Abstract
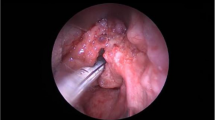
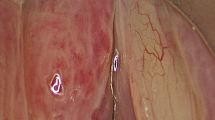
Isolated laryngeal Leishmaniasis is a rare entity in the Indian subcontinent. We describe a case of a 45 year old male with hoarseness and noisy breathing. Patient’s initial histological and serological workup was inconclusive. Final biopsy findings (suggestive of Leishmania donovani), positive rK-39 serology and his native place being Bihar (endemic for Leishmaniasis) led us to the diagnosis. He was treated with high dose liposomal Amphotericin B to which he responded well. This case report highlights the importance of remaining aware of rare infectious causes of laryngitis. Timely diagnosis and intervention are crucial.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Status of endemicity of visceral leishmaniasis worldwide (2015) Countries reporting imported VL cases, 2015
Status of endemicity of cutaneous leishmaniasis worldwide (2015), 2017
General C, Who I (2014) Leishmaniasis, 2013–2014
Marsden PD (1986) Mucosal leishmaniasis. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg 80:859–876
Tayal S, Khatiwada S, Sehrawat P, Nischal N, Jorwal P, Soneja M et al (2015) Laryngeal leishmaniasis with extra-pulmonary tuberculosis. J Assoc Physicians India 2015(63):71–73
Kumar B, Ghimire A, Karki S, Upadhyaya P (2009) Primary laryngeal leishmaniasis: a rare case report. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 52(1):62–64
Leoncini E, Ricciardi W, Cadoni G, Arzani D, Petrelli L, Paludetti G et al (2014) Adult height and head and neck cancer: a pooled analysis within the INHANCE Consortium. Head Neck 36(10):1391
Zijlstra EE, Daifalla NS, Kager PA, Khalil EAG, El-Hassan AM, Reed SG et al (1998) rK39 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for diagnosis of Leishmania donovani infection. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 5(5):717–720
Vaish M, Singh OP, Chakravarty J, Sundar S (2012) rK39 antigen for the diagnosis of visceral leishmaniasis by using human saliva. Am J Trop Med Hyg 86(4):598–600
NASCOP (2014) Guidelines on use of rk39-NVBDCP. https://nvbdcp.gov.in
Sundar S, Chakarvarty J, Agarwal D, Rai M, Murray HW (2010) Single-dose liposomal Amphotericin-B for visceral leishmaniasis in India. N Engl J Med 362(6):504–512
Toledo SJ, Valda L, Balderrama M, Rea I, Parra R, Ardiles J et al (2007) Treatment of bolivian mucosal leishmaniasis with miltefosine. Clin Infect Dis 44(3):350–356
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge the efforts of our pathologists at the institute to have helped us in reaching closer to the diagnosis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors do not hold any conflicts of interest.
Ethical Standard
This clinical case report does not describe any interventional research involving human participants or animals, however describes a unique diagnostic dilemma.
Informed Consent
Institutional informed-written consent was taken from the patient at all appropriate times.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aggarwal, K., Kumar, R., Bhardwaj, N. et al. Isolated Laryngeal Leishmaniasis: A Diagnostic Dilemma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 71 (Suppl 1), 872–875 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01639-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-019-01639-5