Abstract
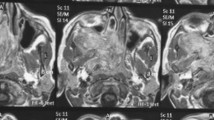
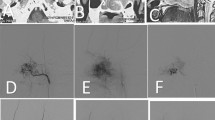
To approach Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma extending to the sphenoid sinus, pterygoid wedge and minimal involvement of the pterygopalatine fossa (Radkowski Stage 2 A) with an endoscopic technique without embolization with no recurrence and minimal morbidity and mortality. This is a retrospective, descriptive study based on the medical records of 15 patients with histologically confirmed JNA who underwent endoscopic binostril four handed endoscopic excision in our centre without embolisation between 2010 and 2015. All 15 patients were young males with a mean age of 14.13 years who underwent endoscopic excision of JNA without embolisation. Nasal obstruction (100 %) and epistaxis (100 %) were the most common symptoms. Average surgery length was 1 h 41 min. Mean blood loss was 67.2 ml and none of patients required blood transfusion. All patients had crusting and septal defect postoperatively, only 3 (20 %) had synechiae. Mean hospitalization time was 3.66 days. 2 (13.33 %) of our patients had a residual tumor and one (6.66 %) had a relapse in pterygoid wedge. There were no cases of death or significant morbidity. The follow up period was 1 year. Endoscopic endo nasal bi nostril four handed technique can achieve complete resection without embolization in case of small to medium sized JNA s in the hands of an experienced surgeon with minimal blood loss, low rates of recurrence and morbidity.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicolai P, Berlucchi M, Tomenzoli D et al (2003) Endoscopic surgery for juvenile angiofibroma: when and how. Laryngoscope 113(5):775–782
Joo D, Chhetri DK, Wang MB (2008) Endoscopic removal of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: a video presentation. Laryngoscope 118(6):e1–e3
Douglas R, Wormald PJ (2006) Endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: where are the limits? Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 14(1):1–5
Ardehali MM, Samimi Ardestani SH, Yazdani N, Goodarzi H, Bastaninejad S (2010) Endoscopic approach for excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: complications and outcomes. Am J Otolaryngol 31(5):343–349
Mehmet A, Orhan S, Suphi M (2006) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: radiological evaluation and pre-operative embolization. KBB Forum 5:58–61
Borghei P, Baradaranfar MH, Borghei SH, Sokhandon F (2006) Transnasal endoscopic resection of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma without preoperative embolization. Ear Nose Throat J 85:740–743
Chaveau C (1906) Histoire des maladies du Pharynx. Balliere, Paris
Andrade NA, Pinto JA, Nóbrega MO et al (2007) Exclusively endoscopic surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 137(3):492–496
Salim Y, İsmail U, Mansur D et al (2013) A giant juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. J Craniofac Surg 24(3):e207–e209
Wormald PJ (2005) Endoscopic medial maxillectomy for maxillary and pterygopalatine fossa tumors. In: Wormold PJ (ed) Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: anatomy, three dimensional reconstruction, and surgical technique (1st ed), Thieme, New York, pp 125–134
Katsiotis P, Tzortzis G, Karaminis C (1979) Transcatheter arterial embolization in nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 20(3):433–438
Roger G, Huy PT, Froehlich P et al (2002) Exclusively endoscopic removal of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: trends and limits. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 128(8):928–935
Strong EB, Bell DA, Johnson LP et al (1995) Intractable epistaxis: transantral ligation vs. embolization efficacy review and cost analysis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 113(6):674–678
Fonseca AS, Vinhaes E, Boaventura V et al (2008) Surgical treatment of non- embolised patients with nasoangiofibroma. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol 74(4):583–587
Moulin G, Chagnaud C, Gras R et al (1995) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: comparison of blood loss during removal in embolized group versus nonembolized group. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 18(3):158–161
Petruson K, Catarino MR, Petrusin B (2002) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: long-term results in preoperative embolized and nonembolized patients. Acta Otolaryngol 122(1):96–100
Pletcher JD, Newton TH, Dedo HH (1975) Preoperative embolization of juvenile angiofibromas of the nasopharynx. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 84(6):740–746
Terzian AE (2000) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma—transantral microsurgical approach. In: Stamm AC, Draf W(eds) Micro-endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses and the skull Base. Chapter 42, Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 515–528
Pryor S, Moore E, Kasperbauer J (2005) Endoscopic vs traditional approaches for excision of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 115:1201–1207
Ardehali MM, Samimi SH, Bakhshaee M (2014) An effective technique for endoscopic resection of advanced stage angiofibroma. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 26(74):25–30
Herman P, Lot G, Chapot R et al (1999) Long-term follow-up of juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibromas: analysis of recurrences. Laryngoscope 109:140–147
Gullane PJ, Davidson J, O’Dwyer T, Forte V (1992) Juvenile angiofibroma: a review of the literature and a case series report. Laryngoscope 102(8):928–933
Jorissen M, Eloy P, Rombaux P et al (2000) Endoscopic sinus surgery for juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Belg 54(2):201–219
Howard DJ, Lloyd G, Lund V (2001) Recurrence and its avoidance in juvenile angiofibroma. Laryngoscope 111(9):1509–1511
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Janakiram, T.N., Sharma, S.B. & Panicker, V.B. Endoscopic Excision of Non-embolized Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: Our Technique. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 68, 263–269 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1013-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1013-1