Abstract
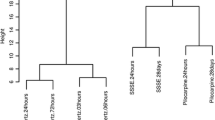
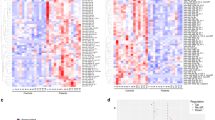
This study aimed to identify key genes (microRNA and messenger RNA (mRNA)) and associated signaling-regulated pathways in a drug-induced epilepsy model in mice by microarray profiling. The related microarray dataset of seizures was obtained from the NCBI Gene Expression Omnibus database (GEO), and differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between two control samples or multi-treated samples and samples were analyzed using the statistical software R. To identify the expected function of DEGs, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was utilized to conduct Gene Ontology (GO) analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis. The interaction relationship between microRNAs (miRNAs) and mRNAs in normal and epilepsy mouse models was identified using Cytoscape software. TargetScan7.1 was applied to determine the binding sites of DEGs. The dual-luciferase assay was used to verify the target relationship between miRNA and mRNA. Four miRNAs were identified as differentially expressed genes in both 24-h and 28-day status epilepticus (SE)-treated samples. Ppp2ca expression in the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway was downregulated in the pilocarpine-induced SE mouse model. The expression of Ppp2ca was also downregulated in the kinase-induced SE model group compared with that in the untreated group and MAP kinase (MEK) inhibitor-treated group of mice. KEGG pathway analysis indicated that the MAPK signaling pathway was upregulated in the kinase-induced SE model group compared with that in both the untreated group and the MEK inhibitor-treated group of mice. miR-203 had a targeted relationship with Ppp2ca in both humans and mice. The miR-203-3p target Ppp2ca aggravates the seizures of the SE model in mice.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alsharafi WA, Xiao B, Abuhamed MM, Luo Z (2015) miRNAs: biological and clinical determinants in epilepsy. Front Mol Neurosci 8:59
Chen K, Chen H, Zhang K, Sun S, Mo J, Lu J, Qian Z, Yang H (2017) MicroRNA profiling and bioinformatics analyses reveal the potential roles of microRNAs in chordoma. Oncol Lett 14:5533–5539
Du TT, Wang L, Duan CL, Lu LL, Zhang JL, Gao G, Qiu XB, Wang XM, Yang H (2015) GBA deficiency promotes SNCA/alpha-synuclein accumulation through autophagic inhibition by inactivated PPP2A. Autophagy 11:1803–1820
Fang C, Li L, Li J (2016) Conditional knockout in mice reveals the critical roles of Ppp2ca in epidermis development. Int J Mol Sci 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050756
Galanopoulou AS, Buckmaster PS, Staley KJ, Moshe SL, Perucca E, Engel J Jr, Loscher W, Noebels JL, Pitkanen A, Stables J, White HS, O'Brien TJ, Simonato M, American Epilepsy Society Basic Science C and The International League Against Epilepsy Working Group On Recommendations For Preclinical Epilepsy Drug D (2012) Identification of new epilepsy treatments: issues in preclinical methodology. Epilepsia 53:571–582
Gorter JA, Iyer A, White I, Colzi A, van Vliet EA, Sisodiya S, Aronica E (2014) Hippocampal subregion-specific microRNA expression during epileptogenesis in experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 62:508–520
Hansen KF, Sakamoto K, Pelz C, Impey S, Obrietan K (2014) Profiling status epilepticus-induced changes in hippocampal RNA expression using high-throughput RNA sequencing. Sci Rep 4:6930
Henshall DC, Hamer HM, Pasterkamp RJ, Goldstein DB, Kjems J, Prehn JHM, Schorge S, Lamottke K, Rosenow F (2016) MicroRNAs in epilepsy: pathophysiology and clinical utility. Lancet Neurol 15:1368–1376
Hu K, Xie YY, Zhang C, Ouyang DS, Long HY, Sun DN, Long LL, Feng L, Li Y, Xiao B (2012) MicroRNA expression profile of the hippocampus in a rat model of temporal lobe epilepsy and miR-34a-targeted neuroprotection against hippocampal neurone cell apoptosis post-status epilepticus. BMC Neurosci 13:115
Jackson SJ, Zhang Z, Feng D, Flagg M, O'Loughlin E, Wang D, Stokes N, Fuchs E, Yi R (2013) Rapid and widespread suppression of self-renewal by microRNA-203 during epidermal differentiation. Development 140:1882–1891
Jimenez-Mateos EM, Bray I, Sanz-Rodriguez A, Engel T, McKiernan RC, Mouri G, Tanaka K, Sano T, Saugstad JA, Simon RP, Stallings RL, Henshall DC (2011) miRNA expression profile after status epilepticus and hippocampal neuroprotection by targeting miR-132. Am J Pathol 179:2519–2532
Karnati HK, Panigrahi MK, Gutti RK, Greig NH, Tamargo IA (2015) miRNAs: key players in neurodegenerative disorders and epilepsy. J Alzheimers Dis 48:563–580
Lee BP, Buric I, George-Pandeth A, Flurkey K, Harrison DE, Yuan R, Peters LL, Kuchel GA, Melzer D, Harries LW (2017a) MicroRNAs miR-203-3p, miR-664-3p and miR-708-5p are associated with median strain lifespan in mice. Sci Rep 7:44620
Lee ST, Jeon D, Chu K, Jung KH, Moon J, Sunwoo J, Park DK, Yang H, Park JH, Kim M, Roh JK, Lee SK (2017b) Inhibition of miR-203 reduces spontaneous recurrent seizures in mice. Mol Neurobiol 54:3300–3308
Lena AM, Shalom-Feuerstein R, Rivetti di Val Cervo P, Aberdam D, Knight RA, Melino G, Candi E (2008) miR-203 represses 'stemness' by repressing DeltaNp63. Cell Death Differ 15:1187–1195
Liu DZ, Tian Y, Ander BP, Xu H, Stamova BS, Zhan X, Turner RJ, Jickling G, Sharp FR (2010) Brain and blood microRNA expression profiling of ischemic stroke, intracerebral hemorrhage, and kainate seizures. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:92–101
McKiernan RC, Jimenez-Mateos EM, Sano T, Bray I, Stallings RL, Simon RP, Henshall DC (2012) Expression profiling the microRNA response to epileptic preconditioning identifies miR-184 as a modulator of seizure-induced neuronal death. Exp Neurol 237:346–354
Moon J, Lee ST, Choi J, Jung KH, Yang H, Khalid A, Kim JM, Park KI, Shin JW, Ban JJ, Yi GS, Lee SK, Jeon D, Chu K (2014) Unique behavioral characteristics and microRNA signatures in a drug resistant epilepsy model. PLoS One 9:e85617
Nudelman AS, DiRocco DP, Lambert TJ, Garelick MG, Le J, Nathanson NM, Storm DR (2010) Neuronal activity rapidly induces transcription of the CREB-regulated microRNA-132, in vivo. Hippocampus 20:492–498
Schratt G (2009) microRNAs at the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:842–849
Tao K, Yang J, Guo Z, Hu Y, Sheng H, Gao H, Yu H (2014) Prognostic value of miR-221-3p, miR-342-3p and miR-491-5p expression in colon cancer. Am J Transl Res 6:391–401
Tian L, Li M, Ge J, Guo Y, Sun Y, Liu M, Xiao H (2014) MiR-203 is downregulated in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and can suppress proliferation and induce apoptosis of tumours. Tumour Biol 35:5953–5963
Wang C, Zheng X, Shen C, Shi Y (2012) MicroRNA-203 suppresses cell proliferation and migration by targeting BIRC5 and LASP1 in human triple-negative breast cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 31:58
Wang W, Wang X, Chen L, Zhang Y, Xu Z, Liu J, Jiang G, Li J, Zhang X, Wang K, Wang J, Chen G, Luo J (2016) The microRNA miR-124 suppresses seizure activity and regulates CREB1 activity. Expert Rev Mol Med 18:e4
Young D, Fong DM, Lawlor PA, Wu A, Mouravlev A, McRae M, Glass M, Dragunow M, During MJ (2014) Adenosine kinase, glutamine synthetase and EAAT2 as gene therapy targets for temporal lobe epilepsy. Gene Ther 21:1029–1040
Zhang F, Yang Z, Cao M, Xu Y, Li J, Chen X, Gao Z, Xin J, Zhou S, Zhou Z, Yang Y, Sheng W, Zeng Y (2014) MiR-203 suppresses tumor growth and invasion and down-regulates MiR-21 expression through repressing ran in esophageal cancer. Cancer Lett 342:121–129
Zhu X, Er K, Mao C, Yan Q, Xu H, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Cui F, Zhao W, Shi H (2013) miR-203 suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis by targeting VEGFA in cervical cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 32:64–73
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere appreciation to the reviewers for their helpful comments on this article.
Funding
This work was supported by the Scientific Research Program of Health and Family Planning Commission of Shanxi Province (No. 201602027) and the Start-up Fund Program for Doctor of Changzhi Medical College (No. BS15004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Consent to Publish
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Li, Y., Ye, X. et al. Bioinformatics Analysis of Microarray Profiling Identifies That the miR-203-3p Target Ppp2ca Aggravates Seizure Activity in Mice. J Mol Neurosci 66, 146–154 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1145-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1145-8