Abstract
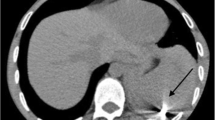
Sharp force injuries are uncommon in routine forensic practice. While the majority of these cases are homicides or suicides, a significant minority of accidental deaths means that a careful investigation of the circumstances of the death is necessary. We present the case of a young man who presented with stab and cut injuries due to a duralumin rod embedded in his chest. Examination of the body revealed that death was due to penetration of the thoracic aorta by a duralumin rod. Careful investigation of the circumstances surrounding the death was able to confim a case of accidental death due to falling from a ladder onto tomato seedlings that were supported by duralumin rods.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vassalini M, Verzeletti A, De Ferrari F. Sharp force injury fatalities: a retrospective study (1982–2012) in Brescia (Italy). J Forensic Sci. 2014;59:1568–74.
Karger B, Niemeyer J, Brinkmann B. Suicides by sharp force: typical and atypical features. Int J Legal Med. 2000;113:259–62.
Prahlow JA, Ross KF, Lene WJW, Kirby DB. Accidental sharp force injury fatalities. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2001;22:358.
Hirt M, Karger B. Fatal brain injury caused by the free-flying blade of a knife – case report and evaluation of the unusual weapon. Int J Legal Med. 1999;112:313–4.
Karger B, Rothschild M, Pfeiffer H. Accidental sharp force fatalities – beware of architectural glass, not knives. Forensic Sci Int. 2001;123:135–9.
Oparah SS, Mandal AK. Penetrating stab wounds of the chest: experience with 200 consecutive cases. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 1976;16:868–72.
Mazzolo GM, Desinan L. Sharp force fatalities: suicide, homicide or accident? A series of 21 cases. Forensic Sci Int. 2005;147:S33–5.
Schmidt U, Pollak S. Sharp force injuries in clinical forensic medicine—findings in victims and perpetrators. Forensic Sci Int. 2006;159:113–8.
Burke MP, Baber Y, Cheung Z., et al. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 2018; https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-9982-x.
Karlsson T. Homicidal and suicidal sharp force fatalities in Stockholm, Sweden.: orientation of entrance wounds in stabs gives information in the classification. Forensic Sci Int. 1998;93:21–32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marecová, K., Uvíra, M., Dokoupil, M. et al. Stab wounds of the chest caused by penetration of duralumin rods. Forensic Sci Med Pathol 14, 558–560 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-0004-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12024-018-0004-9