Abstract
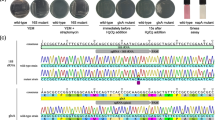
Enhanced tolerance to wilt disease (Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense) was achieved in banana variety Rasthali (AAB) by the transformation of embryogenic cells with two antimicrobial genes viz., Ace-AMP1 and pflp using Agrobacterium mediated transformation. The transgene copy numbers in stable transformants were confirmed by Southern analysis. The expression of stacked genes in the transgenic lines was validated by RT-PCR as well as Northern analysis. Bioassay using Foc race 1 in pot culture experiments demonstrated enhanced tolerance after 180 days of planting. Two independent transformants showed 10–20% Vascular Discoloration Index compared to untransformed banana cv. Rasthali (96%). The stacked lines revealed higher activity of Super Oxide Dismutase and Peroxidase compared to untransformed control which depicted higher tolerance to oxidative stress caused by Foc infection.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ploetz, R. C. (1993). Fusarium wilt (Panama disease). In: Ganry J (ed) Breeding banana and plantain for resistance to disease and pests. CIRAD: In collaboration with INIBAP, Montpellier, p 149–158
Ploetz, R. C. (2006). Panama disease, an old nemesis rears its ugly head: parts 2, the beginnings of the banana export trades. Plant Health Progress,6(1), 18. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHP-2005-1221-01-RV.
Li, C., Chen, S., Zuo, C., Sun, Q., Ye, Q., Yi, G., et al. (2011). The use of GFP-transformed isolates to study infection of banana with Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 4. European Journal of Plant Pathology,131, 327–340.
Ploetz, R. C. (2000). Panama disease: A classic and destructive disease of banana. Plant Health Progress,10, 1–7.
Chakrabarti, A., Ganapathi, T. R., Mukherjee, P. K., & Bapat, V. A. (2003). MSI-99, a magainin analogue, imparts enhanced disease resistance in transgenic tobacco and banana. Planta,216, 587–596.
Pei, X. W., Chen, S. K., Wen, R. M., Ye, S., Huang, J. Q., Zhang, Y. Q., et al. (2005). Creation of transgenic banana expressing human lysozyme gene for Panama wilt resistance. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology,47, 971–977.
Maziah, M., Sreeramanan, S., Puad, A., & Sariah, M. (2007). Production of transgenic banana Rasthali (AAB) via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation with a rice chitinase gene. J Plant Sci,2, 504–517.
Maziah, M., Sariah, M., & Sreeramanan, S. (2007). Transgenic banana Rasthali (AAB) with β-1,3-glucanase gene for tolerance to Fusarium wilt race1 disease via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation system. Plant Pathol J,6, 271–282.
Paul, J. Y., Becker, D. K., Dickman, M. B., Harding, R. M., Khanna, H. K., & Dale, J. L. (2011). Apoptosis-related genes confer resistance to Fusarium wilt in transgenic ‘Lady Finger’ bananas. Plant Biotechnology Journal,9, 1141–1149.
Yip, M. K., Lee, S. W., Su, K. C., Lin, Y. H., Chen, T. Y., & Feng, T. Y. (2011). An easy and efficient protocol in the production of pflp transgenic banana against Fusarium wilt. Plant Biotechnology Reports,5, 245–254.
Mahdavi, F., Sariah, M., & Maziah, M. (2012). Expression of rice thaumatin like proteingene in transgenic banana plants enhances resistance to Fusarium wilt. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology,166, 1008–1019.
Ghag, S. B., Shekhawat, U. K. S., & Ganapathi, T. R. (2012). Petunia floral defensins with unique prodomains as novel candidates for development of Fusarium wilt resistance in transgenic banana plants. PLoS ONE,7, e39557.
Hu, C. H., Wei, Y. R., Huang, Y. H., & Yi, G. J. (2013). An efficient protocol for the production of chit42 transgenic Furenzhi banana (Musa spp. AA group) resistant to Fusarium oxysporum. In Vitro Cellular & Developmental Biology,49, 584–592.
Mohandas, S., Sowmya, H. D., Saxena, A. K., Meenakshi, S., Rania, R. T., & Mahmood, R. (2013). Transgenic banana cv. Rasthali (AAB, Silk gp) harboring Ace-AMP1 gene imparts enhanced resistance to Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense race 1. Scientia Horticulturae,164, 392–399.
Ghag, S. B., Shekhawat, U. K., & Ganapathi, T. R. (2014). Transgenic banana plants expressing a Stellaria media defensin gene (Sm-AMP-D1) demonstrate improved resistance to Fusarium oxysporum. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture (PCTOC),119, 247–255.
Ghag, S. B., Shekhawat, U. K., & Ganapathi, T. R. (2014). Native cell-death genes as candidates for developing wilt resistance in transgenic banana plants. AoB Plants. https://doi.org/10.1093/aobpla/plu037.
Ghag, S. B., Shekhawat, U. K., & Ganapathi, T. R. (2014). Host-induced post-transcriptional hairpin RNA-mediated gene silencing of vital fungal genes confers efficient resistance against Fusarium wilt in banana. Plant Biotechnology Journal,12, 541–553.
Magambo, B., Khanna, H., Arinaitwe, G., Tendo, S., Arinaitwe, I. K., Kubiriba, J., et al. (2016). Inhibition of cell death as an approach for development of transgenic resistance against Fusarium wilt disease. African Journal of Biotechnology,15, 786–797.
Cammue, B. P. A., Thevissen, K., Hendriks, M., Eggermont, K., Goderis, I. J., Proost, P., et al. (1995). Apotent antimicrobial protein from onion seeds showing sequence homology to plant lipid transfer proteins. Plant Physiology,109, 445–455.
Wu, Y., He, Y., & Ge, X. (2011). Functional characterization of the recombinant antimicrobial peptide Trx-Ace-AMP1 and its application on the control of tomato early blight disease. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,90, 1303–1310.
Arondel, V., & Kader, J. C. (1990). Lipid transfer in plants. Experientia,46, 579–585.
Kader, J. C. (1993). Lipid transport in plants. In T. S. Moore (Ed.), Lipid Metabolism in Plants (pp. 309–336). Boca Raton: CRC Press.
Molina, A., & Garcia-Olmedo, F. (1993). Developmental and pathogen induced expression of three barley genes encoding lipid transfer proteins. The Plant Journal,4, 983–991.
Bi, Y. M., Cammue, B. P. A., Goodwin, P. H., Krishnaraj, S., & Saxena, P. K. (1999). Resistance to Botrytis cinerea in scented geranium transformed with a gene encoding the antimicrobial protein Ace-AMP1. Plant Cell Reports,18, 835–840.
Li, X., Gasic, K., Cammue, B., Broekaert, W., & Korban, S. S. (2003). Transgenic rose lines harboring an antimicrobial protein gene, Ace-Amp 1, demonstrate enhanced resistance to powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca pannosa). Planta,218, 226–232.
Patkar, R. N., & Chattoo, B. B. (2006). Transgenic indica rice expressing ns-LTP-like protein shows enhanced resistance to both fungal and bacterial pathogens. Molecular Breeding,17, 159–171.
Roy-Barman, S., Sautter, C., & Chattoo, B. B. (2006). Expression of the lipid transfer protein Ace-AMP1 in transgenic wheat enhances antifungal activity and defense responses. Transgenic Research,15, 435–446.
Biehler, K., & Fock, H. (1996). Evidence for the contribution of the Mehlerperoxidase reaction in dissipating excess electrons in drought-stressed wheat. Plant Physiology,112, 265–272.
Desikan, R., Hancock, J. T., Coffey, M. J., & Neill, S. J. (1996). Generation of active oxygen in elicited cells of Arabidopsis thaliana is mediated by a NADPH oxidase like enzyme. FEBS Letters,382, 213–217.
Lamb, C. J., & Dixon, R. A. (1997). The oxidative burst in plant disease resistance. Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology,48, 251–275.
Khanna, H., Becker, D., Kleidon, J., & Dale, J. L. (2004). Centrifugation assisted Agrobacterium-tumefaciens mediated transformation (CAAT) of embryogenic cell suspensions of banana (Musa spp. Cavendish AAA and Lady finger AAB). Molecular Breeding,14, 239–252.
Dellaporta, S. L., Wood, J., & Hicks, J. B. (1983). A plant DNA mini preparation: version II. Plant Molecular Biology Reporter,1, 19–21.
Smith, L. J., Smith, M. K., Tree, D., O‘Keefe, D., & Galea, V. J. (2008). Development of a small-plant bioassay to assess banana grown from tissue culture for consistent infection by Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. cubense. Australasian Plant Pathology,2, 171–179.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F., & Maniatis, S. (1989). Molecular sloning: A laboratory manual (2nd ed.). New York: Cold spring Harbor CSHL Press, Cold Spring Harbor.
Du, Z., & Bramlage, W. J. (1994). Superoxide dismutase activities in senescing apple fruit (Malus domestica Borkh.). Journal of Food Science,59(3), 581–584.
Chander, S. M. (1990). Enzymatic properties association with resistance to rust and powdery mildew in peas. Indian Journal of Horticulture,47, 341–345.
Vishnevetsky, J., White, T. L., Jr., Palmateer, A. J., Flaishman, M., Cohen, Y., Elad, Y., et al. (2011). Improved tolerance toward fungal diseases in transgenic Cavendish banana (Musa spp. AAA group) cv. Grand Nain. Transgenic Research,20(1), 61–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11248-010-9392-7.
Muwonge, A., Tripathi, J., Kunert, K., & Tripathi, L. (2016). Expressing stacked HRAP and PFLP genes in transgenic banana has no synergistic effect on resistance to Xanthomonas wilt disease. South + A1443 African Journal of Botany,104, 125–133.
Van Loon, L. C., & Van Strien, E. A. (1999). The families of pathogenesis related proteins, their activities, and comparative analysis of PR-1 type proteins. Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology,55, 85–97.
Dayakar, B. V., Lin, H. J., Chen, C. H., Ger, M. J., Lee, B. H., Pai, C. H., et al. (2003). Ferredoxin from sweet pepper(Capsicum annuum L.) intensifying harpinpss mediated hypersensitive response shows an enhanced production of active oxygen species (AOS). Plant Molecular Biology,51, 913–924.
Huang, H. E., Ger, M. J., Yip, M. K., Chen, C. Y., Pandeya, A. K., & Feng, T. Y. (2004). A hypersensitive response was induced by virulent bacteria in transgenic tobacco plants overexpressing a plant ferredoxin-like protein (pflp). Physiological and Molecular Plant Pathology,64, 103–110.
Ganapathi, T. R., Higgs, N. S., Balint-Kurti, P. J., Arntzen, C. J., May, G. D., & Van Eck, J. M. (2001). Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of the embryogenic cell suspen-sion of the banana cultivar Rasthali (AAB). Plant Cell Reports,20, 157–162.
Donnarumma, F., Paffetti, D., Fladung, M., Biricolti, S., Dieter, E., Altosaar, I., et al. (2011). Transgene copy number estimation and analysis of gene expression levels in Populus spp. transgenic lines. BMC Proceedings,5(7), P152.
Karmakar, S., Molla, K. A., Das, K., Sarkar, S. N., Swapan, K., & Datta, K. (2017). Dual gene expression cassette is superior than single gene cassette for enhancing sheath blight tolerance in transgenic rice. Scientific Reports,7, 7900.
Passardi, F., Penel, C., & Dunand, C. (2004). Performing the paradoxical: how plant peroxidases modify the cell wall. Trends in Plant Science,9, 534–540.
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to ICAR-NPTC for funding and constant support to carry out research work and thankful to the Division of Plant Pathology, ICAR-IIHR for screening the transgenic plants. This is a part of Ph.D. dissertation work of first author.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Coordinator of Network Project on Transgenic Crops—Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceived and designed the experiments: Dr. UTR, Dr. SHD and CS. Performed the experiments: CS and Dr. SHD. Analyzed the data: CS, Dr. UTR, Dr. SHD, UM. Paper: CS, Dr. UTR, Dr. SHD. Field evaluation: Dr.AKS and GHR
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors Mrs. Sunisha. C, Dr. Sowmya H.D, Dr. Usharani T.R, Mr. Umesha M, Dr.Arvindkumar Saxena, and Gopalkrishna H.R have received research grants from the National Coordinator of Network Project on Transgenic Crops—Indian Council of Agricultural Research.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sunisha, C., Sowmya, H.D., Usharani, T.R. et al. Deployment of Stacked Antimicrobial Genes in Banana for Stable Tolerance Against Fusarium oxysporum f.sp. cubense Through Genetic Transformation. Mol Biotechnol 62, 8–17 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-019-00219-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-019-00219-w