and thoughts for future directions. Am J Rhinol Allergy 32:412–423
FDA approves first treatment for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps [news release]. Silver Spring, MD: Food and Drug Administration Office of Media Affairs; 2019. Avaliable at: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-treatmentchronic-rhinosinusitis-nasal-polyps. Accessed July 2 2019
Iino Y, Takahashi E, Ida S, Kikuchi S (2019) Clinical efficacy of anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody mepolizumab in the treatment of eosinophilic otitis media. Auris Nasus Larynx 46(196–203):15
Iino Y, Hara M, Hasegawa M et al (2012) Clinical efficacy of anti-IgE therapy for eosinophilic otitis media. Otol Neurotol 33:1218–1224
Iino Y, Hara M, Hasegawa M et al (2014) Effect of omalizumab on biomarkers in middle ear effusion in patients with eosinophilic otitis media. Acta Otolaryngol 134(4):366–372. https://doi.org/10.3109/00016489.2013.868601
El-Qutob D (2016) Off-label uses of omalizumab. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 50:84–96. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-015-8490-y
Markham A (2018) Benralizumab: first global approval. Drugs 78:505–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-018-0876-8
Wada T, Uemaetomari I, Murashita H et al (2006) Successful treatment of eosinophilic otitis media using ramatroban: report of two cases. Auris Nasus Larynx 33(4):455–460. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anl.2006.05.007
Iino Y, Usubuchi H, Kodama K et al (2010) Eosinophilic inflammation in the middle ear induces deterioration of bone-conduction hearing level in patients with eosinophilic otitis media. Otol Neurotol 31:100–104
Iwasaki S, Nagura M, Mizuta K (2006) Cochlear implantation in a patient with eosinophilic otitis media. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 263:365–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-005-1006-2
Sugimoto H, Hatano M, Noda M et al (2017) Cochlear implantation in deaf patients with eosinophilic otitis media using subtotal petrosectomy and mastoid obliteration. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 274:1173–1177. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-016-4091-5
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights
This article contains review of literary data. We havn’t made any research including human participants or animals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shevchik, E., Svistushkin, V., Nikiforova, G. et al. Eosinophilic Otitis Media: Modern Aspects of Pathogenesis, Clinical Features, Diagnosis and Treatment. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 74 (Suppl 1), 132–140 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01903-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-020-01903-z