Abstract
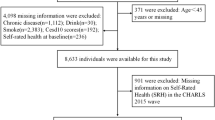
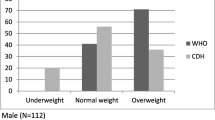
We explored the association of body mass index (BMI) with overall health among middle-aged and older Indian adults. The cross-sectional sample included 42,575 respondents (45 years) from the Longitudinal Aging Study in India (LASI), Wave 1 (2017-18), including middle-aged (23,811) and older adults (18,764). Overall health was assessed by using 19 health indicators, including 10 chronic diseases. Binary logistic regressions were utilized to examine the effect. The overweight and obese older adults were associated with higher life satisfaction (LS), happiness, better handgrip strength (HGS), better cognition (CS), and less insomnia, less depression but a higher prevalence of chronic diseases, i.e., hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, bone or joint diseases, dementia, cholesterol, and vision problems, compared to a normal BMI. In contrast, middle-aged and older adults who were underweight were less likely to have major chronic diseases, but all of their other health conditions were worse than the normal BMI. However, the association between BMI and stroke, cancer, or dementia showed no significant difference due to lower incidence. The results did not show much difference between middle-aged and older adults. The results stress the potential association between BMI and several health measures among middle-aged and older adults, which in the future may help in controlling BMI to achieve successful aging in India.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The study makes use of secondary data, which is available on specific request via https://iipsindia.ac.in/sites/default/files/LASI_DataRequestForm_0.pdf
References
Agrawal, S., & Agrawal, P. K. (2016). Association between body mass index and prevalence of multimorbidity in low-and middle-income countries: a cross-sectional study. International Journal of Medicine and Public Health, 6(2), 73. https://doi.org/10.5530/ijmedph.2016.2.5
Arvanitakis, Z., Capuano, A. W., Bennett, D. A., & Barnes, L. L. (2018). Body mass index and decline in cognitive function in older black and white persons. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 73(2), 198–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/glx152
Ball, K., Crawford, D., & Kenardy, J. (2004). Longitudinal relationships among overweight, life satisfaction, and aspirations in young women. Obesity Research, 12(6), 1019–1030. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2004.125
Beuther, D. A., & Sutherland, E. R. (2007). Overweight, obesity, and incident asthma: a meta-analysis of prospective epidemiologic studies. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 175(7), 661. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200611-1717oc
Boateng, G. O., Adams, E. A., Boateng, M. O., Luginaah, I. N., & Taabazuing, M. M. (2017). Obesity and the burden of health risks among the elderly in Ghana: a population study. PLoS One1, 12(11), e0186947. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186947
Bramhankar, M., Pandey, M., Rana, G. S., Rai, B., Mishra, N. L., & Shukla, A. (2021). An assessment of anthropometric indices and its association with NCDs among the older adults of India: evidence from LASI Wave-1. BMC Public Health, 21(1), 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11421-4
Chang, H. H., & Yen, S. T. (2012). Association between obesity and depression: evidence from a longitudinal sample of the elderly in Taiwan. Aging & Mental Health, 16(2), 173–180. https://doi.org/10.1080/13607863.2011.605053
Chen, Y., Copeland, W. K., Vedanthan, R., Grant, E., Lee, J. E., Gu, D., Gupta, P. C., Ramadas, K., Inoue, M., Tsugane, S., Tamakoshi, A., Gao, Y. T., Yuan, J. M., Shu, X. O., Ozasa, K., Tsuji, I., Kakizaki, M., Tanaka, H., Nishino, Y., & Potter, J. D. (2013). Association between body mass index and cardiovascular disease mortality in east Asians and south Asians: Pooled analysis of prospective data from the Asia Cohort Consortium. BMJ (Online), 347(7927), f5446. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.f5446
Dahl, A. K., & Hassing, L. B. (2013). Obesity and cognitive aging. Epidemiologic Reviews, 35(1), 22–32. https://doi.org/10.1093/epirev/mxs002
Dahl, A. K., Hassing, L. B., Fransson, E. I., Gatz, M., Reynolds, C. A., & Pedersen, N. L. (2013). Body mass index across midlife and cognitive change in late life. International Journal of Obesity, 37(2), 296–302. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2012.37
de Araújo Amaral, C., Amaral, T. L. M. I., Monteiro, G. T. R., de Vasconcellos, M. T. L., & Portela, M. C. (2020). Factors associated with low handgrip strength in older people: data of the study of chronic diseases (Edoc-I). BMC Public Health, 20(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-08504-z
Deckers, K., van Boxtel, M. P. J., Verhey, F. R. J., & Köhler, S. (2016). Obesity and cognitive decline in adults: effect of methodological choices and confounding by age in a longitudinal study. The Journal of Nutrition Health & Aging, 21(2017), 546–553. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12603-016-0757-3
Dixon, A. E., & Peters, U. (2018). The effect of obesity on lung function. Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine, 12(9), 755. https://doi.org/10.1080/17476348.2018.1506331
Dong, Q., Liu, J. J., Zheng, R. Z., Dong, Y. H., Feng, X. M., Li, J., & Huang, F. (2013). Obesity and depressive symptoms in the elderly: a survey in the rural area of Chizhou, Anhui province. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 28(3), 227–232. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.3815
Drumond Andrade, F. C., Nazan, M., Lebrão, A. I. N., M. L., & de Oliveira Duarte, Y. A. (2013). The impact of body mass index and weight changes on disability transitions and mortality in Brazilian older adults. Journal of Aging Research, 2013, 11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/905094
Faubel, M. (1989). Body image and depression in women with early and late onset obesity. Journal of Psychology: Interdisciplinary and Applied, 123(4), 385–395. https://doi.org/10.1080/00223980.1989.10542993
Flegal, K. M., Kit, B. K., Orpana, H., & Graubard, B. I. (2013). Association of all-cause mortality with overweight and obesity using standard body mass index categories: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the American Medical Association, 309(1), 71. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.113905
Ganguli, M., Beer, J. C., Zmuda, J. M., Ryan, C. M., Sullivan, K. J., Chang, C. C. H., & Rao, R. H. (2020). Aging, diabetes, obesity, and cognitive decline: a population-based study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 68(5), 991–998. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgs.16321
Herman, K. M., Hopman, W. M., & Rosenberg, M. W. (2013). Self-rated health and life satisfaction among Canadian adults: associations of perceived weight status versus BMI. Quality of Life Research, 2013 22:10(10), 2693–2705. https://doi.org/10.1007/S11136-013-0394-9
IIPS, NPHCE, MoHFW, HSPH & USC (2020). Longitudinal ageing study in India (LASI) Wave-I, 2017–18, India Report. International Institute for Population Sciences, Mumbai. https://www.iipsindia.ac.in/sites/default/files/LASI_India_Report_2020_compressed.pdf
Imai, K., Gregg, E. W., Chen, Y. J., Zhang, P., de Rekeneire, N., & Williamson, D. F. (2008). The association of BMI with functional status and self-rated health in US adults. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 16(2), 402–408. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2007.70
Khan, S. S., Ning, H., Wilkins, J. T., Allen, N., Carnethon, M., Berry, J. D., Sweis, R. N., & Lloyd-Jones, D. M. (2018). Association of body mass index with lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease and compression of morbidity. JAMA Cardiology, 3(4), 280–287. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2018.0022
Kim, J., Noh, J. W., Park, J., & Kwon, Y. D. (2014). Body mass index and depressive symptoms in older adults: a cross-lagged panel analysis. PLoS One, 9(12), e114891. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114891
Kim, S., Kim, Y., & Park, S. M. (2016). Body mass index and decline of cognitive function. PLoS One, 11(2), e0148908. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0148908
Kuriyama, S., Koizumi, Y., Matsuda-Ohmori, K., Seki, T., Shimazu, T., Hozawa, A., Awata, S., & Tsuji, I. (2006). Obesity and depressive symptoms in elderly Japanese: The Tsurugaya Project. Journal of Psychosomatic Research, 60(3), 229–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychores.2005.07.010
Larrieu, S., Pérès, K., Letenneur, L., Berr, C., Dartigues, J. F., Ritchie, K., Février, B., Alpérovitch, A., & Barberger-Gateau, P. (2004). Relationship between body mass index and different domains of disability in older persons: the 3C study. International Journal of Obesity, 23(12), 1555–1560. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijo.0802755
Li, Z., bin, Ho, S. Y., Chan, W. M., Ho, K. S., Li, M. P., Leung, G. M., & Lam, T. H. (2004). Obesity and depressive symptoms in Chinese elderly. International Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry, 19(1), 68–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/gps.1040
Lloyd-Sherlock, P., Beard, J., Minicuci, N., Ebrahim, S., & Chatterji, S. (2014). Hypertension among older adults in low- and middle-income countries: prevalence, awareness and control. International Journal of Epidemiology, 43(1), 116–128. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyt215
Monda, V., Marra, M., Perrella, R., Caviglia, G., Iavarone, A., Chieffi, S., Messina, G., Carotenuto, M., Monda, M., & Messina, A. (2017). Diabetes, metabolic syndrome and obesity: targets and therapy dovepress obesity and brain illness: from cognitive and psychological evidences to obesity paradox. https://doi.org/10.2147/dmso.s148392
Moreno-Vecino, B., Arija-Blázquez, A., Pedrero-Chamizo, R., Gómez-Cabello, A., Alegre, L. M., Pérez-López, F. R., González-Gross, M., Casajús, J. A., & Ara, I. (2017). Sleep disturbance, obesity, physical fitness and quality of life in older women: EXERNET study group. Climacteric: The Journal of the International Menopause Society, 20(1), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/13697137.2016.1264934
Ni Mhurchu, C., Rodgers, A., Pan, W. H., Gu, D. F., Woodward, M., Parag, V., Lin, R., Bennett, D. A., Hoorn, Barzi, S., MacMahon, F., Lam, S., Lawes, T. H., Suh, C., Ueshima, I., Okayama, H., Maegawa, A., Aoki, H., Nakamura, N., & Yao, M. (2004). Body mass index and cardiovascular disease in the Asia-Pacific Region: an overview of 33 cohorts involving 310 000 participants. International Journal of Epidemiology, 33(4), 751–758. https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/dyh163
Nóbrega, J. C. L., Medeiros, J. B., Santos, T. T., de Alves, M., Freitas, S. A. V., Silva, J. L. G., Simões, J. M. M., Brito, R. F. M., de Weller, A., Santos, M., de Menezes, J. L., Duarte, T. N., de Zatz, Y. A., Matheson, M., D., & Santos, S. (2021). Socioeconomic factors and health status disparities associated with difficulty in ADLs and IADLs among long-lived populations in Brazil: A cross-sectional study. Inquiry (United States), 58. https://doi.org/10.1177/00469580211007264
Noh, J. W., Kwon, Y. D., Park, J., & Kim, J. (2015). Body mass index and depressive symptoms in middle aged and older adults. BMC Public Health, 15(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-015-1663-z
Noh, J. W., Kim, J., Yang, Y., Park, J., Cheon, J., & Kwon, Y. D. (2017). Body mass index and self-rated health in East Asian countries: comparison among South Korea, China, Japan, and Taiwan. PLoS One, 12(8), e0183881. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183881
Nyamdorj, R., Qiao, Q., Lam, T. H., Tuomilehto, J., Ho, S. Y., Pitkäniemi, J., Nakagami, T., Mohan, V., Janus, E. D., & Ferreira, S. R. G. (2008). BMI compared with central obesity indicators in relation to diabetes and hypertension in Asians. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.), 16(7), 1622–1635. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2008.73
Pandav, R., Fillenbaum, G., Ratcliff, G., Dodge, H., & Ganguli, M. (2002). Sensitivity and specificity of cognitive and functional screening instruments for dementia: the Indo-U.S. dementia epidemiology study. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 50(3), 554–561. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50126.x
Pengpid, S., & Peltzer, K. (2018). Hand grip strength and its sociodemographic and health correlates among older adult men and women (50 years and older) in Indonesia. Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3265041
Pengpid, S., & Peltzer, K. (2021). Prevalence and correlates of functional disability among community-dwelling older adults in India: results of a National Survey in 2017–2019. Elderly Health Journal, 7(1), 18–25. https://doi.org/10.18502/ehj.v7i1.6547
Prickett, C., Brennan, L., & Stolwyk, R. (2015). Examining the relationship between obesity and cognitive function: a systematic literature review. Obesity Research & Clinical Practice, 9(2), 93–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.orcp.2014.05.001
Radloff, L. S. (1977). The CES-D scale: a self-report depression scale for research in the general population. Applied Psychological Measurement, 1(3), 385–401. https://doi.org/10.1177/014662167700100306
Ramlagan, S., Peltzer, K., & Phaswana-Mafuya, N. (2014). Hand grip strength and associated factors in non-institutionalised men and women 50 years and older in South Africa. BMC Research Notes, 7(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-7-8
Rejeski, W. J., Marsh, A. P., Chmelo, E., & Rejeski, J. J. (2010). Obesity, intentional weight loss and physical disability in older adults. Obesity Reviews, 11(9), 671–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789x.2009.00679.x
Selvamani, Y., & Singh, P. (2018). Socioeconomic patterns of underweight and its association with self-rated health, cognition and quality of life among older adults in India. PLoS One, 13(3), e0193979. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193979
Shochat, T., Shefer-Hilel, G., & Zisberg, A. (2016). Relationships between body mass index and sleep quality and duration in adults 70 years and older. Sleep Health, 2(4), 266–271. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2016.09.001
Sowers, J. R. (2003). Obesity as a cardiovascular risk factor. The American Journal of Medicine, 115(8), 37–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2003.08.012
Sung, E. S., Choi, C. K., Jeong, J. A., & Shin, M. H. (2020). The relationship between body mass index and poor self-rated health in the South Korean population. PLoS One, 15(8), e0219647. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219647
Thu Tran, N. T., Blizzard, C. L., Luong, K. N., van Truong, N., Tran, B. Q., Otahal, P., Nelson, M., Magnussen, C., Gall, S., van Bui, T., Srikanth, V., Au, T. B., Ha, S. T., Phung, H. N., Tran, M. H., & Callisaya, M. (2018). The importance of waist circumference and body mass index in cross-sectional relationships with risk of cardiovascular disease in Vietnam. PLoS One, 13(5), e0198202. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198202
Tobias, D. K., Pan, A., Jackson, C. L., O’Reilly, E. J., Ding, E. L., Willett, W. C., Manson, J. E., & Hu, F. B. (2014). Body-mass index and mortality among adults with incident type 2 diabetes. The New England Journal of Medicine, 370(3), 233–244. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1304501
Tsai, H. J., & Chang, F. K. (2017). Associations between body mass index, mid-arm circumference, calf circumference, and functional ability over time in an elderly Taiwanese population. PloS One, 12(4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0175062
Wang, A., & Arah, O. A. (2019). Body mass index and poor self-rated health in 49 low-income and middle-income countries, by sex, 2002–2004. Preventing Chronic Disease, 12(8). https://doi.org/10.5888/pcd12.150070
Wang, S. K., Ma, W., Wang, S., Yi, X. R., Jia, H. Y., & Xue, F. (2014). Obesity and its relationship with hypertension among adults 50 years and older in Jinan, China. PLoS One, 9(12), e114424. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0114424
WHO/NUT/NCD (1998). Obesity: preventing and managing the global epidemic: report of a WHO Consultation on Obesity, Geneva, 3–5 June 1997. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/63854
Wormser, D., Kaptoge, S., di Angelantonio, E., Wood, A. M., Pennells, L., Thompson, A., Sarwar, N., Kizer, J. R., Lawlor, D. A., Nordestgaard, B. G., Ridker, P., Salomaa, V., Stevens, J., Woodward, M., Sattar, N., Collins, R., Thompson, S. G., Whitlock, G., Danesh, J., & White, I. R. (2011). Separate and combined associations of body-mass index and abdominal adiposity with cardiovascular disease: collaborative analysis of 58 prospective studies. Lancet (London England), 377(9771), 1085–1095. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60105-0
Zhang, L., Liu, K., Li, H., Li, D., Chen, Z., Zhang, L., li, & Guo, L. L. (2016). Relationship between body mass index and depressive symptoms: the “fat and jolly” hypothesis for the middle-aged and elderly in China. BMC Public Health, 16(1), 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-016-3864-5
Zhang, L., Zhang, W. H., Zhang, L., & Wang, P. Y. (2011). Prevalence of overweight/obesity and its associations with hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, and metabolic syndrome: a survey in the suburban area of Beijing, 2007. Obesity Facts, 4(4), 284. https://doi.org/10.1159/000331014
Zhang, W., He, K., Zhao, H., Hu, X., Yin, C., Zhao, X., & Shi, S. (2021). Association of body mass index and waist circumference with high blood pressure in older adults. BMC Geriatrics, 21(1), 1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-021-02154-5
Zheng, W., McLerran, D. F., Rolland, B., Zhang, X., Inoue, M., Matsuo, K., He, J., Gupta, P. C., Ramadas, K., Tsugane, S., Irie, F., Tamakoshi, A., Gao, Y. T., Wang, R., Shu, X. O., Tsuji, I., Kuriyama, S., Tanaka, H., Satoh, H., & Potter, J. D. (2011). Association between body-mass index and risk of death in more than 1 million Asians. New England Journal of Medicine, 364(8), 719–729. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa1010679
Acknowledgments
We are thankful to the International Institute for Population Sciences (IIPS) for helping us with the survey data, and we are also grateful to the LASI research as well as the field team for their data collection. The authors are also thankful to all anonymous reviewers for giving important observations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AR: conceptualization and designing of the research paper, data analysis, and manuscript writing; PB: helping during the analyses, and participation in constructive discussions. All authors read carefully and finally approved the manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The data are easily accessible from the public domain on specific requests. The authorities responsible for data collection from the field survey have taken informed consent before surveying the respondents. Ethical approval and the necessary guidance for conducting the survey have been given by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and all other institutions.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Experimental Subjects/Animals
No experimental treatment on humans or animals was conducted.
Competing Interests
The authors mentioned that there were no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 15.3 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roy, A., Barman, P. Does BMI Really Matter to Our Overall Health? Findings from a Cross-sectional Analysis of Middle-aged and Older Adults in India. Population Ageing 17, 71–89 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12062-023-09413-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12062-023-09413-w