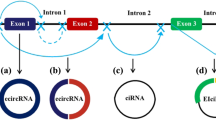
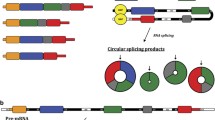
Abstract
Circular RNAs (circRNA) are covalently closed single-stranded RNA molecules that act as important regulators of gene expression through different mechanisms. Meanwhile, cancer stem cells (CSCs) are a small subpopulation of cells, with properties similar to normal stem cells that arise during the development of cancer and support tumor growth, induce resistance to therapy, and are responsible for metastatic spread. Since the elimination of CSCs is an important goal of cancer treatment, the circRNAs that participate in regulating gene expression and signaling pathways linked to CSCs have aroused attention in recent years, especially because it has been suggested that these molecules may function as therapeutic targets and/or clinical biomarkers. Thus, the proposal of this work is to enumerate a series of circRNAs that have been shown to play a relevant role in CSCs and explain in detail the molecular regulatory mechanisms that they establish to perform that function.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melton D. ‘Stemness’: definitions, criteria, and standards. Essentials stem cell biology. Amsterdam: Elsevier; 2014. p. 7–17.
Yu Z, Pestell TG, Lisanti MP, Pestell RG. Cancer stem cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2012;44:2144–51.
Peiris-Pagès M, Martinez-Outschoorn UE, Pestell RG, Sotgia F, Lisanti MP. Cancer stem cell metabolism. Breast Cancer Res. 2016;18:55.
Zhang Z, Xie Q, He D, Ling Y, Li Y, Li J, et al. Circular RNA: new star, new hope in cancer. BMC Cancer. 2018;18:834.
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J. The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet. 2019;20:675–91.
Matsui WH. Cancer stem cell signaling pathways. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:S8–19.
Liu A, Yu X, Liu S. Pluripotency transcription factors and cancer stem cells: small genes make a big difference. Chin J Cancer. 2013;32:483–7.
Feng Z, Meng S, Zhou H, Xu Z, Tang Y, Li P, et al. Functions and potential applications of circular RNAs in cancer stem cells. Front Oncol. 2019;9:1–10.
Ranji P, Salmani Kesejini T, Saeedikhoo S, Alizadeh AM. Targeting cancer stem cell-specific markers and/or associated signaling pathways for overcoming cancer drug resistance. Tumor Biol. 2016;37:13059–75.
Hanekamp D, Cloos J, Schuurhuis GJ. Leukemic stem cells: identification and clinical application. Int J Hematol. 2017;105:549–57.
Wang T, Shigdar S, Gantier MP, Hou Y, Wang L, Li Y, et al. Cancer stem cell targeted therapy: progress amid controversies. Oncotarget. 2015;6:44191–206.
Belousova EA, Filipenko ML, Kushlinskii NE. Circular RNA: new regulatory molecules. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2018;164:803–15.
Li X, Yang L, Chen L-L. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 2018;71:428–42.
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J, Hansen TB. Circular RNAs: identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1859:163–8.
Chen L, Kong R, Wu C, Wang S, Liu Z, Liu S, et al. Circ-MALAT1 functions as both an mRNA translation brake and a microRNA sponge to promote self-renewal of hepatocellular cancer stem cells. Adv Sci. 2020;7:1900949.
Zhu P, Zhu X, Wu J, He L, Lu T, Wang Y, et al. IL-13 secreted by ILC2s promotes the self-renewal of intestinal stem cells through circular RNA circPan3. Nat Immunol. 2019;20:183–94.
Xia P, Wang S, Ye B, Du Y, Li C, Xiong Z, et al. A circular RNA protects dormant hematopoietic stem cells from DNA sensor cGAS-mediated exhaustion. Immunity. 2018;48(688–701):e7.
Li X, Zheng Y, Zheng Y, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Jia L, et al. Circular RNA CDR1as regulates osteoblastic differentiation of periodontal ligament stem cells via the miR-7/GDF5/SMAD and p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9:232.
Peng W, Zhu S, Chen J, Wang J, Rong Q, Chen S. Hsa_circRNA_33287 promotes the osteogenic differentiation of maxillary sinus membrane stem cells via miR-214-3p/Runx3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1709–17.
Zhu Y, Gui W, Lin X, Li H. Knock-down of circular RNA H19 induces human adipose-derived stem cells adipogenic differentiation via a mechanism involving the polypyrimidine tract-binding protein 1. Exp Cell Res. 2019;11:1753.
Yan N, Xu H, Zhang J, Xu L, Zhang Y, Zhang L, et al. Circular RNA profile indicates circular RNA VRK1 is negatively related with breast cancer stem cells. Oncotarget. 2017;8:95704–18.
Liu R, Shi P, Nie Z, Liang H, Zhou Z, Chen W, et al. Mifepristone suppresses basal triple-negative breast cancer stem cells by down-regulating KLF5 expression. Theranostics. 2016;6:533–44.
He Y, Mingyan E, Wang C, Liu G, Shi M, Liu S. CircVRK1 regulates tumor progression and radioresistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating miR-624–3p/PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Int J Biol Macromol. 2019;125:116–23.
Li H, Gao Q, Guo L, Lu SH. The PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway regulates stem-like cells in primary esophageal carcinoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;11:950–8.
Zhu Y-J, Zheng B, Luo G-J, Ma X-K, Lu X-Y, Lin X-M, et al. Circular RNAs negatively regulate cancer stem cells by physically binding FMRP against CCAR1 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics. 2019;9:3526–40.
Yao Z, Luo J, Hu K, Lin J, Huang H, Wang Q, et al. ZKSCAN1 gene and its related circular RNA (circ ZKSCAN1) both inhibit hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth, migration, and invasion but through different signaling pathways. Mol Oncol. 2017;11:422–37.
Bi J, Liu H, Dong W, Xie W, He Q, Cai Z, et al. Circular RNA circ-ZKSCAN1 inhibits bladder cancer progression through miR-1178-3p/p21 axis and acts as a prognostic factor of recurrence. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:133.
Liu H, Bi J, Dong W, Yang M, Shi J, Jiang N, et al. Invasion-related circular RNA circFNDC3B inhibits bladder cancer progression through the miR-1178-3p/G3BP2/SRC/FAK axis. Mol Cancer. 2018;17:161.
Gupta N, Badeaux M, Liu Y, Naxerova K, Sgroi D, Munn LL, et al. Stress granule-associated protein G3BP2 regulates breast tumor initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2017;114:1033–8.
Xiao T, Xue J, Shi M, Chen C, Luo F, Xu H, et al. Circ008913, via miR-889 regulation of DAB2IP/ZEB1, is involved in the arsenite-induced acquisition of CSC-like properties by human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Metallomics. 2018;10:1328–38.
Zhao F, He X, Wang Y, Shi F, Wu D, Pan M, et al. Decrease of ZEB1 expression inhibits the B16F10 cancer stem-like properties. Biosci Trends. 2015;9:325–34.
Zhang K, Che S, Su Z, Zheng S, Zhang H, Yang S, et al. CD90 promotes cell migration, viability and sphere-forming ability of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Mol Med. 2017;41:946–54.
Xue J, Chen C, Luo F, Pan X, Xu H, Yang P, et al. CircLRP6 regulation of ZEB1 via miR-455 is involved in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition during arsenite-induced malignant transformation of human keratinocytes. Toxicol Sci. 2018;162:450–61.
Zheng S, Qian Z, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J, Chen H, et al. CircRNA LRP6 promotes the development of osteosarcoma via negatively regulating KLF2 and APC levels. Am J Transl Res. 2019;11:4126–38.
Wellner U, Schubert J, Burk UC, Schmalhofer O, Zhu F, Sonntag A, et al. The EMT-activator ZEB1 promotes tumorigenicity by repressing stemness-inhibiting microRNAs. Nat Cell Biol. 2009;11:1487–95.
Xu Y, He J, Wang Y, Zhu X, Pan Q, Xie Q, et al. miR-889 promotes proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinomas through DAB2IP. FEBS Lett. 2015;589:1127–35.
Yun E-J, Baek ST, Xie D, Tseng S-F, Dobin T, Hernandez E, et al. DAB2IP regulates cancer stem cell phenotypes through modulating stem cell factor receptor and ZEB1. Oncogene. 2015;34:2741–52.
Li Y-J, Ping C, Tang J, Zhang W. MicroRNA-455 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer through targeting ZEB1. Cell Biol Int. 2016;40:621–8.
Xue J, Liu Y, Luo F, Lu X, Xu H, Liu X, et al. Circ100284, via miR-217 regulation of EZH2, is involved in the arsenite-accelerated cell cycle of human keratinocytes in carcinogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2017;1863:753–63.
Wen Y, Cai J, Hou Y, Huang Z, Wang Z. Role of EZH2 in cancer stem cells: from biological insight to a therapeutic target. Oncotarget. 2017;8:37974–900.
Zhou W, Song F, Wu Q, Liu R, Wang L, Liu C, et al. miR-217 inhibits triple-negative breast cancer cell growth, migration, and invasion through targeting KLF5. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0176395.
Dai X, Chen C, Yang Q, Xue J, Chen X, Sun B, et al. Exosomal circRNA_100284 from arsenite-transformed cells, via microRNA-217 regulation of EZH2, is involved in the malignant transformation of human hepatic cells by accelerating the cell cycle and promoting cell proliferation. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:454.
Chen J, Chen T, Zhu Y, Li Y, Zhang Y, Wang Y, et al. circPTN sponges miR-145-5p/miR-330-5p to promote proliferation and stemness in glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019;38:398.
Ozen M, Karatas OF, Gulluoglu S, Bayrak OF, Sevli S, Guzel E, et al. Overexpression of miR-145–5p inhibits proliferation of prostate cancer cells and reduces SOX2 expression. Cancer Invest. 2015;33:251–8.
Wang R, Dong H-X, Zeng J, Pan J, Jin X-Y. LncRNA DGCR5 contributes to CSC-like properties via modulating miR-330-5p/CD44 in NSCLC. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233:7447–566.
Xiao Y, Li Y, Tao H, Humphries B, Li A, Jiang Y, et al. Integrin α5 down-regulation by miR-205 suppresses triple negative breast cancer stemness and metastasis by inhibiting the Src/Vav2/Rac1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2018;433:199–209.
Zhi X, Zhang J, Cheng Z, Bian L, Qin J. circLgr4 drives colorectal tumorigenesis and invasion through Lgr4‐targeting peptide. Int J Cancer. 2019;ijc.32549.
Wang Y, Dong J, Li D, Lai L, Siwko S, Li Y, et al. Lgr4 regulates mammary gland development and stem cell activity through the pluripotency transcription factor Sox2. Stem Cells. 2013;31:1921–31.
Wu Y, Zhang Y, Niu M, Shi Y, Liu H, Yang D, et al. Whole-transcriptome analysis of CD133+CD144+ cancer stem cells derived from human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47:1696–710.
Senfter D, Samadaei M, Mader RM, Gojo J, Peyrl A, Krupitza G, et al. High impact of miRNA-4521 on FOXM1 expression in medulloblastoma. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10:696.
Gu C, Zhou N, Wang Z, Li G, Kou Y, Yu S, et al. circGprc5a promoted bladder oncogenesis and metastasis through Gprc5a-targeting peptide. Mol Ther - Nucleic Acids. 2018;13:633–41.
Wei Y, Chen X, Liang C, Ling Y, Yang X, Ye X, et al. A noncoding regulatory RNAs network driven by Circ-CDYL acts specifically in the early stages hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 2019;0:hep.30795.
Cherubini A, Barilani M, Rossi RL, Jalal MMK, Rusconi F, Buono G, et al. FOXP1 circular RNA sustains mesenchymal stem cell identity via microRNA inhibition. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019;47:5325–40.
Wang W, Li Y, Li X, Liu B, Han S, Li X, et al. Circular RNA circ-FOXP1 induced by SOX9 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via sponging miR-875-3p and miR-421. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109517.
Ye W, Ni Z, Yicheng S, Pan H, Huang Y, Xiong Y, et al. Anisomycin inhibits angiogenesis in ovarian cancer by attenuating the molecular sponge effect of the lncRNA-Meg3/miR-421/PDGFRA axis. Int J Oncol. 2019;55:1296–312.
Bhatia V, Yadav A, Tiwari R, Nigam S, Goel S, Carskadon S, et al. Epigenetic silencing of miRNA-338–5p and miRNA-421 drives SPINK1-positive prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2018;25:clincanres.3230.2018.
Wang S, Zhang Y, Cai Q, Ma M, Jin LY, Weng M, et al. Circular RNA FOXP1 promotes tumor progression and Warburg effect in gallbladder cancer by regulating PKLR expression. Mol Cancer. 2019;18:145.
Liu P-P, Liao J, Tang Z-J, Wu W-J, Yang J, Zeng Z-L, et al. Metabolic regulation of cancer cell side population by glucose through activation of the Akt pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21:124–35.
Lv H, Tong J, Yang J, Lv S, Li W-P, Zhang C, et al. Dysregulated pseudogene HK2P1 may contribute to preeclampsia as a competing endogenous RNA for hexokinase 2 by impairing decidualization. Hypertension. 2018;71:648–58.
Zhan W, Liao X, Wang Y, Li L, Li J, Chen Z, et al. circCTIC1 promotes the self-renewal of colon TICs through BPTF-dependent c-Myc expression. Carcinogenesis. 2019;40:560–8.
Yu C-Y, Li T-C, Wu Y-Y, Yeh C-H, Chiang W, Chuang C-Y, et al. The circular RNA circBIRC6 participates in the molecular circuitry controlling human pluripotency. Nat Commun. 2017;8:1149.
Huang J, Li J. Tumor molecular marker circBIRC6 and Inhibitor and use thereof [Internet]. China. https://patentscope.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2019169710&tab=PCTBIBLIO (2019).
Qu D, Yan B, Xin R, Ma T. A novel circular RNA hsa_circ_0020123 exerts oncogenic properties through suppression of miR-144 in non-small cell lung cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8:1387–402.
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P, Rajewsky N. circBase: a database for circular RNAs. RNA. 2014;20:1666–700.
Meng X, Hu D, Zhang P, Chen Q, Chen M. CircFunBase: a database for functional circular RNAs. Database. 2019;2019:1–6.
Chen X, Han P, Zhou T, Guo X, Song X, Li Y. circRNADb: A comprehensive database for human circular RNAs with protein-coding annotations. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34985.
Acknowledgments
FALR is recipient of a doctoral scholarship (Application Number 2018-000012-01NACF-07226) from the National Council of Science and Technology, CONACyT.
Funding
This work did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lagunas-Rangel, F.A. Circular RNAs and their participation in stemness of cancer. Med Oncol 37, 42 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01373-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-020-01373-x