Abstract
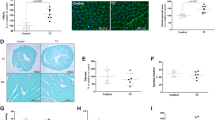
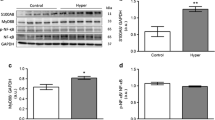
Hyperthyroidism can lead to the activation of proteins which are associated with inflammation, apoptosis, hypertrophy, and heart failure. This study aimed to explore the inflammatory and apoptotic proteins involved in the hyperthyroidism-induced cardiac hypertrophy establishment. Male Wistar rats were divided into control and hyperthyroid (12 mg/L L-thyroxine, in drinking water for 28 days) groups. The expression of inflammatory and apoptotic signaling proteins was quantified in the left ventricle by Western blot. Hyperthyroidism was confirmed by evaluation of T3 and T4 levels, as well as cardiac hypertrophy development. There was no change in the expression of HSP70, HIF1-α, TNF-α, MyD88, p-NFκB, NFκB, p-p38, and p38. Reduced expression of p53 and PGC1-α was associated with increased TLR4 and decreased IL-10 expression. Decreased Bcl-2 expression and increased Bax/Bcl-2 ratio were also observed. The results suggest that reduced PGC1-α and IL-10, and elevated TLR4 proteins expression could be involved with the diminished mitochondrial biogenesis and anti-inflammatory response, as well as cell death signaling, in the establishment of hyperthyroidism-induced maladaptive cardiac hypertrophy.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo ASR, Diniz GP, Seibel FER, Branchini G, Ribeiro MFM, Brum IS, Khaper N, Barreto-Chaves ML and Belló-Klein A 2011 Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species balance in the determination of thyroid hormones-induced cardiac hypertrophy mediated by renin–angiotensin system. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 333 78–84
Araujo ASR, Enzveiler AT, Schenkel P, Fernandes TRG, Ribeiro MFM, Partata WA, Llesuy S and Belló-Klein A 2007 Oxidative stress activates insulin-like growth factor I receptor protein expression, mediating cardiac hypertrophy induced by thyroxine. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 303 89–95
Araujo ASR, Ribeiro MFM, Enzveiler A, Schenkel P, Fernandes TRG, Partata WA, Irigoyen MC, Llesuy S and Belló-Klein A 2006 Myocardial antioxidant enzyme activities and concentration and glutathione metabolism in experimental hyperthyroidism. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 249 133–139
Araujo ASR, Schenkel P, Enzveiler AT, Fernandes TRG, Partata WA, Llesuy S, Ribeiro MF, Khaper N, Singal PK and Belló-Klein A 2008 The role of redox signaling in cardiac hypertrophy induced by experimental hyperthyroidism. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 41 423–430
Bartekova M, Radosinska J, Jelemensky M and Dhalla NS 2018 Role of cytokines and inflammation in heart function during health and disease. Heart Fail. Rev. [Epub ahead of print] doi: 10.1007/s10741-018-9716-x.
Chaudhari M, Jayaraj R, Bhaskar ASB and Lakshmana Rao PV 2009 Oxidative stress induction by T-2 toxin causes DNA damage and triggers apoptosis via caspase pathway in human cervical cancer cells. Toxicology 262 153–161
da Rosa Araujo AS, Fernandes T, Ribeiro MF, Khaper N and Belló-Klein A 2010 Redox Regulation of Myocardial Erk 1/2 Phosphorylation in Experimental Hyperthyroidism: Role of Thioredoxin-Peroxiredoxin System. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 56 513–517
Darehgazani R, Peymani M, Hashemi M-S, Omrani MD, Movafagh A, Ghaedi K and Nasr-Esfahani MH 2016 PPARγ ameliorated LPS induced inflammation of HEK cell line expressing both human Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) and MD2. Cytotechnology 68 1337–148
Dijsselbloem N, Goriely S, Albarani V, Gerlo S, Francoz S, Marine J-C, Goldman M, Haegeman G and Vanden Berghe W 2007 A critical role for p53 in the control of NF-kappaB-dependent gene expression in TLR4-stimulated dendritic cells exposed to Genistein. J. Immunol. 178 5048–5057
Dillmann W 2010 Cardiac hypertrophy and thyroid hormone signaling. Heart Fail. Rev. 15 125–132
Fazio S, Palmieri EA, Lombardi G and Biondi B 2004 Effects of thyroid hormone on the cardiovascular system. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 59 31–50.
Feng Y and Chao W 2011 Toll-like receptors and myocardial inflammation. Int. J. Inflam. 2011 170352
Ferreira A and Ávila S 2013 Diagnóstico Laboratorial das Principais Doenças Infecciosas e Auto-imunes. 2nd ed. (Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan).
Garnier A, Fortin D, Deloménie C, Momken I, Veksler V and Ventura-Clapier R 2003 Depressed mitochondrial transcription factors and oxidative capacity in rat failing cardiac and skeletal muscles. J. Physiol. 551 491–501
Goldenthal MJ, Weiss HR and Marín-García J 2004 Bioenergetic remodeling of heart mitochondria by thyroid hormone. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 265 97–106
Harsdorf VR, Li PF and Dietz R 1999 Signaling pathways in reactive oxygen species-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Circulation 99 2934–2941
Hu LW, Benvenuti LA, Liberti EA, Carneiro-Ramos MS and Barreto-Chaves MLM 2003 Thyroxine-induced cardiac hypertrophy: influence of adrenergic nervous system versus renin-angiotensin system on myocyte remodeling. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 285 R1473–R1480
Jia S-J, Niu P-P, Cong J-Z, Zhang B-K and Zhao M 2014 TLR4 signaling: A potential therapeutic target in ischemic coronary artery disease. Int. Immunopharmacol. 23 54–59
Khaper N, Bryan S, Dhingra S, Singal R, Bajaj A, Pathak CM and Singal PK 2010 Targeting the vicious inflammation–oxidative stress cycle for the management of heart failure. Antioxid. Redox. Signal. 13 1033–1049
Klein D, Kern RM and Sokol RZ 1995 A method for quantification and correction of proteins after transfer to immobilization membranes. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 36 59–66
Klein I and Ojamaa K 2001 Thyroid hormone and the cardiovascular system. New Engl. J. Med. 344 501–509
Laemmli UK 1970 Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227 680–685
Li H, Yin H, Yao Y, Shen B, Bader M, Chao L and Chao J 2007 Tissue kallikrein protects against pressure overload-induced cardiac hypertrophy through kinin B2 receptor and glycogen synthase kinase-3β activation. Cardiovasc. Res. 73 130–142
Liang H and Ward WF 2006 PGC-1α: a key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 30 145–151
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and Randall RJ 1951 Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193 265–275
Madenspacher JH, Azzam KM, Gowdy KM, Malcolm KC, Nick JA, Dixon D, Aloor JJ, Draper DW, Guardiola JJ, Shatz M, Menendez D, Lowe J, Lu J, Bushel P, Li L, Merrick BA, Resnick MA and Fessler MB 2013 p53 integrates host defense and cell fate during bacterial pneumonia. J. Exp. Med. 210 891–904
Maity S, Kar D, De K, Chander V and Bandyopadhyay A 2013 Hyperthyroidism causes cardiac dysfunction by mitochondrial impairment and energy depletion. J. Endocrinol. 217 215–228
Messarah M, Saoudi M, Boumendjel A, Boulakoud MS and Feki A El 2011 Oxidative stress induced by thyroid dysfunction in rat erythrocytes and heart. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 31 33–41
Mihara S, Suzuki N, Wakisaka S, Suzuki S, Sekita N, Yamamoto S, Saito N, Hoshino T and Sakane T 1999 Effects of thyroid hormones on apoptotic cell death of human lymphocytes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84 1378–1385
Narula J, Pandey P, Arbustini E, Haider N, Narula N, Kolodgie FD, Bello Bd, Semigran MJ, Bielsa-Masdeu A, Dec Gw, Israels S, Ballester M, Virmanii R, Saxena S and Kharbanda S 1999 Apoptosis in heart failure: release of cytochrome c from mitochondria and activation of caspase-3 in human cardiomyopathy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 96 8144–8149
Noble EG and Shen GX 2012 Impact of exercise and metabolic disorders on heat shock proteins and vascular inflammation. Autoimmune. Dis. 2012 836519
Olivetti G, Abbi R, Quaini F, Kajstura J, Cheng W, Nitahara JA, Quaini E, Loreto CD, Beltrami CA, Krajewski S, Reed JC and Anversa P 1997 Apoptosis in the failing human heart. New Engl. J. Med. 336 1131–1141
Puigserver P 2005 Tissue-specific regulation of metabolic pathways through the transcriptional coactivator PGC1-α. Int. J. Obes. 29 S5–S9
Rodriguéz-Goméz I, Banegas I, Wangensteen R, Quesada A, Jiménez R, Gómez-Morales M, O’Valle F, Duarte J and Vargas F 2013 Influence of thyroid state on cardiac and renal capillary density and glomerular morphology in rats. J. Endocrinol. 216 43–51
Satoh M, Shimoda Y, Akatsu T, Ishikawa Y, Minami Y and Nakamura M 2006 Elevated circulating levels of heat shock protein 70 are related to systemic inflammatory reaction through monocyte Toll signal in patients with heart failure after acute myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 8 810–815
Schilling J, Lai L, Sambandam N, Dey CE, Leone TC and Kelly DP 2011 Toll-like receptor-mediated inflammatory signaling reprograms cardiac energy metabolism by repressing peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor coactivator-1 signaling. Circ. Heart Fail. 4 474–482
Sen N, Satija YK and Das S 2011 PGC-1α, a Key Modulator of p53, promotes cell survival upon metabolic stress. Mol. Cell. 44 621–634
Summermatter S, Baum O, Santos G, Hoppeler H and Handschin C 2010 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1α (PGC-1α) promotes skeletal muscle lipid refueling in vivo by activating de novo lipogenesis and the pentose phosphate pathway. J Biol. Chem. 285 32793–32800
Summermatter S, Santos G, Perez-Schindler J and Handschin C 2013 Skeletal muscle PGC-1 controls whole-body lactate homeostasis through estrogen-related receptor-dependent activation of LDH B and repression of LDH A. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 110 8738–8743
Thuringer D, Berthenet K, Cronier L, Jego G, Solary E and Garrido C 2015 Oncogenic extracellular HSP70 disrupts the gap-junctional coupling between capillary cells. Oncotarget 6 10267–10283
Timmers L, Sluijter JPG, van Keulen JK, Hoefer IE, Nederhoff MGJ, Goumans M-J, Doevendans PA, van Echteld CJ, Joles JA, Quax PH, Piek JJ, Pasterkamp G and de Kleijn DP 2008 Toll-Like receptor 4 mediates maladaptive left ventricular remodeling and impairs cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Circ. Res. 102 257–264
Tuomainen T and Tavi P 2017 The role of cardiac energy metabolism in cardiac hypertrophy and failure. Exp. Cell. Res. 360 12–18
Vaez H, Najafi M, Rameshrad M, Toutounchi NS, Garjani M, Barar J, Garjani A 2016 AMPK activation by metformin inhibits local innate immune responses in the isolated rat heart by suppression of TLR 4-related pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 40 501–507
Vallejo JG 2011 Role of Toll-like receptors in cardiovascular diseases. Clin. Sci. 121 1–10
Ventura-Clapier R, Garnier A and Veksler V 2008 Transcriptional control of mitochondrial biogenesis: the central role of PGC-1. Cardiovasc. Res. 79 208–217
Vondriska TM and Wang Y 2008 A new (heat) shocking player in cardiac hypertrophy. Circ. Res. 103 1194–1196
Weltman NY, Wang D, Redetzke RA and Gerdes AM 2012 Longstanding hyperthyroidism is associated with normal or enhanced intrinsic cardiomyocyte function despite decline in global cardiac function. PLoS One 7 e46655
Xu W, Hou D, Jiang X, Lu Z, Guo T, Liu Y, Wang D, Zen K, Yu B and Zhang CY 2012 The protective role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α in hyperthyroid cardiac hypertrophy. J Cell. Physiol. 227 3243–3253
Yang Y, Lv J, Jiang S, Ma Z, Wang D, Hu W, Deng C, Fan C, Di S, Sun Y and Yi W 2016 The emerging role of Toll-like receptor 4 in myocardial inflammation. Cell Death. Dis. 7 e2234–e2234
Yin FC, Spurgeon HA, Rakusan K, Weisfeldt ML and Lakatta EG 1982 Use of tibial length to quantify cardiac hypertrophy: application in the aging rat. Am. J Physiol. 243 H941–H947
Acknowledgments
Veterinary medical support from Dr. André Ricardo Ribeiro Belló is acknowledged. We also acknowledge Professor Ilma Simoni Brum, Physiology Department, UFRGS, for providing the p53 antibody. This paper was written during a scholarship provided by the International Cooperation Program CAPES/DFATD at the University of Manitoba. This study was funded by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e tecnológico, Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul and Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Seyed E Hasnain.
Corresponding editor: Seyed E Hasnain
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, R.B., Barboza, T.E., de Araújo, C.C. et al. Decreased PGC1-α levels and increased apoptotic protein signaling are associated with the maladaptive cardiac hypertrophy in hyperthyroidism. J Biosci 43, 887–895 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-018-9816-8