Abstract
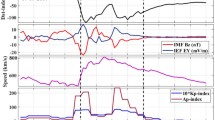
The effect of geomagnetic storms on low latitude ionosphere has been investigated with the help of Global Positioning System Total Electron Content (GPS-TEC) data. The investigation has been done with the aid of TEC data from the Indian equatorial region, Port Blair (PBR) and equatorial ionization anomaly region, Agartala (AGR). During the geomagnetic storms on 24th April and 15th July 2012, significant enhancement up to 150% and depression up to 72% in VTEC is observed in comparison to the normal day variation. The variations in VTEC observed from equatorial to EIA latitudes during the storm period have been explained with the help of electro-dynamic effects (prompt penetration electric field (PPEF) and disturbance dynamo electric field (DDEF)) as well as mechanical effects (storm-induced equatorward neutral wind effect and thermospheric composition changes). The current study points to the fact that the electro-dynamic effect of geomagnetic storms around EIA region is more effective than at the lower latitude region. Drastic difference has been observed over equatorial region (positive storm impact) and EIA region (negative storm impact) around same longitude sector, during storm period on 24th April. This drastic change as observed in GPS-TEC on 24th April has been further confirmed by using the O/N2 ratio data from GUVI (Global Ultraviolet Imager) as well as VTEC map constructed from IGS data. The results presented in the paper are important for the application of satellite-based communication and navigational system.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdu M A, Maruyama T, Batista I S, Saito S and Nakamura M 2007 Ionospheric responses to the October 2003 superstorm: Longitude/local time effects over equatorial low and middle latitudes; J. Geophys. Res. 112 A10306, doi: 10.1029/2006JA012228.
Astafyeva E I 2009a Dayside ionospheric uplift during strong geomagnetic storms as detected by the CHAMP, SAC-C, TOPEX and Jason-1 satellites; Adv. Space Res. 43 1749–1756.
Astafyeva E I 2009b Effects of strong IMF Bz southward events on the equatorial and mid-latitude ionosphere ; Ann. Geophys. 27 1175–1187, doi: 10.5194/angeo-27-1175-2009.
Bauske R and Prolss G W 1997 Modelling the ionospheric response to travelling atmospheric disturbances; J. Geophys. Res. 102 14,555–14,562.
Basu S, Basu S, Valladares C E, Yeh H -C, Su S -Y, MacKenzie E, Sultan P J, Aarons J, Rich F J, Doherty P, Groves K M and Bullett T W 2001 Ionospheric effects of major magnetic storms during the International Space Weather Period of September and October 1999: GPS observations, VHF/UHF scintillations, and in situ density structures at middle and equatorial latitudes; J. Geophys. Res. 106 30,389–30,413, doi: 10.1029/2001JA001116.
Basu S, Makela J J, Sheehan R E, MacKenzie E, Doherty P, Wright J W, Keskinen M J, Pallamraju D, Paxton L J and Berkey F T 2005 Two components of ionospheric plasma structuring at midlatitudes observed during the large magnetic storm of October 30, 2003; Geophys. Res. Lett. 32 L12S06, doi: 10.1029/2004GL021669.
Basu S, Basu S, Makela J J, MacKenzie E, Doherty P, Wright J W, Rich F, Keskinen M J, Sheehan R E and Coster A J 2008 Large magnetic storm-induced nighttime ionospheric flows at midlatitudes and their impacts on GPS-based navigation systems; J. Geophys. Res. 113 A00A06, doi: 10.1029/2008JA013076.
Buonsanto M J 1999 Ionospheric storms – a review; Space Sci. Rev. 88 563–601.
Burns A G, Solomon S C, Wang W and Killeen T L 2007 The ionospheric and thermospheric response to CMEs: Challenges and successes ; J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 69 77–85.
Chakraborty Monti, Sanjay Kumar, Barin Kumar De and Anirban Guha 2014 Latitudinal characteristics of GPS derived ionospheric TEC: A comparative study with IRI 2012 model; Ann. Geophys. 57 (5) A0539, doi: 10.4401/ag-6438.
Christensen A B, Paxton L J, Avery S, Craven J, Crowley G, Humm D C, Kil H, Meier R R, Meng C -I, Morrison D, Ogorzalek B S, Straus P, Strickland D J, Swenson R M, Walterscheid R L, Wolven B and Zhang Y 2003 Initial observations with the Global Ulta-violet Imager (GUVI) in the NASATIMED sattelite mission; J. Geophys. Res. 108 (A12) 1451, doi: 10.1029/2003JA009918.
Fejer B G, Jensen J W, Kikuchi T, Abdu M A and Chau J L 2007 Equatorial ionospheric electric fields during the November 2004 magnetic storm; J. Geophys. Res. 112 A10304, doi: 10.1029/2007JA012376.
Fuller-Rowell T M, Miillward G H, Richmond A D and Codrescu M V 2002 Storm time changes in the upper atmosphere at low latitudes; J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 64 1383–1391.
Galav P, Sharma S and Pandey R 2011 Study of simultaneous penetration of electric fields and variation of total electron content in the day and night sectors during the geomagnetic storm of 23 May 2002; J. Geophys. Res. 116 A12324, doi: 10.1029/2011JA017002.
Hofmann-Wellenhof B, Lichtenegger H and Collins J 2001 Global Positioning System: Theory and Practice; Springer, Berlin.
Hines C O 1960 Internal atmospheric gravity waves at ionospheric heights; Can. J. Phys. 38 1441–1481.
Immel T J, Crowley G, Craven J D and Roble R G 2001 Day side enhancements of thermospheric O/N2 following magnetic storm onset; J. Geophys. Res. 106 15,471–15,488, doi: 10.1029/2000JA000096.
Klobuchar J 1986 Design and characteristics of the GPS ionospheric time-delay algorithm for single-frequency users; In: Procedings of the IEEE Position Location and Navigation Symposium, Las Vegas, November 4–7.
Kumar S and Singh A K 2011a Storm time response of GPS-derived total electron content (TEC) during low solar active period at Indian low latitude station, Varanasi; Astrophys. Space Sci. 331 447–458.
Kumar S and Singh A K 2011b GPS derived ionospheric TEC response to geomagnetic storm on 24 August 2005 at Indian low latitude stations; Adv. Space Res. 47 710–717.
Kutiev I, Watanabe S, Otsuka Y and Saito A 2005 Total electron content behavior over Japan during geomagnetic storms; J. Geophys. Res. 110 A01308, doi: 10.1029/2004JA010586.
Lijo J, Ravindran S, Vineet C, Pant T K and Alex S 2011 Investigation of the response time of the equatorial ionosphere in the context of equatorial electrojet and equatorial ionization anomaly; Ann. Geophys. 29 1267–1275.
Liu C H and Edwards B 1988 WITS Handbook, World Ionosphere/Thermosphere Study, vol. 2, Natl. Sci. Found., Urbana, Ill.
Liu J, Zhao B and Liu L 2010 Time delay and duration of ionospheric total electron content responses to geomagnetic disturbances; Ann. Geophys. 28 795–805, doi: 10.5194/angeo-28-795-2010.
Mendillo M 2006 Storms in the ionosphere: Patterns and processes for total electron content; Rev. Geophys. 44 RG4001, doi: 10.1029/2005RG000193.
Pedatella N M, Lei J, Larson K M and Forbes J M 2009 Observation of the ionospheric response to the 15th December 2006 geomagnetic storm: Long duration positive storm effect; J. Geophys. Res. 114 A12313, doi: 10.1029/2009JA014568.
Prölss G W 1995 Ionospheric F-region storms; In: Handbook of Atmospheric Electrodynamics (ed.) Volland H, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Rama Rao P V S, Gopi Krishna S, Niranjan K and Prasad D S V V D 2006 Temporal and spatial variations in TEC using simultaneous measurements from the IndianGPS network of receivers during the low solar activity period of 2004–2005; Ann. Geophys. 24 3279–3292, doi: 10.5194/angeo-24-3279-2006.
Rama Rao P V S, Gopi Krishna S, Vara Prasad J, Prasad S N V S, Prasad D S V V D and Niranjan K 2009 Geomagnetic storm effects on GPS based navigation; Ann. Geophys. 27 2101–2110.
Rastogi R G and Klobuchar J A 1990 Ionospheric electron content within the equatorial F2 layer anomaly belts; J. Geophys. Res. 95 19,045–19,052, doi: 10.1029/JA095iA11p19045.
Rishbeth H, Fuller-Rowell T J and Rees D 1987 Diffusive equilibrium and vertical motion in the thermosphere during a severe magnetic storm: A computational study; Planet. Space Sci. 35 1157–1165, doi: 10.1016/0032-0633(87)90022-5.
Rishbeth H and Mendillo M 2001 Patterns of F2-layer variability; J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 63 1661–1680.
Singh A K, Sardar N, Rizvi S and Vijay S K 2013 Night-time enhancement of ionospheric parameters; Indian J. Radio Space Phys. 42 240.
Sardon E, Rius A and Zarraoa N 1994 Estimation of the transmitter and receiver differential biases and the ionospheric total electron content from Global Positioning System observations; Radio Sci. 29 (3) 577–586, doi: 10.1029/94RS00449.
Sastri J H, Abdu M A and Sobral J H A 1997 Response of equatorial ionosphere to episodes of asymmetric ring current activity; Ann. Geophys. 15 1316–1323, doi: 10.1007/s00585-997-1316-3.
Sastri J H, Jyoti N, Somayajulu V V, Chandra H and Devasia C V 2000 Ionospheric storm of early November 1993 in the Indian equatorial region; J. Geophys. Res. 105 18,443–18,455, doi: 10.1029/1999JA000372.
Tsurutani B T et al. 2004 Global dayside ionospheric uplift and enhancement associated with interplanetary electric field; J. Geophys. Res. 109 A08302, doi: 10.1029/2003JA010342.
Veenadhari B, Alex S, Kikuchi T, Shinbori A, Singh R and Chandrasekhar E 2010 Penetration of magnetospheric electric fields to the equator and their effects on the low-latitude ionosphere during intense geomagnetic storms; J. Geophys. Res. 115 A03305, doi: 10.1029/2009JA014562.
Zhao B, Wan W and Liu L 2005 Response of equatorial anomaly to the October–November 2003 superstorms; Ann. Geophys. 23 693.
Zhao B, Wan W, Liu L and Mao T 2007 Morphology in the total electron content under geomagnetic disturbed conditions: Results from global ionosphere maps; Ann. Geophys. 25 1555–1568, doi: 10.5194/angeo-31-2085-2013.
Zhao B, Wan W, Tschu K, Igarashi K, Kikuchi T, Nozaki K, Watari S, Li G, Paxton L J, Liu L, Ning B, Liu J -Y, Su S -Y and Bulanon P H 2008 Ionospheric disturbances observed throughout southeast Asia of superstorm of 20–22 November 2003; J. Geophys. Res. 113 A00A04, doi: 10.1029/2008JA013054.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to World Data Center for Geomagnetism at Kyoto University, Japan for providing geomagnetic data and the International GNSS Service (IGS) team for providing the GPS data. The global TEC maps have been plotted from the IGS data using Matlab codes. They also thank the ACE SWEPAM and MAG instrument teams and the ACE science centre for providing the ACE data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chakraborty, M., Kumar, S., De, B.K. et al. Effects of geomagnetic storm on low latitude ionospheric total electron content: A case study from Indian sector. J Earth Syst Sci 124, 1115–1126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0588-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-015-0588-3