Abstract
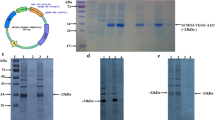
Hirudin is the most potent non-covalent inhibitor of thrombin. Several expression systems have been used to produce recombinant hirudin for pharmaceutical purposes. However, high expression of active hirudin in Escherichia coli cytoplasm has not been successful owing to the fact that heterogenetic small peptide is easily degraded in the cell. To solve this problem, we constructed a recombinant form of the hirudin variant-1 (HV1) as a fusion protein with the small ubiquitin-related modifier gene (SUMO) by use of over-lap PCR. The fusion gene His6-SUMO-HV1 was highly expressed in E. coli BL21 (DE3) in which the SUMO-HV1 accounts for over 30% of the soluble fraction. The fusion protein was purified by Ni–NTA affinity chromatography and cleaved by a SUMO-specific protease Ulp1 to release the HV1 with natural N-terminal. The recombinant HV1 (rHV1) was further purified by Ni–NTA affinity chromatography and then by Q anion-exchange chromatography. N-terminal sequencing result demonstrated the purified rHV1 had the same N-terminal sequence as the native hirudin. MALDI-TOF/MS analysis indicated that the molecular weight of the purified rHV1 protein was 6939.161 Da, which was similar to the theoretical molecular weight of rHV1 6,944 Da. The Chromozym TH assay result showed that the anti-thrombin activity of purified rHV1 was 8,800 ATU/mg and comparable to the specific activity of native hirudin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Markwardt, F. (1970). Hirudin as an inhibitor of thrombin. Methods in Enzymology, 19, 924–931.
Kim, M. D., Rhee, S. K., & Seo, J. H. (2001). Enhanced production of anticoagulant hirudin in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae by chromosomal d-integration. Journal of Biotechnology, 85, 41–48.
Harvey, R. P., Degryse, E., Stefani, L., Schamber, F., Cazenave, J. P., Courtney, M., et al. (1986). Cloning and expression of a cDNA coding for the anticoagulant hirudin from the bloodsucking leech, Hirudo medicinalis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of USA, 83, 1084–1088.
Walker, C. M. (2010). Commentary: Bivalirudin is a safe and effective anticoagulant in the percutaneous treatment of complex infrainguinal disease. Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 17, 37–38.
McClure, R. S., Higgins, J., Swinamer, S. A., Rayman, R., Dobkowski, W. B., et al. (2009). Bivalirudin as an anticoagulant for simultaneous integrated coronary artery revascularization—a novel approach to an inherent concern. Canadian Journal of Cardiology, 25, 425–427.
Palmer, G. J., Sankaran, I. S., Sparkman, G. M., Koster, A., Dyke, C. M., & Ebra, G. (2008). Routine use of the direct thrombin inhibitor bivalirudin for off-pump coronary artery bypass grafting is safe and effective. Heart Surgery Forum, 11, 24–29.
Hu, Z. L., Zhang, N., Gu, F., Li, Y., Deng, X. J., et al. (2009). Expression, purification and characterization of recombinant targeting bifunctional hirudin in Pichia pastoris. African Journal of Biotechnology, 8, 5582–5588.
Sohn, J. H., Kang, H. A., Rao, K. J., Kim, C. H., Choi, E. S., Chung, B. H., et al. (2001). Current status of the anticoagulant hirudin: Its biotechnological production and clinical practice. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 57, 606–613.
Zhou, W. B., & Zhang, Y. X. (2004). Purification and identification of recombinant hirudin and its degradation products expressed in Pichia pastoris. Preparative Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 34, 239–252.
Bi, Q., Zhang, J., Huang, Y., Su, H., Zhou, X., & Zhu, S. (2001). Construction, expression, and characterization of recombinant hirudin in Escherichia coli. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 95, 23–30.
Baneyx, F. (1999). Recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 10, 411–421.
Prinz, W. A., Aslund, F., Holmgren, A., & Beckwith, J. (1997). The role of the thioredoxin and glutaredoxin pathways in reducing protein disulfide bonds in the Escherichia coli cytoplasm. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 272, 15661–15667.
Ahn, J. W., Lee, Y. A., Ahn, J. H., & Cho, C. Y. (2009). Covalent conjugation of Groucho with SUMO-1 modulates its corepressor activity. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 379, 160–165.
Johnson, E. S. (2004). Protein modification by SUMO. Annual Review of Biochemistry, 73, 355–382.
Panavas, T., Sanders, C., & Butt, T. R. (2009). SUMO fusion technology for enhanced protein production in prokaryotic and eukaryotic expression systems. Methods in Molecular Biology, 497, 303–317.
Marblestone, J. G., Edavett, S. C., Lim, Y., Lim, P., Zuo, X., & Butt, T. R. (2006). Comparison of SUMO fusion technology with traditional gene fusion systems: Enhanced expression and solubility with SUMO. Protein Science, 15, 1182–1189.
Malakhov, M. P., Mattern, M. R., Malakhova, O. A., Drinker, M., Weeks, S. D., et al. (2004). SUMO fusions and SUMO-specific protease for efficient expression and purification of proteins. Journal of Structural and Functional Genomics, 5, 75–86.
Lu, W. G., Cao, P., Cai, X. T., Yu, J. M., Hu, C. P., Cao, M., et al. (2009). Molecular cloning, expression, and bioactivity of dove B lymphocyte stimulator (doBAFF). Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology, 128, 5374–5380.
Li, J. F., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Kang, C. T., & Zhang, S. Q. (2011). SUMO mediating fusion expression of antimicrobial peptide CM4 from two joined genes in Escherichia coli. Current Microbiology, 62, 296–300.
Lu, W. G., Cao, P., Lei, H., & Zhang, S. Q. (2010). High-level expression and purification of heparin-binding epidermal growth factor (HB-EGF) with SUMO fusion. Molecular Biotechnology, 44, 198–203.
Griessbach, U., Stürzebecher, J., & Markwardt, F. (1985). Assay of hirudin in plasma using a chromogenic thrombin substrate. Thrombosis Research, 37, 347–350.
Iyer, L., & Fareed, J. (1995). Determination of specific activity of recombinant hirudin using a thrombin titration method. Thrombosis Research, 78, 259–263.
Bergmann, C., Dodt, J., Kohler, S., Fink, E., & Gassen, H. G. (1986). Chemical synthesis and expression of a gene coding for hirudin, the thrombin-specific inhibitor from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 367, 731–740.
Dodt, J., Schmitz, T., Schäfer, T., & Bergmann, C. (1986). Expression, secretion and processing of hirudin in E. coli using the alkaline phosphatase signal sequence. FEBS Letters, 202, 373–377.
Yuan, H., Yang, X., & Hua, Z. C. (2004). Optimization of expression of an annexin V-hirudin chimeric protein in Escherichia coli. Research in Microbiology, 159, 147–156.
Butt, T. R., Edavettal, S. C., Hall, J. P., & Mattern, M. R. (2005). SUMO fusion technology for difficult-to-express proteins. Protein Expression Purification, 43, 1–9.
Tauseef, R., Steven, D., et al. (2007). Methods and compositions for protein expression and purification. United States Patent 7820384.
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by Jiangsu Province’s Outstanding Leader Program of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Jiangsu Province’s Nature Science Foundation (No. SBK20082754, No. SBK2009456).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, W., Cai, X., Gu, Z. et al. Production and Characterization of Hirudin Variant-1 by SUMO Fusion Technology in E. coli . Mol Biotechnol 53, 41–48 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9511-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-012-9511-1