Abstract
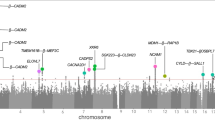
Personality traits like novelty seeking (NS), harm avoidance (HA), and reward dependence (RD) are known to be moderately heritable (30–60%). These personality traits and their comorbidities, such as alcohol dependence (AD), may share genetic components. We examined 11,120 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) genotyped in 292 nuclear families from the Genetic Analysis Workshop 14, a subset from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). A family-based association analysis was performed using the FBAT program. NS, HA, and RD were treated as quantitative traits and AD as a binary trait. Based on a multivariate association test of three quantitative traits in FBAT, we observed 20 SNPs with p < 10−3. Interestingly, several genes (TESK2, TIPARP, THEMIS, ABLIM1, RFX4, STON2 and LILRA1) are associated with three personality traits with p < 10−3 using single trait analysis and AD. Especially, SNP rs727532 within ABLIM1 gene at 10q25 showed the most significant association (p = 6.4 × 10−5) in the multivariate test and strong associations with NS, HA, RD, and AD (p = 4.48 × 10−4, 1.2 × 10−5, 5.6 × 10−5, 3.12 × 10−4, respectively) in the COGA sample. In addition, the association of rs727532 with AD was confirmed in a replication study. This study reports some newly recognized associations between several genetic loci and both AD and three personality traits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrientos T, Frank D, Kuwahara K et al (2007) Two novel members of the ABLIM protein family, ABLIM-2 and -3, associate with STARS and directly bind F-actin. J Biol Chem 282(11):8393–8403
Battaglia M, Przybeck TR, Bellodi L, Cloninger CR (1996) Temperament dimensions explain the comorbidity of psychiatric disorders. Compr Psychiatry 37(4):292–298
Belfer I, Hipp H, McKnight C et al (2006) Association of galanin haplotypes with alcoholism and anxiety in two ethnically distinct populations. Mol Psychiatry 11(3):301–311
Benjamin J, Ebstein RP, Belmaker RH (2002) Personality genetics, 2002. Isr J Psychiatry Relat Sci 39(4):271–279
Bienvenu OJ, Brown C, Samuels JF et al (2001) Normal personality traits and comorbidity among phobic, panic and major depressive disorders. Psychiatry Res 102(1):73–85
Bierut LJ, Agrawal A, Bucholz KK et al (2010) A genome-wide association study of alcohol dependence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(11):5082–5087
Blackshear PJ, Graves JP, Stumpo DJ et al (2003) Graded phenotypic response to partial and complete deficiency of a brain-specific transcript variant of the winged helix transcription factor RFX4. Development 130(19):4539–4552
Cichon S, Schmidt-Wolf G, Schumacher J et al (2001) A possible susceptibility locus for bipolar affective disorder in chromosomal region 10q25–q26. Mol Psychiatry 6(3):342–349
Cloninger CR (1987) A systematic method for clinical description and classification of personality variants. A proposal. Arch Gen Psychiatry 44(6):573–588
Cloninger CR, Sigvardsson S, Gilligan SB et al (1988) Genetic heterogeneity and the classification of alcoholism. Adv Alcohol Subst Abuse 7(3–4):3–16
Cloninger CR, Van Eerdewegh P, Goate A et al (1998) Anxiety proneness linked to epistatic loci in genome scan of human personality traits. Am J Med Genet 81(4):313–317
Contini V, Marques FZ, Garcia CE, Hutz MH, Bau CH (2006) MAOA-uVNTR polymorphism in a Brazilian sample: further support for the association with impulsive behaviors and alcohol dependence. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 141B(3):305–308
Dick DM, Nurnberger J Jr, Edenberg HJ et al (2002) Suggestive linkage on chromosome 1 for a quantitative alcohol-related phenotype. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26(10):1453–1460
Dina C, Nemanov L, Gritsenko I et al (2005) Fine mapping of a region on chromosome 8p gives evidence for a QTL contributing to individual differences in an anxiety-related personality trait: TPQ harm avoidance. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 132B(1):104–108
Ducci F, Enoch MA, Funt S et al (2007) Increased anxiety and other similarities in temperament of alcoholics with and without antisocial personality disorder across three diverse populations. Alcohol 41(1):3–12
Ebstein RP (2006) The molecular genetic architecture of human personality: beyond self-report questionnaires. Mol Psychiatry 11(5):427–445
Edenberg HJ, Bierut LJ, Boyce P et al (2005) Description of the data from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) and single-nucleotide polymorphism genotyping for genetic analysis workshop 14. BMC Genet 6(Suppl 1):S2
Ewald H, Degn B, Mors O, Kruse TA (1998) Significant linkage between bipolar affective disorder and chromosome 12q24. Psychiatr Genet 8(3):131–140
Eysenck SBG, Eyesenck H (1975) Manual of the Eysenck Personality Questionnaire (junior and adult). Hodder and Stoughton, London
Glaser B, Kirov G, Bray NJ et al (2005) Identification of a potential bipolar risk haplotype in the gene encoding the winged-helix transcription factor RFX4. Mol Psychiatry 10(10):920–927
Gong P, Zheng A, Zhang K et al (2010) Association analysis between 12 genetic variants of ten genes and personality traits in a young chinese Han population. J Mol Neurosci 42(1):120–126
Grucza RA, Robert Cloninger C, Bucholz KK et al (2006) Novelty seeking as a moderator of familial risk for alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30(7):1176–1183
Heath AC, Cloninger CR, Martin NG (1994) Testing a model for the genetic structure of personality: a comparison of the personality systems of Cloninger and Eysenck. J Pers Soc Psychol 66(4):762–775
Heck A, Lieb R, Ellgas A et al (2009) Investigation of 17 candidate genes for personality traits confirms effects of the HTR2A gene on novelty seeking. Genes Brain Behav 8(4):464–472
Heiman N, Stallings MC, Young SE, Hewitt JK (2004) Investigating the genetic and environmental structure of Cloninger’s personality dimensions in adolescence. Twin Res 7(5):462–470
Holmans PA, Riley B, Pulver AE et al (2009) Genomewide linkage scan of schizophrenia in a large multicenter pedigree sample using single nucleotide polymorphisms. Mol Psychiatry 14(8):786–795
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zhao S et al (1994) Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States. Results from the National Comorbidity Survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51(1):8–19
Khan AA, Jacobson KC, Gardner CO, Prescott CA, Kendler KS (2005) Personality and comorbidity of common psychiatric disorders. Br J Psychiatry 186:190–196
Kittles RA, Long JC, Bergen AW et al (1999) Cladistic association analysis of Y chromosome effects on alcohol dependence and related personality traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(7):4204–4209
Lange C, Silverman EK, Xu X, Weiss ST, Laird NM (2003) A multivariate family-based association test using generalized estimating equations: FBAT-GEE. Biostatistics 4(2):195–206
Laucht M, Becker K, Blomeyer D, Schmidt MH (2007) Novelty seeking involved in mediating the association between the dopamine D4 receptor gene exon III polymorphism and heavy drinking in male adolescents: results from a high-risk community sample. Biol Psychiatry 61(1):87–92
Li J, Ma H, Deng S, Wu L, Huang Y, Zhu G (2011a) Fyn polymorphisms are associated with distinct personality traits in healthy Chinese-Han subjects. J Mol Neurosci 44(1):1–5
Li J, Ma H, Zhou H, Huang Y, Wu L, Li J, Zhu G (2011b) Association between DARPP-32 gene polymorphism and personality traits in healthy Chinese-Han subjects. J Mol Neurosci 44(1):48–52
Matsushita H, Uenaka A, Ono T et al (2005) Identification of glioma-specific RFX4-E and -F isoforms and humoral immune response in patients. Cancer Sci 96(11):801–809
Merikangas KR, Angst J, Eaton W et al (1996) Comorbidity and boundaries of affective disorders with anxiety disorders and substance misuse: results of an international task force. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 30:58–67
Nery FG, Hatch JP, Glahn DC et al (2008) Temperament and character traits in patients with bipolar disorder and associations with comorbid alcoholism or anxiety disorders. J Psychiatr Res 42(7):569–577
Ongur D, Farabaugh A, Iosifescu DV, Perlis R, Fava M (2005) Tridimensional personality questionnaire factors in major depressive disorder: relationship to anxiety disorder comorbidity and age of onset. Psychother Psychosom 74(3):173–178
Purcell S, Neale B, Todd-Brown K et al (2007) PLINK: a tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am J Hum Genet 81(3):559–575
Rabinowitz D, Laird N (2000) A unified approach to adjusting association tests for population admixture with arbitrary pedigree structure and arbitrary missing marker information. Hum Hered 50(4):211–223
Ray LA, Bryan A, Mackillop J et al (2009) The dopamine D receptor (DRD4) gene exon III polymorphism, problematic alcohol use and novelty seeking: direct and mediated genetic effects. Addict Biol 14(2):238–244
Reich T (1996) A genomic survey of alcohol dependence and related phenotypes: results from the Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA). Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20(8 Suppl):133A–137A
Reif A, Lesch KP (2003) Toward a molecular architecture of personality. Behav Brain Res 139(1–2):1–20
Rice JP, Saccone SF (2005) Alcoholism and related traits: a summary of Group 13 contributions. Genet Epidemiol 29(Suppl 1):S96–S102
Roof DJ, Hayes A, Adamian M, Chishti AH, Li T (1997) Molecular characterization of abLIM, a novel actin-binding and double zinc finger protein. J Cell Biol 138(3):575–588
Savitz JB, Ramesar RS (2004) Genetic variants implicated in personality: a review of the more promising candidates. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 131B(1):20–32
Shifman S, Bhomra A, Smiley S et al (2008) A whole genome association study of neuroticism using DNA pooling. Mol Psychiatry 13(3):302–312
Storey JD (2002) A direct approach to false discovery rates. J R Stat Soc B 64:479–498
Terracciano A, Sanna S, Uda M et al (2010) Genome-wide association scan for five major dimensions of personality. Mol Psychiatry 15(6):647–656
Tikkanen R, Sjoberg RL, Ducci F et al (2009) Effects of MAOA-genotype, alcohol consumption, and aging on violent behavior. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33(3):428–434
van den Oord EJ, Kuo PH, Hartmann AM et al (2008) Genomewide association analysis followed by a replication study implicates a novel candidate gene for neuroticism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65(9):1062–1071
Verweij KJ, Zietsch BP, Medland SE et al (2010) A genome-wide association study of Cloninger’s temperament scales: implications for the evolutionary genetics of personality. Biol Psychol 85(2):306–317
von Trotha KT, Heun R, Schmitz S, Lutjohann D, Maier W, Kolsch H (2006) Influence of lysosomal acid lipase polymorphisms on chromosome 10 on the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and cholesterol metabolism. Neurosci Lett 402(3):262–266
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium (2007) Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447(7145):661–678
Wiesbeck GA, Weijers HG, Wodarz N et al (2004) Serotonin transporter gene polymorphism and personality traits in primary alcohol dependence. World J Biol Psychiatry 5(1):45–48
Williams NM, Norton N, Williams H et al (2003) A systematic genomewide linkage study in 353 sib pairs with schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 73(6):1355–1367
Zhang D, Stumpo DJ, Graves JP et al (2006) Identification of potential target genes for RFX4_v3, a transcription factor critical for brain development. J Neurochem 98(3):860–875
Acknowledgments
The Collaborative Study on the Genetics of Alcoholism (COGA) (H. Begleiter, SUNY HSCB principal investigator, T. Reich, Washington University, co-principal investigator) includes nine centers where data collection, analysis, and/or storage take place. This national collaborative study is supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) grant U10AA08403 from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). The National Institute of General Medical Sciences has provided continuous funding for the Genetic Analysis Workshops (GAW) since 1982, through grant R01 GM31575 to Jean MacCluer (Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research). The GAW14 data were kindly provided by Jean MacCluer (Southwest Foundation for Biomedical Research). We acknowledge the contributions of the COGA, supported by NIH grants U10AA08401 and U10AA08403 (NIAAA), and the contributions of all scientists who have provided genotyping data to the wave I and/or wave II—genetic analysis data. We were granted access to the COGA data by NIAAA.
A funding support for the SAGE was provided through the NIH Genes, Environment, and Health Initiative (GEI) grant U01 HG004422. SAGE is one of the GWAS funded as part of the GENEVA under GEI. Assistance with phenotype harmonization and genotype cleaning, as well as with general study coordination, was provided by the GENEVA Coordinating Center (grant U01 HG004446). Assistance with data cleaning was provided by the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Support for the collection of datasets and samples was provided by COGA (grant U10 AA008401), COGEND (grant P01 CA089392), and FSCD (grant R01 DA013423). Funding support for genotyping, which was performed at the Johns Hopkins University Center for Inherited Disease Research, was provided by NIH GEI grant U01HG004438, the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the National Institute on Drug Abuse, and the NIH contract “High throughput genotyping for studying the genetic contributions to human disease” (HHSN268200782096C).
This study is approved by the Internal Review Board (IRB), East Tennessee State University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Table S1
SNPs associated with AD in SAGE sample based on PLINK (p ≤ 0.05). (XLSX 13 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, KS., Liu, X., Aragam, N. et al. Polymorphisms in ABLIM1 are Associated with Personality Traits and Alcohol Dependence. J Mol Neurosci 46, 265–271 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9530-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-011-9530-6