Abstract
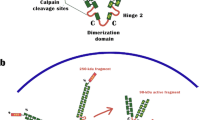
Plectin, as the cytolinker and scaffolding protein, are widely expressed and abundant in many tissues, and has involved in various cellular activities contributing to tumorigenesis, such as cell adhesion, migration, and signal transduction. Due to the specific expression and differential localization of plectin in cancer, most researchers focus on the role of plectin in cancer, and it has emerged as a potent driver of malignant hallmarks in many human cancers, which provides the possibility for plectin to be widely used as a biomarker and therapeutic target in the early diagnosis and targeted drug delivery of the disease. However, there is still a lack of systematic review on the interaction molecules and mechanism of plectin. Herein, we summarized the structure, expression and function of plectin, and mainly focused on recent studies on the functional and physical interactions between plectin and its interacting molecules, shedding light on the potential of targeting plectin for cancer therapy.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author.
References
Wiche G. Role of plectin in cytoskeleton organization and dynamics. J Cell Sci. 1998;11:2477–86.
Wiche G, Winter L. Plectin isoforms as organizers of intermediate filament cytoarchitecture. BioArchitecture. 2011;1:14–20.
Svitkina T, Verkhovsky A, Borisy G. Plectin sidearms mediate interaction of intermediate filaments with microtubules and other components of the cytoskeleton. J Cell Biol. 1996;135:991–1007.
Foisner R, Bohn W, Mannweiler K, Wiche G. Distribution and ultrastructure of plectin arrays in subclones of rat glioma C6 cells differing in intermediate filament protein (vimentin) expression. J Struct Biol. 1995;115:304–17.
Jeon J, Suh H, Kim M, Han H. Glucosamine-induced reduction of integrin β4 and plectin complex stimulates migration and proliferation in mouse embryonic stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2013;22:2975–89.
Osmanagic-Myers S, Gregor M, Walko G, Burgstaller G, Reipert S, Wiche G. Plectin-controlled keratin cytoarchitecture affects MAP kinases involved in cellular stress response and migration. J Cell Biol. 2006;174:557–68.
Takawira D, Budinger G, Hopkinson S, Jones J. A dystroglycan/plectin scaffold mediates mechanical pathway bifurcation in lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:6301–10.
Osmanagic-Myers S, Wiche G. Plectin-RACK1 (receptor for activated C kinase 1) scaffolding: a novel mechanism to regulate protein kinase C activity. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:18701–10.
Andrä K, Nikolic B, Stöcher M, Drenckhahn D, Wiche G. Not just scaffolding: plectin regulates actin dynamics in cultured cells. Gene Dev. 1998;12:3442–51.
Rezniczek G, de Pereda J, Reipert S, Wiche G. Linking integrin alpha6beta4-based cell adhesion to the intermediate filament cytoskeleton: direct interaction between the beta4 subunit and plectin at multiple molecular sites. J Cell Biol. 1998;141:209–25.
Kostan J, Gregor M, Walko G, Wiche G. Plectin isoform-dependent regulation of keratin-integrin alpha6beta4 anchorage via Ca2+/calmodulin. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:18525–36.
Niwa T, Saito H, Imajoh-ohmi S, Kaminishi M, Seto Y, Miki Y, et al. BRCA2 interacts with the cytoskeletal linker protein plectin to form a complex controlling centrosome localization. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:2115–25.
Fish L, Khoroshkin M, Navickas A, Garcia K, Culbertson B, Hänisch B, et al. A prometastatic splicing program regulated by SNRPA1 interactions with structured RNA elements. Science. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc7531.
Yu P, Babicky M, Jaquish D, French R, Marayuma K, Mose E, et al. The RON-receptor regulates pancreatic cancer cell migration through phosphorylation-dependent breakdown of the hemidesmosome. Int J Cancer. 2012;131:1744–54.
Sabbir M, Dillon R, Mowat M. Dlc1 interaction with non-muscle myosin heavy chain II-A (Myh9) and Rac1 activation. Biol Open. 2016;5:452–60.
Katada K, Tomonaga T, Satoh M, Matsushita K, Tonoike Y, Kodera Y, et al. Plectin promotes migration and invasion of cancer cells and is a novel prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J Proteomics. 2012;75:1803–15.
Buckup M, Rice M, Hsu E, Garcia-Marques F, Liu S, Aslan M, et al. Plectin is a regulator of prostate cancer growth and metastasis. Oncogene. 2021;40:663–76.
Shin S, Smith J, Rezniczek G, Pan S, Chen R, Brentnall T, et al. Unexpected gain of function for the scaffolding protein plectin due to mislocalization in pancreatic cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2013;110:19414–9.
Raymond A, Gao B, Girard L, Minna J, Gomika UD. Unbiased peptoid combinatorial cell screen identifies plectin protein as a potential biomarker for lung cancer stem cells. Sci Rep. 2019;9:14954.
Li Y, Zhao Z, Liu H, Fetse J, Jain A, Lin C, et al. Development of a tumor-responsive nanopolyplex targeting pancreatic cancer cells and stroma. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2019;11:45390–403.
Dasa S, Diakova G, Suzuki R, Mills A, Gutknecht M, Klibanov A, et al. Plectin-targeted liposomes enhance the therapeutic efficacy of a PARP inhibitor in the treatment of ovarian cancer. Theranostics. 2018;8:2782–98.
Bausch D, Mino-Kenudson M, Fernández-Del Castillo C, Warshaw A, Kelly K, Thayer S. Plectin-1 is a biomarker of malignant pancreatic intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:1948–54 (discussion 54).
Pytela R, Wiche G. High molecular weight polypeptides (270,000–340,000) from cultured cells are related to hog brain microtubule-associated proteins but copurify with intermediate filaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1980;77:4808–12.
Castañón M, Walko G, Winter L, Wiche G. Plectin-intermediate filament partnership in skin, skeletal muscle, and peripheral nerve. Histochem Cell Biol. 2013;140:33–53.
Foisner R, Wiche G. Structure and hydrodynamic properties of plectin molecules. J Mol Biol. 1987;198:515–31.
Wiche G, Becker B, Luber K, Weitzer G, Castañon M, Hauptmann R, et al. Cloning and sequencing of rat plectin indicates a 466-kD polypeptide chain with a three-domain structure based on a central alpha-helical coiled coil. J Cell Biol. 1991;114:83–99.
Ortega E, Buey R, Sonnenberg A, de Pereda J. The structure of the plakin domain of plectin reveals a non-canonical SH3 domain interacting with its fourth spectrin repeat. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:12429–38.
Fuchs P, Zörer M, Rezniczek G, Spazierer D, Oehler S, Castañón M, et al. Unusual 5’ transcript complexity of plectin isoforms: novel tissue-specific exons modulate actin binding activity. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:2461–72.
Walko G, Vukasinovic N, Gross K, Fischer I, Sibitz S, Fuchs P, et al. Targeted proteolysis of plectin isoform 1a accounts for hemidesmosome dysfunction in mice mimicking the dominant skin blistering disease EBS-Ogna. Plos Genet. 2011;7:e1002396.
Janda L, Damborský J, Rezniczek G, Wiche G. Plectin repeats and modules: strategic cysteines and their presumed impact on cytolinker functions. BioEssays. 2001;23:1064–9.
Nikolic B, Mac Nulty E, Mir B, Wiche G. Basic amino acid residue cluster within nuclear targeting sequence motif is essential for cytoplasmic plectin-vimentin network junctions. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:1455–67.
Kelly K, Bardeesy N, Anbazhagan R, Gurumurthy S, Berger J, Alencar H, et al. Targeted nanoparticles for imaging incipient pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med. 2008;5:e85.
Wu Y, Tang Y, Xie S, Zheng X, Zhang S, Mao J, et al. Chimeric peptide supramolecular nanoparticles for plectin-1 targeted miRNA-9 delivery in pancreatic cancer. Theranostics. 2020;10:1151–65.
Chen X, Zhou H, Li X, Duan N, Hu S, Liu Y, et al. Plectin-1 targeted Dual-modality nanoparticles for pancreatic cancer imaging. EBioMedicine. 2018;30:129–37.
Konkalmatt P, Deng D, Thomas S, Wu M, Logsdon C, French B, et al. Plectin-1 targeted AAV vector for the molecular imaging of pancreatic cancer. Front Oncol. 2013;3:84.
Bausch D, Thomas S, Mino-Kenudson M, Fernández-del C, Bauer T, Williams M, et al. Plectin-1 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Clinical Cancer Res. 2011;17:302–9.
Oto A, Eltorky M, Dave A, Ernst R, Chen K, Rampy B, et al. Mimicks of pancreatic malignancy in patients with chronic pancreatitis: correlation of computed tomography imaging features with histopathologic findings. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 2006;35:199–205.
Liu Y, Ho C, Cheng C, Pei R, Hsu Y, Yeh K, et al. Pleomorphism of cancer cells with the expression of plectin and concept of filament bundles in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 2007;120:43–54.
Cheng C, Lai Y, Lai Y, Hsu Y, Chao W, Sia K, et al. Transient knockdown-mediated deficiency in plectin alters hepatocellular motility in association with activated FAK and Rac1-GTPase. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:29.
Dumas V, Kanitakis J, Charvat S, Euvrard S, Faure M, Claudy A. Expression of basement membrane antigens and matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 in cutaneous basal and squamous cell carcinomas. Anticancer Res. 1999;19:2929–38.
Kadeer A, Maruyama T, Kajita M, Morita T, Sasaki A, Ohoka A, et al. Plectin is a novel regulator for apical extrusion of RasV12-transformed cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:44328.
McInroy L, Määttä A. Plectin regulates invasiveness of SW480 colon carcinoma cells and is targeted to podosome-like adhesions in an isoform-specific manner. Exp Cell Res. 2011;317:2468–78.
Stegh A, Herrmann H, Lampel S, Weisenberger D, Andrä K, Seper M, et al. Identification of the cytolinker plectin as a major early in vivo substrate for caspase 8 during CD95- and tumor necrosis factor receptor-mediated apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 2000;20:5665–79.
Burgstaller G, Gregor M, Winter L, Wiche G. Keeping the vimentin network under control: cell-matrix adhesion-associated plectin 1f affects cell shape and polarity of fibroblasts. Mol Biol Cell. 2010;21:3362–75.
Jiu Y, Lehtimäki J, Tojkander S, Cheng F, Jäälinoja H, Liu X, et al. Bidirectional interplay between vimentin intermediate filaments and contractile actin stress fibers. Cell Rep. 2015;11:1511–8.
Kidd M, Shumaker D, Ridge K. The role of vimentin intermediate filaments in the progression of lung cancer. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;50:1–6.
Sutoh Yoneyama M, Hatakeyama S, Habuchi T, Inoue T, Nakamura T, Funyu T, et al. Vimentin intermediate filament and plectin provide a scaffold for invadopodia, facilitating cancer cell invasion and extravasation for metastasis. Eur J Cell Biol. 2014;93:157–69.
Wang C, Wang C, Wu Y, Feng H, Liu P, Chang Y, et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals a novel role of karyopherin alpha 2 in cell migration through the regulation of vimentin-pErk protein complex levels in lung cancer. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:1739–51.
Chaudhari P, Charles S, D’Souza Z, Vaidya M. Hemidesmosomal linker proteins regulate cell motility, invasion and tumorigenicity in oral squamous cell carcinoma derived cells. Exp Cell Res. 2017;360:125–37.
Cheng C, Chao W, Liao C, Tseng Y, Lai Y, Lai Y, et al. Plectin deficiency in liver cancer cells promotes cell migration and sensitivity to sorafenib treatment. Cell Adhes Migr. 2018;12:19–27.
Andrä K, Lassmann H, Bittner R, Shorny S, Fässler R, Propst F, et al. Targeted inactivation of plectin reveals essential function in maintaining the integrity of skin, muscle, and heart cytoarchitecture. Gene Dev. 1997;11:3143–56.
Bershadsky A, Chausovsky A, Becker E, Lyubimova A, Geiger B. Involvement of microtubules in the control of adhesion-dependent signal transduction. Curr Biol. 1996;6:1279–89.
Andra K, Nikolic B, Stocher M, Drenckhahn D, Wiche G. Not just scaffolding: plectin regulates actin dynamics in cultured cells. Genes Dev. 1998;12:3442–51.
Sweeney HL, Holzbaur ELF. Motor proteins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a021931.
Huxley A. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318.
Hug C, Jay PY, Reddy I, McNally JG, Bridgman PC, Elson EL, et al. Capping protein levels influence actin assembly and cell motility in dictyostelium. Cell. 1995;81:591–600.
Hemler M. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400.
Buck C, Horwitz A. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205.
Hynes R. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992;69:11–25.
Juliano R, Haskill S. Signal transduction from the extracellular matrix. J Cell Biol. 1993;120:577–85.
Dowling J, Yu Q, Fuchs E. Beta4 integrin is required for hemidesmosome formation, cell adhesion and cell survival. J Cell Biol. 1996;134:559–72.
van der Neut R, Krimpenfort P, Calafat J, Niessen CM, Sonnenberg A. Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta 4 null mice. Nat Genet. 1996;13:366–9.
Duronio R, Gordon J, Boguski M. Comparative analysis of the beta transducin family with identification of several new members including PWP1, a nonessential gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that is divergently transcribed from NMT1. Proteins. 1992;13:41–56.
Ron D, Chen CH, Caldwell J, Jamieson L, Orr E, Mochly-Rosen D. Cloning of an intracellular receptor for protein kinase C: a homolog of the beta subunit of G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:839–43.
Guillemot F, Billault A, Auffray C. Physical linkage of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein-related gene to the chicken major histocompatibility complex. P Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:4594–8.
Chou Y, Chou C, Chen Y, Tsai S, Hsieh F, Liu H, et al. Structure and genomic organization of porcine RACK1 gene. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1999;1489:315–22.
Zhang Q, Ragnauth C, Greener M, Shanahan C, Roberts R. The nesprins are giant actin-binding proteins, orthologous to Drosophila melanogaster muscle protein MSP-300. Genomics. 2002;80:473–81.
Simpson JG, Roberts RG. Patterns of evolutionary conservation in the nesprin genes highlight probable functionally important protein domains and isoforms. Biochem Soc Trans. 2008;36:1359–67.
Wilhelmsen K, Litjens SHM, Kuikman I, Tshimbalanga N, Janssen H, van den Bout I, et al. Nesprin-3, a novel outer nuclear membrane protein, associates with the cytoskeletal linker protein plectin. J Cell Biol. 2005;171:799–810.
Postel R, Ketema M, Kuikman I, de Pereda JM, Sonnenberg A. Nesprin-3 augments peripheral nuclear localization of intermediate filaments in zebrafish. J Cell Sci. 2011;124:755–64.
Ketema M, Wilhelmsen K, Kuikman I, Janssen H, Hodzic D, Sonnenberg A. Requirements for the localization of nesprin-3 at the nuclear envelope and its interaction with plectin. J Cell Sci. 2007;120:3384–94.
Lombardi M, Jaalouk D, Shanahan C, Burke B, Roux K, Lammerding J. The interaction between nesprins and sun proteins at the nuclear envelope is critical for force transmission between the nucleus and cytoskeleton. J Biol Chem. 2011;286:26743–53.
Geerts D, Fontao L, Nievers MG, Schaapveld RQ, Purkis PE, Wheeler GN, et al. Binding of integrin alpha6beta4 to plectin prevents plectin association with F-actin but does not interfere with intermediate filament binding. J Cell Biol. 1999;147:417–34.
Koster J, Geerts D, Favre B, Borradori L, Sonnenberg A. Analysis of the interactions between BP180, BP230, plectin and the integrin alpha6beta4 important for hemidesmosome assembly. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:387–99.
Pellegrini L, Venkitaraman A. Emerging functions of BRCA2 in DNA recombination. Trends Biochem Sci. 2004;29:310–6.
Esashi F, Christ N, Gannon J, Liu Y, Hunt T, Jasin M, et al. CDK-dependent phosphorylation of BRCA2 as a regulatory mechanism for recombinational repair. Nature. 2005;434:598–604.
Gonczy P. Centrosomes: hooked on the nucleus. Curr Biol. 2004;14:R268-70.
Kim Y, Lee J, Kim H, Lee M, Son M, Yoo C, et al. The unique spliceosome signature of human pluripotent stem cells is mediated by SNRPA1, SNRPD1, and PNN. Stem Cell Res. 2017;22:43–53.
Angeloni D, Danilkovitch-Miagkova A, Ivanov S, Breathnach R, Johnson B, Leonard E, et al. Gene structure of the human receptor tyrosine kinase RON and mutation analysis in lung cancer samples. Genes Chromosom Cancer. 2000;29:147–56.
Yao H, Zhou Y, Zhang R, Wang M. MSP-RON signalling in cancer: pathogenesis and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Cancer. 2013;13:466–81.
Boczonadi V, Määttä A. Annexin A9 is a periplakin interacting partner in membrane-targeted cytoskeletal linker protein complexes. FEBS Lett. 2012;586:3090–6.
Boczonadi V, McInroy L, Määttä A. Cytolinker cross-talk: periplakin N-terminus interacts with plectin to regulate keratin organisation and epithelial migration. Exp Cell Res. 2007;313:3579–91.
Long H, Boczonadi V, McInroy L, Goldberg M, Määttä A. Periplakin-dependent re-organisation of keratin cytoskeleton and loss of collective migration in keratin-8-downregulated epithelial sheets. J Cell Sci. 2006;119:5147–59.
Braun A, Olayioye M. Rho regulation: DLC proteins in space and time. Cell Signal. 2015;27:1643–51.
Gregor M, Osmanagic-Myers S, Burgstaller G, Wolfram M, Fischer I, Walko G, et al. Mechanosensing through focal adhesion-anchored intermediate filaments. FASEB J. 2014;28:715–29.
Holeiter G, Heering J, Erlmann P, Schmid S, Jähne R, Olayioye M. Deleted in liver cancer 1 controls cell migration through a Dia1-dependent signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2008;68:8743–51.
Sabbir M, Wigle N, Loewen S, Gu Y, Buse C, Hicks G, et al. Identification and characterization of Dlc1 isoforms in the mouse and study of the biological function of a single gene trapped isoform. BMC Biol. 2010;8:17.
Goldfarb D, Corbett A, Mason D, Harreman M, Adam S. Importin alpha: a multipurpose nuclear-transport receptor. Trends Cell Biol. 2004;14:505–4.
Christiansen A, Dyrskjøt L. The functional role of the novel biomarker karyopherin α 2 (KPNA2) in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2013;331:18–23.
Gousias K, Becker A, Simon M, Niehusmann P. Nuclear karyopherin a2: a novel biomarker for infiltrative astrocytomas. J Neurooncol. 2012;109:545–53.
Craig A, Zirngibl R, Greer P. Disruption of coiled-coil domains in Fer protein-tyrosine kinase abolishes trimerization but not kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:19934–42.
Orlovsky K, Ben-Dor I, Priel-Halachmi S, Malovany H, Nir U. N-terminal sequences direct the autophosphorylation states of the FER tyrosine kinases in vivo. Biochemistry. 2000;39:11084–91.
Lunter PC, Wiche G. Direct binding of plectin to Fer kinase and negative regulation of its catalytic activity. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2002;296:904–10.
Rezniczek G, Konieczny P, Nikolic B, Reipert S, Schneller D, Abrahamsberg C, et al. Plectin 1f scaffolding at the sarcolemma of dystrophic (mdx) muscle fibers through multiple interactions with beta-dystroglycan. J Cell Biol. 2007;176:965–77.
Capetanaki Y. Desmin cytoskeleton: a potential regulator of muscle mitochondrial behavior and function. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2002;12:339–48.
Paulin D, Li Z. Desmin: a major intermediate filament protein essential for the structural integrity and function of muscle. Exp Cell Res. 2004;301:1–7.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Science and Technology Project of Xuzhou (KC20119), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81972377).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JD: the conception and design of this manuscript; KG and ZG: writing and editing; MX: collecting and preparing related papers; HL: supervision and revision.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, K., Gao, Z., Xia, M. et al. Role of plectin and its interacting molecules in cancer. Med Oncol 40, 280 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02132-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-023-02132-4