Abstract
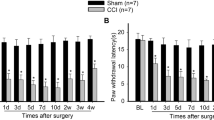
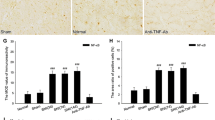
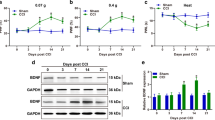
Fibroblast growth factor-inducible-14 (Fn14), a receptor for tumor necrosis-like weak inducer of apoptosis, is expressed in the neurons of dorsal root ganglion (DRG). Its mRNA is increased in the injured DRG following peripheral nerve injury. Whether this increase contributes to neuropathic pain is unknown. We reported here that peripheral nerve injury caused by spinal nerve ligation (SNL) increased the expression of Fn14 at both protein and mRNA levels in the injured DRG. Blocking this increase attenuated the development of SNL-induced mechanical, thermal, and cold pain hypersensitivities. Conversely, mimicking this increase produced the increases in the levels of phosphorylated extracellular signal-regulated kinase ½ and glial fibrillary acidic protein in ipsilateral dorsal horn and the enhanced responses to mechanical, thermal, and cold stimuli in the absence of SNL. Mechanistically, the increased Fn14 activated the NF-κB pathway through promoting the translocation of p65 into the nucleus of the injured DRG neurons. Our findings suggest that Fn14 may be a potential target for the therapeutic treatment of peripheral neuropathic pain.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
DiBonaventura MD, Sadosky A, Concialdi K, Hopps M, Kudel I, Parsons B, Cappelleri JC, Hlavacek P et al (2017) The prevalence of probable neuropathic pain in the US: results from a multimodal general-population health survey. J Pain Res 10:2525–2538. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S127014
van Hecke O, Austin SK, Khan RA, Smith BH, Torrance N (2014) Neuropathic pain in the general population: a systematic review of epidemiological studies. Pain 155(4):654–662. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.11.013
Mitka M (2003) “Virtual textbook” on pain developed: effort seeks to remedy gap in medical education. Jama 290(18):2395. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.290.18.2395
Vorobeychik Y, Gordin V, Mao J, Chen L (2011) Combination therapy for neuropathic pain: a review of current evidence. CNS Drugs 25(12):1023–1034. https://doi.org/10.2165/11596280-000000000-00000
Dworkin RH, O'Connor AB, Kent J, Mackey SC, Raja SN, Stacey BR, Levy RM, Backonja M et al (2013) Interventional management of neuropathic pain: NeuPSIG recommendations. Pain 154(11):2249–2261. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2013.06.004
Yang DZ, Sin B, Beckhusen J, Xia D, Khaimova R, Iliev I (2018) Opioid-induced hyperalgesia in the nonsurgical setting: A systematic review. Am J Ther:1. https://doi.org/10.1097/MJT.0000000000000734
Raffa RB, Pergolizzi JV Jr (2013) Opioid-induced hyperalgesia: is it clinically relevant for the treatment of pain patients? Pain management nursing : official journal of the American Society of Pain Management. Nurses 14(3):e67–e83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmn.2011.04.002
Bekhit MH (2010) Opioid-induced hyperalgesia and tolerance. Am J Ther 17(5):498–510. https://doi.org/10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ed83a0
Meyer R, Patel AM, Rattana SK, Quock TP, Mody SH (2014) Prescription opioid abuse: a literature review of the clinical and economic burden in the United States. Popul Health Manag 17(6):372–387. https://doi.org/10.1089/pop.2013.0098
Polavarapu R, Gongora MC, Winkles JA, Yepes M (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis increases the permeability of the neurovascular unit through nuclear factor-kappa B pathway activation. J Neurosci 25(44):10094–10100. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3382-05.2005
Qi X, Qin L, Du R, Chen Y, Lei M, Deng M, Wang J (2017) Lipopolysaccharide upregulated intestinal epithelial cell expression of Fn14 and activation of Fn14 signaling amplify intestinal TLR4-mediated inflammation. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 7:315. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcimb.2017.00315
Liu Y, Xu M, Min X, Wu K, Zhang T, Li K, Xiao S, Xia Y (2017) TWEAK/Fn14 activation participates in Ro52-mediated photosensitization in cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol 8:651. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2017.00651
Xia Y, Campbell SR, Broder A, Herlitz L, Abadi M, Wu P, Michaelson JS, Burkly LC et al (2012) Inhibition of the TWEAK/Fn14 pathway attenuates renal disease in nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Clin Immunol 145(2):108–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2012.08.008
Zou Y, Bao S, Wang F, Guo L, Zhu J, Wang J, Deng X, Li J (2018) FN14 blockade on pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells improves the outcome of sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Shock 49(2):213–220. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000915
Sato S, Ogura Y, Kumar A (2014) TWEAK/Fn14 signaling axis mediates skeletal muscle atrophy and metabolic dysfunction. Front Immunol 5:18. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00018
Mittal A, Bhatnagar S, Kumar A, Lach-Trifilieff E, Wauters S, Li H, Makonchuk DY, Glass DJ (2010) The TWEAK-Fn14 system is a critical regulator of denervation-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice. J Cell Biol 188(6):833–849. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200909117
Wilhelm A, Shepherd EL, Amatucci A, Munir M, Reynolds G, Humphreys E, Resheq Y, Adams DH et al (2016) Interaction of TWEAK with Fn14 leads to the progression of fibrotic liver disease by directly modulating hepatic stellate cell proliferation. J Pathol 239(1):109–121. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4707
Tanabe K, Bonilla I, Winkles JA, Strittmatter SM (2003) Fibroblast growth factor-inducible-14 is induced in axotomized neurons and promotes neurite outgrowth. J Neurosci 23(29):9675–9686. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2202-4-27
Yepes M (2007) TWEAK and the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 35(3):255–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-007-0024-z
Yepes M (2007) Tweak and FN14 in central nervous system health and disease. Front Biosci 12:2772–2781. https://doi.org/10.2741/2271
Desplat-Jego S, Creidy R, Varriale S, Allaire N, Luo Y, Bernard D, Hahm K, Burkly L et al (2005) Anti-TWEAK monoclonal antibodies reduce immune cell infiltration in the central nervous system and severity of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Clin Immunol 117(1):15–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2005.06.005
Wen J, Chen CH, Stock A, Doerner J, Gulinello M, Putterman C (2016) Intracerebroventricular administration of TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis induces depression-like behavior and cognitive dysfunction in non-autoimmune mice. Brain Behav Immun 54:27–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2015.12.017
Frauenknecht K, Bargiotas P, Bauer H, von Landenberg P, Schwaninger M, Sommer C (2010) Neuroprotective effect of Fn14 deficiency is associated with induction of the granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) pathway in experimental stroke and enhanced by a pathogenic human antiphospholipid antibody. J Neuroimmunol 227(1–2):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2010.05.043
Pelekanou V, Notas G, Kampa M, Tsentelierou E, Stathopoulos EN, Tsapis A, Castanas E (2013) BAFF, APRIL, TWEAK, BCMA, TACI and Fn14 proteins are related to human glioma tumor grade: immunohistochemistry and public microarray data meta-analysis. PLoS One 8(12):e83250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0083250
Rigaud M, Gemes G, Barabas ME, Chernoff DI, Abram SE, Stucky CL, Hogan QH (2008) Species and strain differences in rodent sciatic nerve anatomy: implications for studies of neuropathic pain. Pain 136(1–2):188–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2008.01.016
Li Z, Gu X, Sun L, Wu S, Liang L, Cao J, Lutz BM, Bekker A et al (2015) Dorsal root ganglion myeloid zinc finger protein 1 contributes to neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve trauma. Pain 156(4):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000000103
Zhao X, Tang Z, Zhang H, Atianjoh FE, Zhao JY, Liang L, Wang W, Guan X et al (2013) A long noncoding RNA contributes to neuropathic pain by silencing Kcna2 in primary afferent neurons. Nat Neurosci 16(8):1024–1031. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3438
Liaw WJ, Zhu XG, Yaster M, Johns RA, Gauda EB, Tao YX (2008) Distinct expression of synaptic NR2A and NR2B in the central nervous system and impaired morphine tolerance and physical dependence in mice deficient in postsynaptic density-93 protein. Mol Pain 4:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1744-8069-4-45
He Y, Tian X, Hu X, Porreca F, Wang ZJ (2012) Negative reinforcement reveals non-evoked ongoing pain in mice with tissue or nerve injury. J Pain 13(6):598–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpain.2012.03.011
Tao YX, Rumbaugh G, Wang GD, Petralia RS, Zhao C, Kauer FW, Tao F, Zhuo M et al (2003) Impaired NMDA receptor-mediated postsynaptic function and blunted NMDA receptor-dependent persistent pain in mice lacking postsynaptic density-93 protein. J Neurosci 23(17):6703–6712. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.23-17-06703.2003
Wu S, Marie Lutz B, Miao X, Liang L, Mo K, Chang YJ, Du P, Soteropoulos P et al (2016) Dorsal root ganglion transcriptome analysis following peripheral nerve injury in mice. Mol Pain 12:174480691662904. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806916629048
Guo D, Hu X, Zhang H, Lu C, Cui G, Luo X (2018) Orientin and neuropathic pain in rats with spinal nerve ligation. Int Immunopharmacol 58:72–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2018.03.013
Liang L, Zhao JY, Gu X, Wu S, Mo K, Xiong M, Marie Lutz B, Bekker A et al (2016) G9a inhibits CREB-triggered expression of mu opioid receptor in primary sensory neurons following peripheral nerve injury. Mol Pain 12:174480691668224. https://doi.org/10.1177/1744806916682242
Yepes M, Brown SA, Moore EG, Smith EP, Lawrence DA, Winkles JA (2005) A soluble Fn14-Fc decoy receptor reduces infarct volume in a murine model of cerebral ischemia. Am J Pathol 166(2):511–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62273-0
Hosokawa Y, Hosokawa I, Shindo S, Ozaki K, Nakae H, Matsuo T (2012) Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis increases CC chemokine ligand 20 production in interleukin 1beta-stimulated human gingival fibroblasts. Hum Immunol 73(5):470–473. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2012.02.021
Echeverry R, Wu F, Haile WB, Wu J, Yepes M (2012) The cytokine tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis and its receptor fibroblast growth factor-inducible 14 have a neuroprotective effect in the central nervous system. J Neuroinflammation 9:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-45
Bao Q, Li C, Xu C, Zhang R, Zhao K, Duan Z (2018) Porcine enterocyte protein Btnl5 negatively regulates NF-kappa B pathway by interfering p65 nuclear translocation. Gene 646:47–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.11.070
Zhang YC, Huo FC, Wei LL, Gong CC, Pan YJ, Mou J, Pei DS (2017) PAK5-mediated phosphorylation and nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB-p65 promotes breast cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Clin Cancer Res : CR 36(1):146. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0610-5
Tomita H, Tabata K, Takahashi M, Nishiyama F, Sugano E (2016) Light induces translocation of NF-kappaB p65 to the mitochondria and suppresses expression of cytochrome c oxidase subunit III (COX III) in the rat retina. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 473(4):1013–1018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.04.008
Chen Y, Chen X, Yu J, Xu X, Wei X, Gu X, Liu C, Zhang D et al (2016) JAB1 is involved in neuropathic pain by regulating JNK and NF-kappaB activation after chronic constriction injury. Neurochem Res 41(5):1119–1129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-015-1802-z
Xu T, Li D, Zhou X, Ouyang HD, Zhou LJ, Zhou H, Zhang HM, Wei XH et al (2017) Oral application of magnesium-L-Threonate attenuates vincristine-induced allodynia and hyperalgesia by normalization of tumor necrosis factor-alpha/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling. Anesthesiology 126(6):1151–1168. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0000000000001601
Yu HM, Wang Q, Sun WB (2017) Silencing of FKBP51 alleviates the mechanical pain threshold, inhibits DRG inflammatory factors and pain mediators through the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Gene 627:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2017.06.029
Zhang HH, Hu J, Zhou YL, Hu S, Wang YM, Chen W, Xiao Y, Huang LY et al (2013) Promoted interaction of nuclear factor-kappaB with demethylated cystathionine-beta-synthetase gene contributes to gastric hypersensitivity in diabetic rats. J Neurosci 33(21):9028–9038. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1068-13.2013
Zhang HH, Hu J, Zhou YL, Qin X, Song ZY, Yang PP, Hu S, Jiang X et al (2015) Promoted interaction of nuclear factor-kappaB with demethylated purinergic P2X3 receptor gene contributes to neuropathic pain in rats with diabetes. Diabetes 64(12):4272–4284. https://doi.org/10.2337/db15-0138
Funding
This work was supported by the grants (NS094664, NS094224, and DA033390) from the National Institutes of Health (Bethesda, Maryland, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at New Jersey Medical School, Rutgers approved all experimental procedures (IACUC approved number 13035A2E0716).
Conflict of Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, LN., Zou, Y., Wu, SG. et al. Fn14 Participates in Neuropathic Pain Through NF-κB Pathway in Primary Sensory Neurons. Mol Neurobiol 56, 7085–7096 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1545-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1545-y