Abstract
Purpose
Risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) is increased in Graves’ disease (GD). CVD is predicted by increased pulse wave velocity (PWV) and blood pressure (BP). GD and these risk factors are all associated with lower levels of vitamin D. We aimed to assess the effect of supplemental vitamin D on PWV and BP in GD.
Methods
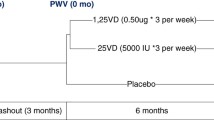
In a double-blinded trial, newly diagnosed GD patients were randomized to vitamin D3 70 µg/day (n = 44) or placebo (n = 42) as add-on to anti-thyroid medication. At baseline, 3 and 9 months PWV, BP and wave analysis were performed in office and 24 h setting. Between-group differences in change at 9 months were analyzed using linear mixed modelling. In subanalysis, effect of intervention in regard to baseline vitamin D insufficiency (25(OH)D < 50 nmol/L) was investigated. (The DAGMAR study, clinicaltrials.gov ID NCT02384668).
Results
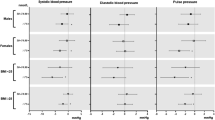
PWV was unaffected by intervention in main analysis. However in the subanalysis, comparing the response to intervention in the vitamin D insufficient (n = 28) and the vitamin D replete patients, supplemental vitamin D induced a significant decrease in office PWV of 1.2 (95% CI: −2.3; −0.1) m/s compared to placebo. Of notice, baseline PWV was non-significantly higher among the vitamin D insufficient as compared to the replete participants. In response to vitamin D, office central systolic BP (−3.9 (95% CI: −7.5; −0.3) and brachial mean BP (−3.3 (95% CI: −6.5; −0.3) declined whereas 24 h measurements were unaffected.
Conclusions
High-dose vitamin D supplementation did not affect PWV. We observed significant reduction in office but not 24 h BP. Subanalysis showed a clinically relevant PWV reduction among vitamin D insufficient participants, although regression towards the mean might contribute to findings. Further studies on supplemental vitamin D in GD should focus on patients with vitamin D insufficiency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Franklyn, K. Boelaert, Thyrotoxicosis. Lancet 379, 1155–1166 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60782-4
R.A. Nordyke, F.I. Gilbert, A.S.M. Harada, Graves’ disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 148, 626 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.1988.00380030132023
F. Brandt, M. Thvilum, D. Almind, K. Christensen, A. Green, L. Hegedüs, T.H. Brix, Graves’ disease and toxic nodular goiter are both associated with increased mortality but differ with respect to the cause of death: a Danish population-based register study. Thyroid 23, 408–413 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2012.0500
O.M. Dekkers, E. Horváth-Puhó, S.C. Cannegieter, J.P. Vandenbroucke, H.T. Sørensen, J.O.L. Jørgensen, Acute cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in patients with hyperthyroidism: a population-based cohort study. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 176, 1–9 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1530/EJE-16-0576
P. Giesecke, M. Rosenqvist, V. Frykman, L. Friberg, G. Wallin, J. Höijer, S. Lönn, O. Törring, Increased cardiovascular mortality and morbidity in patients treated for toxic nodular goiter compared to Graves’ disease and Nontoxic Goiter. Thyroid 27, 878–885 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2017.0029
P. Hall, G. Lundell, L.E. Holm, Mortality in patients treated for hyperthyroidism with iodine-131. Acta Endocrinol. 128, 230–234 (1993)
S. Lewington, R. Clarke, N. Qizilbash, R. Peto, R. Collins, Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: A meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 360, 1903–1913 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(02)11911-8
S. Laurent, P. Boutouyrie, R. Asmar, I. Gautier, B. Laloux, L. Guize, P. Ducimetiere, A: Benetos, Aortic stiffness Is an independent predictor of all-Cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 37, 1236–1241 (2001)
R. Zhang, B. Li, X. Gao, R. Tian, Y. Pan, Y. Jiang, H. Gu, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, G. Liu, Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and the risk of cardiovascular disease: dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 105, 810–819 (2017). https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.116.140392
I. Al Mheid, R. Patel, J. Murrow, A. Morris, A. Rahman, L. Fike, N. Kavtaradze, I. Uphoff, C. Hooper, V. Tangpricha, R.W. Alexander, K. Brigham, A.A. Quyyumi, Vitamin D status is associated with arterial stiffness and vascular dysfunction in healthy humans. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 58, 186–192 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2011.02.051
K.S. Vimaleswaran, A. Cavadino, D.J. Berry, C. Power, E. Hyppönen, R. Jorde, G. Grimnes, A.K. Dieff enbach, B. Schöttker, K.U. Saum, H. Brenner, C. Lu, M.R. Järvelin, I. Tzoulaki, H.J.L. Heerspink, I.M. Nolte, H. Snieder, P.J. van der Most, R.P. Stolk, C.A. Hartman, R.A. de Boer, P. van der Harst, G. Navis, M.H. de Borst, E. Tikkanen, J. Eriksson, M. Lorentzon, D. Mellström, C. Ohlsson, A. Wong, R. Hardy, D. Kuh, J.A. Cooper, J. Acharya, S.E. Humphries, A.D. Hingorani, M. Kumari, M. Kivimaki, M. Mangino, T.D. Spector, K.A. Jablonski, D.K. Houston, S.B. Kritchevsky, K.K. Lohman, T.S. Ahluwalia, T.I.A. Sørensen, D. Pasko, T.M. Frayling, L. Zgaga, H. Campbell, E. Theodoratou, R.M. Fraser, J.F. Wilson, I. Rudan, J.F. Price, S. McLachlan, V. Vitart, P. Navarro, J.E. Huffman, C. Hayward, A.F. Wright, E. Thiering, C.M.T. Tiesler, J. Heinrich, M.I. McCarthy, E. Ingelsson, C. Cooper, N. Arden, J. Dupuis, K.H. Herzig, S. Sebert, A.C. Alves, A. Pouta, J. Laitinen, M.E. Kleber, W. März, K. Jameson, C. Osmond, O. Raitakari, S. Ripatti, J. Lahti, J.G. Eriksson, B.W. Penninx, L.K. Billings, J.C. Florez, L. Rejnmark, B.L. Langdahl, L. Paternoster, D.G. Hernandez, L. Byberg, K. Michaëlsson, E. Hagström, H. Melhus, O. Ljunggren, L. Lind, A. Jula, O. Polasek, V. Salomaa, M. Karlsson, S. Bandinelli, T. Lehtimäki, T.J. Wang, S. Pilz, J.C. Whittaker, E. Hyppönen, Association of vitamin D status with arterial blood pressure and hypertension risk: a Mendelian randomisation study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2, 719–729 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-8587(14)70113-5
J. Wang, S. Lv, G. Chen, C. Gao, J. He, H. Zhong, Y. Xu, Meta-analysis of the association between vitamin D and autoimmune thyroid disease. Nutrients 7, 2485–2498 (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu7042485
S. Malmstroem, D. Grove-Laugesen, A.L. Riis, B. Johannessen Bruun, E. Ebbehoj, K.W. Hansen, T. Watt, L. Rejnmark, Muscle performance and postural stability are reduced in patients with newly diagnosed Graves’ disease. Thyroid. Jun 2019. Ahead of print. https://doi.org/10.1089/thy.2018.0318
Y. Dong, I.S. Stallmann-Jorgensen, N.K. Pollock, R.A. Harris, D. Keeton, Y. Huang, K. Li, R. Bassali, D.H. Guo, J. Thomas, G.L. Pierce, J. White, M.F. Holick, H. Zhu, A 16-week randomized clinical trial of 2000 international units daily vitamin D3supplementation in black youth: 25-hydroxyvitamin D, adiposity, and arterial stiffness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 4584–4591 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2010-0606
T. Larsen, F.H. Mose, J.N. Bech, A.B. Hansen, E.B. Pedersen, Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation during winter months in patients with hypertension: a Randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Am. J. Hypertens. 25, 1215–1222 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/ajh.2012.111
M.H. Hwang, J.K. Yoo, H.K. Kim, C.L. Hwang, K. Mackay, O. Hemstreet, W.W. Nichols, D.D. Christou, Validity and reliability of aortic pulse wave velocity and augmentation index determined by the new cuff-based SphygmoCor Xcel. J. Hum. Hypertens. 28, 475–481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/jhh.2013.144
J. Baulmann, U. Schillings, S. Rickert, S. Uen, R. Düsing, M. Illyes, A. Cziraki, G. Nickering, T. Mengden, A new oscillometric method for assessment of arterial stiffness: comparison with tonometric and piezo-electronic methods. J. Hypertens. 26, 523–528 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e3282f314f7
C. Vlachopoulos, K. Aznaouridis, C. Stefanadis, Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 55, 1318–1327 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JACC.2009.10.061
L. Wang, Y. Song, J.E. Manson, S. Pilz, W. März, K. Michaëlsson, A. Lundqvist, S.K. Jassal, E. Barrett-Connor, C. Zhang, C.B. Eaton, H.T. May, J.L. Anderson, H.D. Sesso, Circulating 25-hydroxy-vitamin D and risk of cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of prospective studies. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 5, 819–829 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCOUTCOMES.112.967604
H. Dobnig, S. Pilz, H. Scharnagl, W. Renner, U. Seelhorst, B. Wellnitz, J. Kinkeldei, B.O. Boehm, G. Weihrauch, W. Maerz, Independent association of low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D levels with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 168, 1340 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.168.12.1340
Y.C. Li, G. Qiao, M. Uskokovic, W. Xiang, W. Zheng, J. Kong, Vitamin D: a negative endocrine regulator of the renin–angiotensin system and blood pressure. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 89–90, 387–392 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.JSBMB.2004.03.004
J.R. Wu-Wong, M. Nakane, J. Ma, X. Ruan, P.E. Kroeger, VDR-mediated gene expression patterns in resting human coronary artery smooth muscle cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 100, 1395–1405 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21133
T. Aspelund, M.R. Grübler, A.V. Smith, E.F. Gudmundsson, M. Keppel, M.F. Cotch, T.B. Harris, R. Jorde, G. Grimnes, R. Joakimsen, H. Schirmer, T. Wilsgaard, E.B. Mathiesen, I. Njølstad, M.L. Løchen, W. März, M.E. Kleber, A. Tomaschitz, D. Grove-Laugesen, L. Rejnmark, K.M.A. Swart, I.A. Brouwer, P. Lips, N.M. van Schoor, C.T. Sempos, R.A. Durazo-Arvizu, Z. Škrabáková, K.G. Dowling, K.D. Cashman, M. Kiely, S. Pilz, V. Gudnason, G. Eiriksdottir, Effect of genetically low 25-hydroxyvitamin D on mortality risk: Mendelian randomization analysis in 3 large european cohorts. Nutrients 11, (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11010074
S. Afzal, P. Brøndum-Jacobsen, S.E. Bojesen, B.G. Nordestgaard, Genetically low vitamin D concentrations and increased mortality: Mendelian randomisation analysis in three large cohorts. BMJ 349, 1–12 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g6330
J.E. Manson, N.R. Cook, I.-M. Lee, W. Christen, S.S. Bassuk, S. Mora, H. Gibson, D. Gordon, T. Copeland, D. D’Agostino, G. Friedenberg, C. Ridge, V. Bubes, E.L. Giovannucci, W.C. Willett, J.E. Buring, Vitamin D supplements and prevention of cancer and cardiovascular disease. N. Engl. J. Med. NEJMoa 1809944 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1809944
R. Scragg, A.W. Stewart, D. Waayer, C.M.M. Lawes, L. Toop, J. Sluyter, J. Murphy, K.-T. Khaw, C.A. Camargo, Effect of monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation on cardiovascular disease in the vitamin D assessment study. JAMA Cardiol. 2, 608 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamacardio.2017.0175
S.H. Wu, S.C. Ho, L. Zhong, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure. South. Med. J. 103, 729–737 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181e6d389
M.D. Witham, M.A. Nadir, A.D. Struthers, Effect of vitamin D on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Hypertens. 27, 1948–1954 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832f075b
L. Shu, K. Huang, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure parameters in patients with vitamin D deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 12, 488–496 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2018.04.009
L.A. Beveridge, A.D. Struthers, F. Khan, R. Jorde, R. Scragg, H.M. Macdonald, J.A. Alvarez, R.S. Boxer, A. Dalbeni, A.D. Gepner, N.M. Isbel, T. Larsen, J. Nagpal, W.G. Petchey, H. Stricker, F. Strobel, V. Tangpricha, L. Toxqui, M.P. Vaquero, L. Wamberg, A. Zittermann, M.D. Witham, D-PRESSURE Collaboration, for the D.-P., Effect of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure: a systematic review and meta-analysis incorporating individual patient data. JAMA Intern. Med. 175, 745–754 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2015.0237
D. Qi, X. Nie, J. Cai, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on hypertension in non-CKD populations: asystemic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Cardiol. 227, 177–186 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.11.040
S.K. Kunutsor, S. Burgess, P.B. Munroe, H. Khan, META-ANALYSIS Vitamin D and high blood pressure: causal association or epiphenomenon? Eur. J. Epidemiol. 29, 1–14 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10654-013-9874-z
A.G. Pittas, M. Chung, T. Trikalinos, J. Mitri, M. Brendel, K. Patel, A.H. Lichtenstein, J. Lau, E.M. Balk, Vitamin D and cardiometabolic outcomes: a systematic review. Ann. Intern. Med. 152, 307–314 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1059/0003-4819-152-5-201003020-00009
M. Golzarand, S. Shab-Bidar, G. Koochakpoor, J.,R. Speakman, K. Djafarian, Effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on blood pressure in adults: an updated meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 26, 663–673 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/J.NUMECD.2016.04.011
A. Manousopoulou, N.M. Al-Daghri, S.D. Garbis, G.P. Chrousos, Vitamin D and cardiovascular risk among adults with obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 45, 1113–1126 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.12510
J.D. Sluyter, C.A. Camargo, A.W. Stewart, D. Waayer, C.M.M. Lawes, L. Toop, K.T. Khaw, S.A.M.G. Thom, B. Hametner, S. Wassertheurer, K.H. Parker, A.D. Hughes, R. Scragg, Effect of monthly, high-dose, long-term vitamin D supplementation on central blood pressure parameters: a randomized controlled trial substudy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 6, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.006802
T. Hansen, J. Jeppesen, S. Rasmussen, H. Ibsen, C. Torppedersen, Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring and risk of cardiovascular disease: a population based study. Am. J. Hypertens. 19, 243–250 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjhyper.2005.09.018
L.A. Beveridge, F. Khan, A.D. Struthers, J. Armitage, I. Barchetta, I. Bressendorff, M.G. Cavallo, R. Clarke, R. Dalan, G. Dreyer, A. D. Gepner, N.G. Forouhi, R.A. Harris, G.A. Hitman, T. Larsen, R. Khadgawat, P. Marckmann, F.H. Mose, S. Pilz, A. Scholze, M. Shargorodsky, S.I. Sokol, H. Stricker, C. Zoccali, M.D. Witham, Effect of vitamin D supplementation on markers of vascular function: a systematic review and individual participant meta‐analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 7, (2018). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.008273
V. Kumar, A. Kumar Yadav, A. Lal, V. Kumar, M. Singhal, L. Billot, K. Lal Gupta, D. Banerjee, V. Jha, A randomized trial of vitamin D supplementation on vascular function in CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 28, 3100–3108 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017010003
A. Raed, J. Bhagatwala, H. Zhu, N.K. Pollock, S.J. Parikh, Y. Huang, R. Havens, I. Kotak, D.-H. Guo, Y. Dong, Dose responses of vitamin D 3 supplementation on arterial stiffness in overweight African Americans with vitamin D deficiency: a placebo controlled randomized trial. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188424
L.S. Bislev, L. Langagergaard Rødbro, J.N. Bech, E.B. Pedersen, A.D. Kjaergaard, S.A. Ladefoged, L. Rolighed, T. Sikjaer, L. Rejnmark, The effect of vitamin D3 supplementation on markers of cardiovascular health in hyperparathyroid, vitamin D insufficient women: a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Endocrine 62, 182–194 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-018-1659-4
J. Tomson, H. Hin, J. Emberson, R. Kurien, M. Lay, J. Cox, M. Hill, L. Arnold, P. Leeson, J. Armitage, R. Clarke, Effects of vitamin D on blood pressure, arterial stiffness, and cardiac function in older people after 1 year: BEST-D (biochemical efficacy and safety trial of vitamin D). J. Am. Heart Assoc. 6, (2017). https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.005707
C. Mcgreevy, M. Barry, C. Davenport, B. Byrne, C. Donaghy, G. Collier, W. Tormey, D. Smith, K. Bennett, D. Williams, The effect of vitamin D supplementation on arterial stiffness in an elderly community-based population. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 9, 176–183 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2014.12.019
M.D. Witham, R.J.G. Price, A.D. Struthers, P.T. Donnan, C.-M. Messow, I. Ford, M.E.T. McMurdo, Cholecalciferol treatment to reduce blood pressure in older patients with isolated systolic hypertension. JAMA Intern. Med. 173, 1672–1679 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1001/jamainternmed.2013.9043
Y.F. Yiu, K.H. Yiu, C.W. Siu, Y.H. Chan, S.W. Li, L.Y. Wong, S.W.L. Lee, S. Tam, E.W.K. Wong, C.P. Lau, B.M.Y. Cheung, H.F. Tse, Randomized controlled trial of vitamin D supplement on endothelial function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 227, 140–146 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2012.12.013
O.-H. Ryu, W. Chung, S. Lee, K.-S. Hong, M.-G. Choi, H.J. Yoo, The effect of high-dose vitamin D supplementation on insulin resistance and arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes. Korean J. Intern. Med. 29, 620 (2014). https://doi.org/10.3904/kjim.2014.29.5.620
I. Bressendorff, L. Brandi, M. Schou, B. Nygaard, N.E. Frandsen, K. Rasmussen, L. Ødum, O.V. Østergaard, D. Hansen, The effect of high dose cholecalciferol on arterial stiffness and peripheral and central blood pressure in healthy humans: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS ONE 11, e0160905 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0160905
P. Marckmann, H. Agerskov, S. Thineshkumar, E.-M. Bladbjerg, J.J. Sidelmann, J. Jespersen, M. Nybo, L.M. Rasmussen, D. Hansen, A. Scholze, Randomized controlled trial of cholecalciferol supplementation in chronic kidney disease patients with hypovitaminosis D. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 27, 3523–3531 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfs138
G. Dreyer, A.T. Tucker, S.M. Harwood, R.M. Pearse, M.J. Raftery, M.M. Yaqoob, Ergocalciferol and microcirculatory function in chronic kidney disease and concomitant vitamin D deficiency: an exploratory, double blind, randomised controlled trial. PLoS ONE 9, e99461 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099461
A.M. Hussin, A.W. Ashor, I. Schoenmakers, T. Hill, J.C. Mathers, M. Siervo, Effects of vitamin D supplementation on endothelial function: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Eur. J. Nutr. 56, 1095–1104 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1159-3
S. Upala, A. Sanguankeo, S. Congrete, V. Jaruvongvanich, Effect of cholecalciferol supplementation on arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 50, 230–235 (2016). https://doi.org/10.3109/14017431.2016.1173226
Y.J. Chung, W. Lee, J.-Y. Kim, J.H. Jung, Y.-K. Min, M.-S. Lee, M.-K. Lee, K.-W. Kim, J.H. Chung, Continued suppression of serum TSH level may be attributed to TSH receptor antibody activity as well as the severity of thyrotoxicosis and the time to recovery of thyroid hormone in treated Euthyroid Graves’ Patients. Thyroid 16, 1251–1257 (2006)
H. Yu, P. Farahani, Thyroid stimulating hormone suppression post-therapy in patients with Graves’ disease: a systematic review of pathophysiology and clinical data. Clin. Invest. Med. 38, E31–E44 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This study received funding from the Toyota Fonden and Orkla Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee (The Danish Biomedical Research Ethics Committee 1-10-72-568-12) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grove-Laugesen, D., Malmstroem, S., Ebbehoj, E. et al. Effect of 9 months of vitamin D supplementation on arterial stiffness and blood pressure in Graves’ disease: a randomized clinical trial. Endocrine 66, 386–397 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01997-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-019-01997-8