Abstract
Background
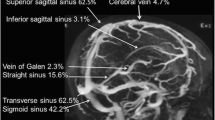
Severe cerebral venous-sinus thrombosis (CVT) is a rare disease, and its clinical course, imaging correlates, as well as long-term prognosis have not yet been investigated systematically.
Methods
Multicenter retrospective study. Inclusion criteria were CVT, Glasgow coma scale ≤9, and treatment in the intensive care unit. Primary outcome was death or dependency, assessed by a modified Rankin Score (mRS) >2 at last follow-up.
Results
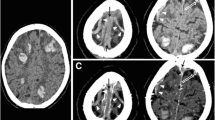
114 patients were included. At last follow-up (median 2.5 years), 38 patients (33.3 %) showed no or minor residual symptoms (mRS = 0 or 1), 12 (10.5 %) had a mild (mRS = 2), 13 (11.4 %) a moderate (mRS = 3), 12 (10.5 %) a severe disability (mRS = 4 or 5), and 39 (34.2 %) had died. In bivariate analysis, predictors of poor outcome were any signs of mass effect on imaging, clinical deterioration after admission, and age. In contrast, clinical symptoms on admission and parenchymal lesions per se, such as edema, infarction, or hemorrhage were not predictive. Multivariate predictors of poor outcome were an increase in National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale ≥3 after admission [odds ratio (OR) 6.7], bilateral motor signs in the further course (OR 9.2), and midline shift (OR 5.1).
Conclusion
The outcome of severe CVT is almost equally divided between severe impairment or death and survival with no or only mild handicap. Specifically, space-occupying mass effect and associated neurologic deterioration seem to determine a poor outcome. Therefore, early detection and treatment of mass effect should be the focus of critical care.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saposnik G, Barinagarrementeria F, Brown RD Jr, American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, et al. Diagnosis and management of cerebral venous thrombosis: a statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2011;42:1158–92.
Bousser MG, Ferro JM. Cerebral venous thrombosis: an update. Lancet Neurol. 2007;6:162–70.
Ferro JM, Canhao P, Stam J, Bousser MG, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT Investigators. Prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT). Stroke. 2004;35:664–70.
Ferro JM, Lopes MG, Rosas MJ, Ferro MA, Fontes J, Cerebral Venous Thrombosis Portuguese Collaborative Study Group (VENOPORT). Long-term prognosis of cerebral vein and dural sinus thrombosis: results of the VENOPORT Study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2002;13:272–8.
Wasay M, Bakshi R, Bobustuc G, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis: analysis of a multicenter cohort from the United States. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2008;17:49–54.
Khealani BA, Wasay M, Saadah M, et al. Cerebral venous thrombosis: a descriptive multicenter study of patients in Pakistan and Middle East. Stroke. 2008;39:2707–11.
Stolz E, Rahimi A, Gerriets T, Kraus J, Kaps M. Cerebral venous thrombosis: an all or nothing disease? Prognostic factors and long-term outcome. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2005;10:99–107.
Guo XB, Guan S, Fan Y, Song LJ. Local thrombolysis for severe cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012;33:1187–90.
Siddiqui F, Dandapat S, Banerjee C, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in cerebral venous thrombosis: systematic review of 185 cases. Stroke. 2015;46:1263–8.
Haghighi AB, Mahmoodi M, Edgell RC, et al. Mechanical thrombectomy for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: a comprehensive literature review. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2013;20:507–15.
Zhang A, Collinson RL, Hurst RW, Weigele JB. Rheolytic thrombectomy for cerebral sinus thrombosis. Neurocrit Care. 2008;9:17–26.
Ferro JM, Crassard I, Coutinho JM, Second International Study on Cerebral Vein and Dural Sinus Thrombosis (ISCVT 2) Investigators, et al. Decompressive surgery in cerebrovenous thrombosis: a multicenter registry and a systematic review of individual patient data. Stroke. 2011;42:2825–31.
Coutinho JM, Majoie CB, Coert BA, Stam J. Decompressive hemicraniectomy in cerebral sinus thrombosis: consecutive case series and review of the literature. Stroke. 2009;40:2233–5.
Zuurbier SM, Coutinho JM, Majoie CB, Coert BA, van den Munckhof P, Stam J. Decompressive hemicraniectomy in severe cerebral venous thrombosis: a prospective case series. J Neurol. 2012;259:1099–105.
Théaudin M, Crassard I, Bresson D, et al. Should decompressive surgery be performed in malignant cerebral venous thrombosis?: a series of 12 patients. Stroke. 2010;41:727–31.
Aaron S, Alexander M, Moorthy RK, et al. Decompressive craniectomy in cerebral venous thrombosis: a single centre experience. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013;84:995–1000.
Dohmen C, Galldiks N, Moeller-Hartmann W, Fink GR, Timmermann L. Sequential escalation of therapy in “malignant” cerebral venous and sinus thrombosis. Neurocrit Care. 2010;12:98–102.
Canhão P, Ferro JM, Lindgren AG, Bousser MG, Stam J, Barinagarrementeria F, ISCVT Investigators. Causes and predictors of death in cerebral venous thrombosis. Stroke. 2005;36:1720–5.
Pfefferkorn T, Crassard I, Linn J, Dichgans M, Boukobza M, Bousser M. Clinical features, course and outcome in deep cerebral venous system thrombosis: an analysis of 32 cases. J Neurol. 2009;256:1839–45.
Coutinho JM, Ferro JM, Zuurbier SM, et al. Thrombolysis or anticoagulation for cerebral venous thrombosis: rationale and design of the TO-ACT trial. Int J Stroke. 2013;8:135–40.
Funding
There were no sources of funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Statement
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from individual participants if they were contacted in order to obtain follow up information especially for this study. For retrospective data acquisition formal consent is not required.
Additional information
On behalf of IGNITE (Initiative of German Neurointensive Trial Engagement)
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kowoll, C.M., Kaminski, J., Weiß, V. et al. Severe Cerebral Venous and Sinus Thrombosis: Clinical Course, Imaging Correlates, and Prognosis. Neurocrit Care 25, 392–399 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-016-0256-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-016-0256-8