Abstract
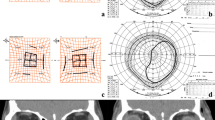
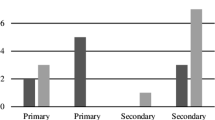
Endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS) is the mainstay of the treatment in sinus disorders, to re-establish the drainage of the affected sinus. The close proximity of the orbital structures to paranasal sinuses makes them vulnerable to inadvertent injury during the sinus surgery. Medial rectus (MR) muscle is the most commonly injured extraocular muscle during ESS due to its anatomic proximity to the thin medial wall of the orbit. This is a non-comparative, retrospective, interventional case series of six patients presenting with MR injury after ESS. We discuss the management, outcome and review the published literature. A total of six patients met the inclusion criteria. The presenting complaints were diplopia, squinting and limitation of ocular movements. Two patients underwent surgical exploration of the MR muscle and reattachment of the muscle along with injection botulinum to the antagonist lateral rectus muscle. Two patients who had small angle strabismus and who were able to fuse were advised orthoptic exercises and prisms as management. Remaining two patients were advised surgical intervention to correct strabismus but they declined further surgical intervention. Management of MR injury following ESS is complex, often resulting in suboptimal outcomes. Since early intervention is associated with better outcomes, early referral by otolaryngologists to ophthalmologists would result in better outcome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen NA, Kennedy DW (2005) Endoscopic sinus surgery: where we are–and where we’re going. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 13:32–38
Bhatti MT, Stankiewicz JA (2003) Ophthalmic complications of endoscopic sinus surgery. Surv Ophthalmol 48:389–402
Rene C, Rose GE, Lenthall R, Moseley I (2001) Major orbital complications of endoscopic sinus surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 85:598–603
Neuhaus RW (1990) Orbital complications secondary to endoscopic sinus surgery. Ophthalmology 97:1512–1518
Bhatti MT, Giannoni CM, Raynor E, Monshizadeh R, Levine LM (2001) Ocular motility complications after endoscopic sinus surgery with powered cutting instruments. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:501–509
Corey JP, Bumsted R, Panje W et al (1993) Orbital complications in functional endoscopic sinus surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 109:814–820
Lim JC, Hadfield PJ, Ghiacy S et al (1999) Medial orbital protrusion: a potentially hazardous anomaly during endo-scopic sinus surgery. J Laryngol Otol 113:754–755
Moulin G, Dessi P, Chagnaud C et al (1994) Dehiscence of the lamina papyracea of the ethmoid bone: CT findings. Am J Neuroradiol 15:151–153
Fuji K, Chambers SM, Rhoton AL Jr (1979) Neurovascular relationships of the sphenoid sinus: a microsurgical study. J Neurosurg 50:31–39
DeLano MC, Fun FY, Zinreich SJ (1996) Relationship of the optic nerve to the posterior paranasal sinuses: a CT anatomic study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:669–675
Driben JS, Bolger WE, Robles HA et al (1998) The reliability of computerized tomographic detection of the Onodi (sphenoethmoid) cell. Am J Rhinol 12:105–111
Huang CM, Meyer DR, Patrinely JR et al (2003) Medial rectus muscle injuries associated with functional endoscopic sinus surgery: characterization and management. Ophthal Plast Reconstr Surg 19:25–37
Thacker NM, Velez FG, Demer JL, Rosenbaum AL (2004) Strabismic complications following endoscopic sinus surgery: diagnosis and surgical management. J AAPOS 8:488–494
Underdahl JP, Demer JL, Goldberg RL, Rosenbaum AL (2001) Orbital wall approach with preoperative orbital imaging for identification and retrieval of lost or transacted extraocular muscles. J AAPOS 5:230–237
Ela-Dalman N, Velez FG, Rosenbaum AL (2006) Importance of sagittal orbital imaging in evaluating extraocular muscle trauma following endoscopic sinus surgery. Br J Ophthalmol 90:682–685
Thacker NM, Velez FG, Krieger A et al (2004) Retinal hemorrhages as a complication of endoscopic sinus surgery. Arch Ophthalmol 122:1724–1725
Awad AH, Shin GS, Rosenbaum AL, Goldberg RL (1997) Autogenous Fascia augmentation of a partially extirpated muscle with a subperiosteal medial orbitotomy approach. J AAPOS 1:138–142
Olitsky SE, Brooks S (2001) Treatment of subtotal medial rectus myectomy complicating functional endoscopic sinus surgery. J AAPOS 5:64
Saunders RA, Bluestein EC, Wilson ME, Berland JE (1994) Anterior segment ischemia after strabismus surgery. Surv Ophthalmol 38:456–466
Rosenbaum AL, Kuschner BJ, Kirschen D (1989) Vertical rectus muscle transposition and botulinum toxin (oculinum) to medial rectus for abducens palsy. Arch Ophthalmol 107:820–823
Paysse EA, Brady McCreery KM, Ross A, Coats DK (2002) Use of augmented rectus muscle transposition surgery for complex strabismus. Ophthalmology 109:1309–1314
Murray AD (1998) Slipped and lost muscles and other tales of the unexpected. J AAPOS 2:133–143
Cho YA, Rah SH, Kim MM, Lee JY (2008) Vertical rectus muscles transposition in large exotropia with medial rectus muscle transection following endoscopic sinus surgery. Korean J Ophthalmol 22:104–110
Acknowledgments
Dr. Sumathi V. Consultant Otolaryngologist, Sundaram Medical Foundation, Chennai. Dr. Olma Veena Noronha, Consultant Radiologist, VRR Scans, Chennai.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The Authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mukherjee, B., Priyadarshini, O., Ramasubramanian, S. et al. Iatrogenic Injury to Medial Rectus After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 67, 394–402 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0887-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-015-0887-7