Abstract
Purpose
Gastric cancer is an important health burden characterized by high prevalence and mortality rate. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy coupled with biopsy is the primary means in which gastric cancer is diagnosed, and most of machine learning (ML) tools are developed in this area. This systematic review focuses on the applications of ML in gastric cancer that do not involve endoscopic image recognition.
Methods
A systematic review of ML applications that do not involve endoscopy and are relevant to gastric cancer was performed in two databases and independently evaluated by the two authors. Information collected from the included studies are year of publication, ML algorithm, ML performance, specimen used to create the ML model, and clinical application of the model.
Results
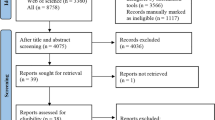
From 791 screened studies, 63 studies were included in the systematic review. The included studies demonstrate that the non-endoscopic applications of ML can be divided into three main categories, which are diagnostics, predicting response to therapy, and prognosis prediction. Various specimen and algorithms were found to be used for these applications. Most of its clinical use includes histopathologic slide reading in the diagnosis of gastric cancer and a risk scoring system to determine the survival of patients or to determine the important variables that may affect the patient’s prognosis.
Conclusion
The systematic review suggests that there are numerous examples of non-endoscopic applications of ML that are relevant to gastric cancer. These studies have utilized various specimens, even non-conventional ones, thus showing great promise for the development of more non-invasive techniques. However, most of these studies are still in the early stages and will take more time before they can be clinically deployed. Moving forward, researchers in this field of study are encouraged to improve data curation and annotation, improve model interpretability, and compare model performance with the currently accepted standard in the clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Petryszyn P, Chapelle N, Matysiak-Budnik T. Gastric cancer: where are we heading? Dig. Dis. S. Karger AG; 2020;280–5.
Global Cancer Observatory. Stomach . [cited 2022 Dec 22]. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/7-Stomach-fact-sheet.pdf.
Wanebo HJ, Kennedy BJ, Chmiel J, Steele G, Winchester D, Osteen R. Cancer of the stomach a patient care study by the American College of Surgeons summary background data. Ann. Surg. 1993.
Mukkamalla SK, Recio-Boiles A, Babiker H. Gastric cancer. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
Cohen S. Chapter 2 - the basics of machine learning: strategies and techniques. In: Cohen S, editor. Artif Intell Deep Learn Pathol. Elsevier. 2021;13–40. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/B9780323675383000026.
Nakaura T, Higaki T, Awai K, Ikeda O, Yamashita Y. A primer for understanding radiology articles about machine learning and deep learning. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2020;101:765–770. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2211568420302461.
Hassan C, Spadaccini M, Iannone A, Maselli R, Jovani M, Thoguluva Chandrasekar V, et al. Performance of artificial intelligence in colonoscopy for adenoma and polyp detection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021;93:77–85. https://www.giejournal.org.
Chen PC, Lu YR, Kang YN, Chang CC. The accuracy of artificial intelligence in the endoscopic diagnosis of early gastric cancer: pooled analysis study. J Med Internet Res. JMIR Publications Inc.; 2022;24.
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. [Internet]. Vienna, Austria: R Foundation for Statistical Computing; 2021. Available from: https://www.r-project.org/.
Gu Z, Gu L, Eils R, Schlesner M, Brors B. circlize implements and enhances circular visualization in R. Bioinformatics [Internet]. 2014;30:2811–2. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu393.
Liu D, Wang X, Li L, Jiang Q, Li X, Liu M, et al. Machine learning-based model for the prognosis of postoperative gastric cancer. Cancer Manag Res. Dove Medical Press Ltd; 2022;14:135–55.
Xu Y-G, Cheng M, Zhang X, Sun S-H, BI W-M. Mutual information network-based support vector machinestrategy identifies salivary biomarkers in gastric cancer. J BUON [Internet]. 2017;22:119–25. Available from: http://www.ebi.
Sharma H, Zerbe N, Klempert I, Hellwich O, Hufnagl P. Deep convolutional neural networks for automatic classification of gastric carcinoma using whole slide images in digital histopathology. Comput Med Imaging Graph [Internet]. 2017;61:2–13. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0895611117300502.
Zhang F, Xu W, Liu J, Liu X, Huo B, Li B, et al. Optimizing miRNA-module diagnostic biomarkers of gastric carcinoma via integrated network analysis. PLoS One [Internet]. Public Library of Science; 2018;13:e0198445-. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198445.
Wang X-X, Ding Y, Wang S-W, Dong D, Li H-L, Chen J, et al. Intratumoral and peritumoral radiomics analysis for preoperative Lauren classification in gastric cancer. Cancer Imaging [Internet]. 2020;20:83. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-020-00358-3.
Rasmussen SA, Arnason T, Huang WY. Deep learning for computer-assisted diagnosis of hereditary diffuse gastric cancer. J Pathol Transl Med. Seoul National University; 2021;55:118–24.
Saito R, Yoshimura K, Shoda K, Furuya S, Akaike H, Kawaguchi Y, et al. Diagnostic significance of plasma lipid markers and machine learning-based algorithm for gastric cancer. Oncol Lett. Spandidos Publications; 2021;21.
Qiao X, Li Z, Li L, Ji C, Li H, Shi T, et al. Preoperative T2-weighted MR imaging texture analysis of gastric cancer: prediction of TNM stages. Abdom Radiol [Internet]. 2021;46:1487–97. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02802-1.
Aslam MA, Xue C, Chen Y, Zhang A, Liu M, Wang K, et al. Breath analysis based early gastric cancer classification from deep stacked sparse autoencoder neural network. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2021;11:4014. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-83184-2.
Li M, He H, Huang G, Lin B, Tian H, Xia K, et al. A novel and rapid serum detection technology for non-invasive screening of gastric cancer based on Raman spectroscopy combined with different machine learning methods. Front Oncol. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2021;11.
Dong C, Rao N, Du W, Gao F, Lv X, Wang G, et al. mRBioM: an algorithm for the identification of potential mRNA biomarkers from complete transcriptomic profiles of gastric adenocarcinoma. Front Genet. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2021;12.
Hong Y, Heo YJ, Kim B, Lee D, Ahn S, Ha SY, et al. Deep learning-based virtual cytokeratin staining of gastric carcinomas to measure tumor–stroma ratio. Sci Rep [Internet]. 2021;11:19255. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98857-1.
Zhang B, Yao K, Xu M, Wu J, Cheng C. Deep learning predicts EBV status in gastric cancer based on spatial patterns of lymphocyte infiltration. Cancers (Basel) [Internet]. 2021;13. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/23/6002.
Meng L, Dong D, Chen X, Fang M, Wang R, Li J, et al. 2D and 3D CT radiomic features performance comparison in characterization of gastric cancer: a multi-center study. IEEE J Biomed Heal Informatics. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.; 2021;25:755–63.
Hinata M, Ushiku T. Detecting immunotherapy-sensitive subtype in gastric cancer using histologic image-based deep learning. Sci Rep. Nature Research; 2021;11.
Wang X, Chen Y, Gao Y, Zhang H, Guan Z, Dong Z, et al. Predicting gastric cancer outcome from resected lymph node histopathology images using deep learning. Nat Commun [Internet]. 2021;12:1637. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21674-7.
Gholami E, Kamel Tabbakh SR, kheirabadi M. Increasing the accuracy in the diagnosis of stomach cancer based on color and lint features of tongue. Biomed Signal Process Control. Elsevier Ltd; 2021;69.
Jiang Y, Liang X, Wang W, Chen C, Yuan Q, Zhang X, et al. Noninvasive prediction of occult peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer using deep learning. JAMA Netw Open [Internet]. 2021;4:e2032269–e2032269. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.32269.
Muti HS, Heij LR, Keller G, Kohlruss M, Langer R, Dislich B, et al. Development and validation of deep learning classifiers to detect Epstein-Barr virus and microsatellite instability status in gastric cancer: a retrospective multicentre cohort study. Lancet Digit Heal [Internet]. Elsevier; 2021;3:e654–64. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(21)00133-3.
Kanavati F, Ichihara S, Rambeau M, Iizuka O, Arihiro K, Tsuneki M. Deep learning models for gastric signet ring cell carcinoma classification in whole slide images. Technol Cancer Res Treat. SAGE Publications Inc.; 2021;20.
Wu J, Yang Y, Cheng L, Wu J, Xi L, Ma Y, et al. GCdiscrimination: identification of gastric cancer based on a milliliter of blood. Brief Bioinform Oxford University Press. 2021;22:536–44.
Koopaie M, Ghafourian M, Manifar S, Younespour S, Davoudi M, Kolahdooz S, et al. Evaluation of CSTB and DMBT1 expression in saliva of gastric cancer patients and controls. BMC Cancer. BioMed Central Ltd; 2022;22.
Polaka I, Bhandari MP, Mezmale L, Anarkulova L, Veliks V, Sivins A, et al. Modular point-of-care breath analyzer and shape taxonomy-based machine learning for gastric cancer detection. Diagnostics. MDPI; 2022;12.
Guan X, Lu N, Zhang J. Evaluation of epidermal growth factor receptor 2 status in gastric cancer by CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram. Front Oncol [Internet]. 2022;12. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2022.905203.
Zheng X, Wang R, Zhang X, Sun Y, Zhang H, Zhao Z, et al. A deep learning model and human-machine fusion for prediction of EBV-associated gastric cancer from histopathology. Nat Commun. Nature Research; 2022;13.
Jiang S, Gao H, He J, Shi J, Tong Y, Wu J. Machine learning: a non-invasive prediction method for gastric cancer based on a survey of lifestyle behaviors. Front Artif Intell [Internet]. 2022;5. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/frai.2022.956385.
Jiang Y, Liu W, Li T, Hu Y, Chen S, Xi S, et al. Prognostic and predictive value of p21-activated kinase 6 associated support vector machine classifier in gastric cancer treated by 5-fluorouracil/Oxaliplatin Chemotherapy. eBioMedicine [Internet]. Elsevier; 2017;22:78–88. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.06.028.
Li Z, Zhang D, Dai Y, Dong J, Wu L, Li Y, et al. Computed tomography-based radiomics for prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy outcomes in locally advanced gastric cancer: a pilot study. Chinese J Cancer Res [Internet]. 2018;30:406–14. Available from: http://www.cjcrcn.org/article/html_9816.html.
Jiang Y, Xie J, Han Z, Liu W, Xi S, Huang L, et al. Immunomarker support vector machine classifier for prediction of gastric cancer survival and adjuvant chemotherapeutic benefit. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2018;24:5574–84. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-0848.
Lu S, Yan M, Li C, Yan C, Zhu Z, Lu W. Machine-learning-assisted prediction of surgical outcomes in patients undergoing gastrectomy. Chinese J Cancer Res [Internet]. 2019;31:797–805. Available from: https://doi.org/10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2019.05.09?viewType=HTML.
Jiang Y, Xie J, Huang W, Chen H, Xi S, Han Z, et al. Tumor immune microenvironment and chemosensitivity signature for predicting response to chemotherapy in gastric cancer. Cancer Immunol Res [Internet]. 2019;7:2065–73. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-19-0311.
Xie K, Cui Y, Zhang D, He W, He Y, Gao D, et al. Pretreatment contrast-enhanced computed tomography radiomics for prediction of pathological regression following neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced gastric cancer: a preliminary multicenter study. Front Oncol [Internet]. 2022;11. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.770758.
Chen Y, Wei K, Liu D, Xiang J, Wang G, Meng X, et al. A machine learning model for predicting a major response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced gastric cancer. Front Oncol. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2021;11.
Xu Q, Sun Z, Li X, Ye C, Zhou C, Zhang L, et al. Advanced gastric cancer: CT radiomics prediction and early detection of downstaging with neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2021;31:8765–74. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-021-07962-2.
Jiang Y, Jin C, Yu H, Wu J, Chen C, Yuan Q, et al. Development and validation of a deep learning CT signature to predict survival and chemotherapy benefit in gastric cancer: a multicenter, retrospective study. Ann Surg [Internet]. 2021;274. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/annalsofsurgery/Fulltext/2021/12000/Development_and_Validation_of_a_Deep_Learning_CT.415.aspx.
Xu D, Liu R, Xu H, Zhang Z, Li W, Zhang Y, et al. Adoption of two-dimensional ultrasound gastrointestinal filling contrast on artificial intelligence algorithm in clinical diagnosis of gastric cancer. Comput Math Methods Med. Hindawi Limited; 2022;2022.
Chen T, Li X, Mao Q, Wang Y, Li H, Wang C, et al. An artificial intelligence method to assess the tumor microenvironment with treatment outcomes for gastric cancer patients after gastrectomy. J Transl Med. BioMed Central Ltd; 2022;20.
Cheong JH, Wang SC, Park S, Porembka MR, Christie AL, Kim H, et al. Development and validation of a prognostic and predictive 32-gene signature for gastric cancer. Nat Commun. Nature Research; 2022;13.
Cui Y, Zhang J, Li Z, Wei K, Lei Y, Ren J, et al. A CT-based deep learning radiomics nomogram for predicting the response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced gastric cancer: a multicenter cohort study. eClinicalMedicine [Internet]. Elsevier; 2022;46. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101348.
Tang X, Wu X, Guo T, Jia F, Hu Y, Xing X, et al. Focal adhesion-related signatures predict the treatment efficacy of chemotherapy and prognosis in patients with gastric cancer. Front Oncol. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2022;12.
Terranova N, French J, Dai H, Wiens M, Khandelwal A, Ruiz-Garcia A, et al. Pharmacometric modeling and machine learning analyses of prognostic and predictive factors in the JAVELIN Gastric 100 phase III trial of avelumab. CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol. American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics; 2022;11:333–47.
Sundar R, Barr Kumarakulasinghe N, Huak Chan Y, Yoshida K, Yoshikawa T, Miyagi Y, et al. Machine-learning model derived gene signature predictive of paclitaxel survival benefit in gastric cancer: results from the randomised phase III SAMIT trial. Gut BMJ Publishing Group. 2022;71:676–85.
Kong JH, Ha D, Lee J, Kim I, Park M, Im SH, et al. Network-based machine learning approach to predict immunotherapy response in cancer patients. Nat Commun. Nature Res. 2022;13.
korhani Kangi A, Bahrampour A. Predicting the survival of gastric cancer patients using artificial and Bayesian neural networks. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev [Internet]. 2018;19:487–90. Available from: https://journal.waocp.org/article_55156.html.
Oh SE, Seo SW, Choi M-G, Sohn TS, Bae JM, Kim S. Prediction of overall survival and novel classification of patients with gastric cancer using the survival recurrent network. Ann Surg Oncol [Internet]. 2018;25:1153–9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-018-6343-7.
Que SJ, Chen QY, Zhong Q, Liu ZY, Wang J Bin, Lin JX, et al. Application of preoperative artificial neural network based on blood biomarkers and clinicopathological parameters for predicting long-term survival of patients with gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. Baishideng Publishing Group Co; 2019;25:6451–64.
Li J, Dong D, Fang M, Wang R, Tian J, Li H, et al. Dual-energy CT–based deep learning radiomics can improve lymph node metastasis risk prediction for gastric cancer. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2020;30:2324–33. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06621-x.
Wang S, Feng C, Dong D, Li H, Zhou J, Ye Y, et al. Preoperative computed tomography-guided disease-free survival prediction in gastric cancer: a multicenter radiomics study. Med Phys [Internet]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2020;47:4862–71. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14350.
Dong D, Fang M-J, Tang L, Shan X-H, Gao J-B, Giganti F, et al. Deep learning radiomic nomogram can predict the number of lymph node metastasis in locally advanced gastric cancer: an international multicenter study. Ann Oncol [Internet]. Elsevier; 2020;31:912–20. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.003.
Li Z, Wu X, Gao X, Shan F, Ying X, Zhang Y, et al. Development and validation of an artificial neural network prognostic model after gastrectomy for gastric carcinoma: an international multicenter cohort study. Cancer Med [Internet]. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd; 2020;9:6205–15. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.3245.
Wang X, Li C, Fang M, Zhang L, Zhong L, Dong D, et al. Integrating No.3 lymph nodes and primary tumor radiomics to predict lymph node metastasis in T1–2 gastric cancer. BMC Med Imaging [Internet]. 2021;21:58. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-021-00587-3.
Liu Q, Li J, Xin B, Sun Y, Feng D, Fulham MJ, et al. 18F-FDG PET/CT radiomics for preoperative prediction of lymph node metastases and nodal staging in gastric cancer. Front Oncol. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2021;11.
Xu J, Wen J, Li S, Shen X, You T, Huang Y, et al. Immune-related nine-microRNA signature for predicting the prognosis of gastric cancer. Front Genet. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2021;12.
Kim J, Han SH, Kim H Il. Detection of sarcopenic obesity and prediction of long-term survival in patients with gastric cancer using preoperative computed tomography and machine learning. J Surg Oncol. John Wiley and Sons Inc; 2021;124:1347–55.
Hao D, Li Q, Feng Q-X, Qi L, Liu X-S, Arefan D, et al. Identifying prognostic markers from clinical, radiomics, and deep learning imaging features for gastric cancer survival prediction. Front Oncol [Internet]. 2022;11. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2021.725889.
Zhou CM, Wang Y, Ye HT, Yan S, Ji M, Liu P, et al. Machine learning predicts lymph node metastasis of poorly differentiated-type intramucosal gastric cancer. Sci Rep. Nature Res. 2021;11.
Zhou C, Hu J, Wang Y, Ji MH, Tong J, Yang JJ, et al. A machine learning-based predictor for the identification of the recurrence of patients with gastric cancer after operation. Sci Rep. Nature Res. 2021;11.
Rahman SA, Maynard N, Trudgill N, Crosby T, Park M, Wahedally H, et al. Prediction of long-term survival after gastrectomy using random survival forests. Br J Surg NLM (Medline). 2021;108:1341–50.
Wang Y, Wang YG, Hu C, Li M, Fan Y, Otter N, et al. Cell graph neural networks enable the precise prediction of patient survival in gastric cancer. npj Precis Oncol. Nature Res. 2022;6.
Zhang C, Xie M, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Feng C, Wu Z, et al. Determination of survival of gastric cancer patients with distant lymph node metastasis using prealbumin level and prothrombin time: contour plots based on random survival forest algorithm on high-dimensionality clinical and laboratory datasets. J Gastric Cancer. Korean Gastric Cancer Association; 2022;22:120–34.
Li XY, Wang SL, Chen DH, Liu H, You JX, Su LX, et al. Construction and validation of a m7G-related gene-based prognostic model for gastric cancer. Front Oncol. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2022;12.
Zhang A, Zhao H, Li F, Liang P, Gao J, Cheng M. Computed tomography-based deep-learning prediction of lymph node metastasis risk in locally advanced gastric cancer. Front Oncol [Internet]. 2022;12. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fonc.2022.969707.
Wei X, Yan XJ, Guo YY, Zhang J, Wang GR, Fayyaz A, et al. Machine learning-based gray-level co-occurrence matrix signature for predicting lymph node metastasis in undifferentiated-type early gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. Baishideng Publishing Group Inc; 2022;28:5338–50.
Ko Y, Shin H, Shin J, Hur H, Huh J, Park T, et al. Artificial intelligence mortality prediction model for gastric cancer surgery based on body morphometry, nutritional, and surgical information: feasibility study. Appl Sci. MDPI; 2022;12.
Jung JO, Crnovrsanin N, Wirsik NM, Nienhüser H, Peters L, Popp F, et al. Machine learning for optimized individual survival prediction in resectable upper gastrointestinal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH; 2022;
Zhou L, Niu Z, Wang Y, Zheng Y, Zhu Y, Wang C, et al. Senescence as a dictator of patient outcomes and therapeutic efficacies in human gastric cancer. Cell Death Discov. Springer Nature; 2022;8.
Tian HK, Ning ZK, Zong Z, Liu J, Hu CG, Ying HQ, et al. Application of machine learning algorithms to predict lymph node metastasis in early gastric cancer. Front Med. Frontiers Media S.A.; 2022;8.
Jiang Y, Zhang Z, Yuan Q, Wang W, Wang H, Li T, et al. Predicting peritoneal recurrence and disease-free survival from CT images in gastric cancer with multitask deep learning: a retrospective study. Lancet Digit Heal Elsevier Ltd. 2022;4:e340–50.
Na J-E, Lee Y-C, Kim T-J, Lee H, Won H-H, Min Y-W, et al. Machine learning model to stratify the risk of lymph node metastasis for early gastric cancer: a single-center cohort study. Cancers (Basel) [Internet]. 2022;14. Available from: https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/5/1121.
Sohn BH, Hwang J-E, Jang H-J, Lee H-S, Oh SC, Shim J-J, et al. Clinical significance of four molecular subtypes of gastric cancer identified by The Cancer Genome Atlas Project. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2017;23:4441–9. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-16-2211.
Rawla P, Barsouk A. Epidemiology of gastric cancer: global trends, risk factors and prevention. Prz. Gastroenterol. Termedia Publishing House Ltd.; 2019. p. 26–38.
Hosmer D, Lemeshow S. Applied Logistic Regression. 2nd ed. New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; 2000.
Chicco D, Jurman G. The advantages of the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) over F1 score and accuracy in binary classification evaluation. BMC Genomics [Internet]. 2020;21:6. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12864-019-6413-7.
Ragunath K. Artificial intelligence in gastrointestinal endoscopy: how intelligent can it get? Lancet Oncol [Internet]. Elsevier; 2019;20:1616–7. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30677-1.
Tampu IE, Eklund A, Haj-Hosseini N. Inflation of test accuracy due to data leakage in deep learning-based classification of OCT images. Sci Data [Internet]. 2022;9:580. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41597-022-01618-6.
Tan RR, Aviso KB, Janairo JIB, Promentilla MAB. A hyperbox classifier model for identifying secure carbon dioxide reservoirs. J Clean Prod. 2020;272.
Janairo JIB, Aviso KB, Promentilla MAB, Tan RR. Enhanced hyperbox classifier model for nanomaterial discovery. Ai. 2020;1:299–311.
Molnar C. Interpretable machine learning [internet]. 2nd ed. 2022 [cited 2023 May 27]. Available from: https://christophm.github.io/interpretable-ml-book.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Both authors conceptualized and wrote the paper. Both authors contributed equally to the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Animal and Human Studies
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sy-Janairo, M.L.L., Janairo, J.I.B. Non-endoscopic Applications of Machine Learning in Gastric Cancer: A Systematic Review. J Gastrointest Canc 55, 47–64 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-023-00960-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12029-023-00960-1