Abstract
Purpose
Acromegaly is considered an important cause of secondary osteoporosis. However, studies on bone mineral density (BMD) have yielded conflicting results and there are few studies that evaluate an accurate imaging method for early diagnosis of osteoporosis in these patients. The objective of this study was to assess whether entropy and uniformity on computed tomography (CT) scans are useful parameters for optimization of assessment of bone fragility in patients with acromegaly.
Methods
We included 34 patients and 36 controls matched for age and sex in a cross-sectional study. Patients and controls underwent CT scan of the lumbosacral spine, dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) and blood tests. A software was developed to calculate the entropy and uniformity by a region of interest (ROI) of the trabecular bone of the first lumbar vertebra (L1).
Results
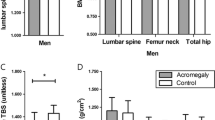
The acromegalic group presented higher mean bone entropy (6.87 ± 0.98 vs. 6.03 ± 1.68, p = 0.013) and lower mean bone uniformity (0.035 ± 0.704 vs. 0.113 ± 0.205, p = 0.035) than control group. Analyzing only acromegalics, mean bone entropy was higher and bone uniformity was lower in patients with hypogonadism than patients without hypogonadism (7.28 ± 0.36 vs. 6.74 ± 1.08, p = 0.038 and 0.008 ± 0.002 vs. 0.043 ± 0.079, p = 0.031) respectively. Patients with acromegaly presented higher BMD and Z-score in the femoral neck than control group (1.156 ± 0.108 vs. 0.925 ± 0.326 g/cm2, p = 0.043 and 0.6 ± 0.6 vs. −0.05 ± 0.8, p = 0.041, respectively). Entropy was negatively correlated with T-score of the lumbar spine (rp = −0.357, p = 0.033) in control group and uniformity was positively correlated with T-score of the lumbar spine, neck, and total hip, respectively (rp = 0.371, p = 0.031; rp = 0.348, p = 0.043 and rp = 0.341, p = 0.049) in acromegalic group.
Conclusions
The study identified that entropy and uniformity are a relevant parameters data in bone fragility assessment in acromegalic patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
I.M. Holdaway, C. Rajasoorya, Epidemiology of acromegaly. Pituitary 2, 29–34 (1999)
A. Giustina, G. Mazziotti, E. Canalis, Growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, and the skeleton. Endocr. Rev. 29, 535–559 (2008)
S. Ezzat, S. Melmed, D. Endres, D.R. Eyre, F.R. Singer, Biochemical assessment of bone formation and resorption in acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 76, 1452–1457 (1993)
P.G. Lacativa, M.L. de Farias, Office practice of osteoporosis evaluation. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 50, 674–684 (2006)
E.M. Lewiecki, A.J. Laster, Clinical review: clinical applications of vertebral fracture assessment by dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 4215–4222 (2006)
M. Bolanowski, J. Daroszewski, M. Medras, B. Zadrozna-Sliwka, Bone mineral density and turnover in patients with acromegaly in relation to sex, disease activity, and gonadal function. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 24, 72–78 (2006)
M.J. Wassenaar, N.R. Biermasz, N.A. Hamdy, M.C. Zillikens, J.B. van Meurs, F. Rivadeneira, A. Hofman, A.G. Uitterlinden, M.P. Stokkel, F. Roelfsema, M. Kloppenburg, H.M. Kroon, J.A. Romijn, A.M. Pereira, High prevalence of vertebral fractures despite normal bone mineral density in patients with long-term controlled acromegaly. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 164, 475–83 (2011)
J.T. Schousboe, T. Vokes, S.B. Broy, L. Ferrar, F. McKiernan, C. Roux, N. Binkley, Vertebral fracture assessment: the 2007 ISCD official positions. J. Clin. Densitom. Off. J. Int. Soc. Clin. Densitom. 11, 92–108 (2008)
P.J. Pickhardt, B.D. Pooler, T. Lauder, A.M. del Rio, R.J. Bruce, N. Binkley, Opportunistic screening for osteoporosis using abdominal computed tomography scans obtained for other indications. Ann. Intern. Med. 158, 588–595 (2013)
C. Eller-Vainicher, A. Falchetti, L. Gennari, E. Cairoli, F. Bertoldo, F. Vescini, A. Scillitani, L. Chiodini, Evaluation of bone fragility in endocrine disorders. Imaging Endocr. Osteoporos. 180, 213–232 (2019)
E.T. Jaynes, Information theory and statistical mechanics. Phys. Rev. J. Arch. 106, 620–630 (1957)
S. Melmed, F.F. Casanueva, A. Klibanski, M.D. Bronstein, P. Chanson, S.W. Lamberts, C.J. Strasburger, J.A. Wass, A. Giustina, A consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly complications. Pituitary 16, 294–302 (2013)
J. Halupczok-Żyła, A. Jawiarczyk-Przybyłowska, M. Bolanowski, Patients with active acromegaly are at high risk of 25(OH) D deficiency. Front. Endocrinol. 2, 89–95 (2015)
J.T. Schousboe, J.A. Shepherd, J.P. Bilezikian, S. Baim, Executive summary of the 2013 International Society for Clinical Densitometry Position Development Conference on bone densitometry. J. Clin. Densitom. 16, 455–466 (2013)
B. Ganeshan, K.A. Miles, R.C. Young, C.R. Chatwin, Hepatic entropy and uniformity: additional parameters that can potentially increase the effectiveness of contrast enhancement during abdominal CT. Clin. Radiol. 62, 761–768 (2007)
R. M. Gray, Entropy and Information Theory. (Springer, 2011)
J. E. Shore, R. M. Gray, Minimum cross-entropy pattern classification and cluster analysis. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 1, 11–17 (1982)
T. Jalava, S. Sarna, L. Pylkkanen, B. Mawer, J.A. Kanis, P. Selby, M. Davies, J. Adams, R.M. Francis, J. Robinson, E. McCloskey, Association between vertebral fracture and increased mortality in osteoporotic patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 18, 1254–1260 (2003)
K. Fujimoto, T. Tonan, S. Azuma, M. Kage, T. Nakashima, J. Naofumi, H. Koji, K. Takumi, M. Sata, A. Qayyum, Evaluation of the mean and entropy of apparent diffusion coefficient values in chronic hepatitis C: correlation with pathologic fibrosis stage and inflammatory activity grade. Radiology 258, 739–748 (2011)
M. Kolancinski, M. Kozakiewicz, A. Materka, Textual entropy as a potential feature for quantitative assessment of a jaw bone healing process. Arch. Med. Sci. 11, 78–84 (2015)
L. Dercle, S. Ammari, M. Bateson, Limits of radiomic-based entropy as a surrogate of tumor heterogeneity: ROI-area, acquisition protocol and tissue site exert substantial influence. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–10 (2017)
G.P. Lesse, W.D. Fraser, R. Farquharson, L. Hipkin, J.P. Vora, Gonadal status is an important determinant of bone density in acromegaly. Clin. Endocrinol. 48, 59–65 (1998)
S. Bonadonna, G. Mazziotti, M. Nuzzo, A. Bianchi, A. Fusco, L. De Marinis, A. Giustina, Increased prevalence of radiological spinal deformities in active acromegaly: a cross-sectional study in postmenopausal women. J. Bone Miner. Res. 20, 1837–1844 (2005)
G. Mazziotti, A. Bianchi, S. Bonadonna, V. Cimino, I. Patelli, A. Fusco, A. Pontecorvi, L. De Marinis, A. Giustina, Prevalence of vertebral fractures in men with acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 93, 4649–4655 (2008)
A. Scillitani, C. Battista, I. Chiodini, V. Carnevale, S. Fusilli, E. Ciccarelli, M. Terzolo, G. Oppizzi, M. Arosio, M. Gasperi, G. Arnaldi, A. Colao, R. Baldelli, M.R. Ghiggi, D. Gaia, C. Di Somma, V. Trischitta, A. Liuzzi, Bone mineral density in acromegaly: the effect of gender, disease activity and gonadal status. Clin. Endocrinol. 58, 725–731 (2003)
W. Zgliczynski, M. Kochman, W. Misiorowski, P. Zdunowski, In acromegaly, increased bone mineral density (BMD) is determined by GH-excess, gonadal function and gender. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 28, 621–628 (2007)
M. Madeira, V.L. Neto, F.P.P. Neto, I.C.B.L. Lima, L.M.C.M. Mendonça, M.R. Gadelha, M.L.F. Farias, Acromegaly has a negative influence on trabecular bone, but not on cortical bone, as assessed by high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 98, 1734–1741 (2013)
G. Mazziotti, M. Gola, M. Bianchi, T. Porcelli, A. Giampietro, V. Cimino, M. Doga, C. Gazzaruso, L. Marinis, A. Giustina, Influence of diabetes mellitus on vertebral fractures in men with acromegaly. Endocrine 40, 102–108 (2011)
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful for the help of Dra. Jane Lynn Garrison Dytz and Edison Dytz who contributed significantly to this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed consents
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Health Sciences of the University of Brasilia (approval number 1.178.769) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Castro Dytz, O., de Azevedo Berger, P., Dytz, M.G. et al. Entropy and uniformity as additional parameters to optimize the effectiveness of bone CT in the evaluation of acromegalic patients. Endocrine 69, 368–376 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02358-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-020-02358-6