Abstract
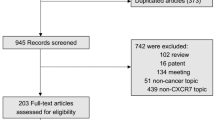
Chemokine receptor CXCR4 has been identified to affect glioma progression by dominating cancer cell survival, proliferation, and migration in vitro recently. However, the implications and utilities of CXCR4 in clinical grade and prognosis were rarely reported. Thus, it is essential to carry out a meta-analysis to draw a convincing conclusion. The relevant articles were included through careful assessment, and then, odds ratios (ORs), standard mean differences (SMDs), and hazard ratios (HRs) with 95 % confidence intervals (95 % CIs) were estimated. Heterogeneity and funnel plots evaluation were conducted. In this meta-analysis, all 13 eligible studies involving 785 patients were included and conducted in China. Ten studies revealed altered CXCR4 expression in glioma tissues was closely associated with high WHO grade (III + IV) (n = 10, OR 5.46, 95 % CI 3.81–7.84; p = 0.000); besides, six studies also demonstrated CXCR4 expression intensity extremely correlated to high grade (n = 6, SMD −2.45, 95 % CI −2.78, −2.12; p = 0.000). Most importantly, three articles identified that CXCR4 expression significantly correlated to 3-year overall survival (OS) (HR 7.32, 95 % CI 4.16–12.90; p = 0.000) in glioma patients. No heterogeneity and publication bias were observed across all studies. Taken together, this meta-analysis suggests CXCR4 expression in gliomas can be recommended as evidence of WHO grade and indeed predict 3-year overall survival. We also provided a scientific rationale for clinically pathological detection of CXCR4 that is required for treatment of glioma patients.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woolf EC, Scheck AC (2012) Metabolism and glioma therapy. CNS Oncol 1(1):7–10
Mack F, Schäfer N, Kebir S, Stuplich M, Schaub C, Niessen M, Scheffler B, Herrlinger U, Glas M (2014) Carmustine (BCNU) plus teniposide (VM26) in recurrent malignant glioma. Oncology 86(5–6):369–372
Kleihues P, Louis DN, Scheithauer BW, Rorke LB, Reifenberger G, Burger PC, Cavenee WK (2002) The WHO classification of tumors of the nervous system. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61(3):215–225
Collins VP, Ichimura K, Di Y, Pearson D, Chan R, Thompson LC, Gabe R, Brada M, Stenning SP, BR12 Collaborators (2014) Prognostic and predictive markers in recurrent high grade glioma; results from the BR12 randomised trial. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:68
Teicher BA, Fricker SP (2010) CXCL12 (SDF-1)/CXCR4 pathway in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 16(11):2927–2931
Folkins C, Shaked Y, Man S, Tang T, Lee CR, Zhu Z, Hoffman RM, Kerbel RS (2009) Glioma tumor stem-like cells promote tumor angiogenesis and vasculogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor and stromal-derived factor 1. Cancer Res 69(18):7243–7251
Jahnke K, Coupland SE, Na IK, Loddenkemper C, Keilholz U, Korfel A, Stein H, Thiel E, Scheibenbogen C (2005) Expression of the chemokine receptors CXCR4, CXCR5, and CCR7 in primary central nervous system lymphoma. Blood 106(1):384–385
Rubin JB, Kung AL, Klein RS, Chan JA, Sun Y, Schmidt K, Kieran MW, Luster AD, Segal RA (2003) A small-molecule antagonist of CXCR4 inhibits intracranial growth of primary brain tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(23):13513–13518
Yang L, Jackson E, Woerner BM, Perry A, Piwnica-Worms D, Rubin JB (2007) Blocking CXCR4-mediated cyclic AMP suppression inhibits brain tumor growth in vivo. Cancer Res 67(2):651–658
Steels E, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, Branle F, Lemaitre F, Mascaux C, Meert AP, Vallot F, Lafitte JJ, Sculier JP (2001) Role of p53 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: a systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis. Eur Respir J 18(4):705–719
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR (2007) Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 8(1):16
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17(24):2815–2834
Yang S, Bian X, Jiang X (2005) Clinical significance of chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in human gliomas. Chin Minim Invasive Neurosurg 10(8):360–362
Bian XW, Yang SX, Chen JH, Ping YF, Zhou XD, Wang QL, Jiang XF, Gong W, Xiao HL, Du LL, Chen ZQ, Zhao W, Shi JQ, Wang JM (2007) Preferential expression of chemokine receptor CXCR4 by highly malignant human gliomas and its association with poor patient survival. Neurosurgery 61(3):570–578, discussion 578–9
Wu N, Zeng F, Ping Y, Xin R, Jiang T, Bian X (2007) Expression of SDF-l and CXCR4 in astrocytoma and its relationship with angiogenesis. Chongqing Med 36(11):1053–1054
Liu Y, Wang L, Fu X, Wang D (2008) Expression and significance of CXCR4 and hTEFIT in gliomas. Shandong Med 48(12):15–16
Wang D, Liu Y, Gao B (2008) Expressions and significance of CXCR4 and EGFR in gliomas. J Shanxi Med 37(9):1226–1228
Li G (2010) Expression and correlation of CXCR4 and VEGF with microvascular dense in human gliomas. Zhengzhou Univ 1(1):15–20
Lin Y, Zhang N, Lai T (2010) Expression and significance of SDF-1 and CXCR4 in gliomas. Natl Med Front Chin 5(13):1–2
Lu W, Fu L, Yang J, Qian T (2010) Expression of chemokine CXCL12 and its receptor CXCR4 in human astrocytomas and its clinical significance. J Brain Nerv Dis 18(3):205–208
Cong L, Hu H, Jiao B (2011) Expression and significance of chemokine receptor CXCR4 in gliomas. J Hebei Med Univ 32(7):770–773
Liu H (2012) Expression and significance of CXCLl2 and CXCR4 in human gliomas. Zhengzhou Univ 1(1):21–23
Xu Y, Wang J, Xu Y, Huan F, Xiao H (2012) A pilot study on the expression of CXCR4 in glioma and its effect on glioma angiogenesis. Acta Univ Med Nanjing 32(5):598–603
Zhang J, Li Y, Zhou W (2012) Role of CXCR4 in human glioma angiogenesis. Chin J Neuromed 11(7):681–683
Tian YD, Zhang J, Tian W, E Q, Wang D (2013) Expression and correlation of CXCR4 and hTERT with microvascular dense and prognosis in glioma. Acta Univ Med Nanjing 33(8):1110–5.
Bajetto A, Barbieri F, Dorcaratto A, Barbero S, Daga A, Porcile C, Ravetti JL, Zona G, Spaziante R, Corte G, Schettini G, Florio T (2006) Expression of CXC chemokine receptors 1-5 and their ligands in human glioma tissues: role of CXCR4 and SDF1 in glioma cell proliferation and migration. Neurochem Int 49(5):423–432
Munson JM, Bellamkonda RV, Swartz MA (2013) Interstitial flow in a 3D microenvironment increases glioma invasion by a CXCR4-dependent mechanism. Cancer Res 73(5):1536–1546
Redjal N, Chan JA, Segal RA, Kung AL (2006) CXCR4 inhibition synergizes with cytotoxic chemotherapy in gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 12(22):6765–6771
Song F, Khan KS, Dinnes J, Sutton AJ (2002) Asymmetric funnel plots and publication bias in meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy. Int J Epidemiol 31(1):88–95
Deeks JJ, Macaskill P, Irwig L (2005) The performance of tests of publication bias and other sample size effects in systematic reviews of diagnostic test accuracy was assessed. J Clin Epidemiol 58(9):882–893
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Shandong University Science Technology Innovation Foundation (201410422123). We greatly thank Sera Kwon in Sandy lab for the valuable suggestions and writing.
Conflict of Interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shunzeng Lv and Bowen Sun contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, S., Sun, B., Zhong, X. et al. The Clinical Implications of Chemokine Receptor CXCR4 in Grade and Prognosis of Glioma Patients: A Meta-Analysis. Mol Neurobiol 52, 555–561 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8894-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8894-3