Abstract
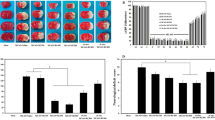
The present study was designed to determine the effect of different doses of oxytocin (OXT) on neuronal injury, spatial memory, blood-brain barrier (BBB) integrity and to explore possible underlying molecular mechanisms in the early stage of stroke in mice. Stroke model was generated by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) for 60 min and 24 h reperfusion in mice. OXT at doses of 1, 2, 4 and 8 IU/per mouse was administrated intranasally at the beginning of brain ischemia. Brain injury, BBB integrity, and spatial memory were evaluated by standard methods. Changes in the expression of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), and TUNEL positive cell were detected by immunohistochemistry. The levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), aquaporin-4 (AQP4) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) proteins were determined by western blotting and ELISA methods. OXT at doses of 4 and 8 IU/per mouse reduced the infarct size by 42% and 52%, respectively, and improved spatial memory function (p < 0.001). OXT (8 IU/per mouse) significantly reduced brain edema, BBB disruption and upregulated the AQP4 expression (p < 0.001). Finally, OXT significantly diminished the number of apoptotic, NF-κB positive cells and enhanced the expression of BDNF and VEGF proteins in the brain tissue (p < 0.001). These findings provide important evidences that OXT significantly suppresses neuronal damage in the early stage of stroke by inhibiting apoptotic and NF-κB signaling pathway, increasing the expression of VEGF, AQP4 and BDNF proteins and reducing the BBB leakage.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullahi, W., Tripathi, D., & Ronaldson, P. T. (2018). Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke: Targeting tight junctions and transporters for vascular protection. American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology, 315(3), C343–C356.
Afzal, M., Sidra, T., & Cheng, L. (2017). Oxytocin system in neuropsychiatric disorders: Old concept, new insights. Acta Physiologica Sinica, 69(2), 196–206.
Ahmed, M. A., & ELosaily, G. M. (2011). Role of oxytocin in deceleration of early atherosclerotic inflammatory processes in adult male rats. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine, 4(3), 169.
Akdemir, A., Erbas, O., Gode, F., Ergenoglu, M., Yeniel, O., Oltulu, F., et al. (2014). Protective effect of oxytocin on ovarian ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Peptides, 55, 126–130.
Akman, T., Akman, L., Erbas, O., Terek, M. C., Taskiran, D., & Ozsaran, A. (2015). The preventive effect of oxytocin to cisplatin-induced neurotoxicity: An experimental rat model. BioMed research international, 2015.
Al-Amran, F., & Shahkolahi, M. Oxytocin ameliorates the immediate myocardial injury in rat heart transplant through downregulation of neutrophil-dependent myocardial apoptosis. In Transplantation proceedings, 2013 (Vol. 6, 45, pp. 2506–2512). New York: Elsevier
Andero, R., Choi, D. C., & Ressler, K. J. (2014). BDNF–TrkB receptor regulation of distributed adult neural plasticity, memory formation, and psychiatric disorders. In Progress in molecular biology and translational science (Vol. 122, pp. 169–192). New York: Elsevier.
Arcienega, I., Brunet, J., Bloch, J., & Badaut, J. (2010). Cell locations for AQP1, AQP4 and 9 in the non-human primate brain. Neuroscience, 167(4), 1103–1114.
Asadi, Y., Gorjipour, F., Behrouzifar, S., & Vakili, A. (2018). Irisin peptide protects brain against ischemic injury through reducing apoptosis and enhancing BDNF in a rodent model of stroke. Neurochemical Research, 43(8), 1549–1560.
Behrouzifar, S., Vakili, A., Bandegi, A. R., & Kokhaei, P. (2018). Neuroprotective nature of adipokine resistin in the early stages of focal cerebral ischemia in a stroke mouse model. Neurochemistry International, 114, 99–107.
Bekinschtein, P., Cammarota, M., & Medina, J. H. (2014). BDNF and memory processing. Neuropharmacology, 76, 677–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.04.024.
Berti, R., Williams, A. J., Moffett, J. R., Hale, S. L., Velarde, L. C., Elliott, P. J., et al. (2002). Quantitative real-time RT—PCR analysis of inflammatory gene expression associated with ischemia—Reperfusion brain injury. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 22(9), 1068–1079.
Bethlehem, R. A., van Honk, J., Auyeung, B., & Baron-Cohen, S. (2013). Oxytocin, brain physiology, and functional connectivity: A review of intranasal oxytocin fMRI studies. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 38(7), 962–974.
Boccia, M., Petrusz, P., Suzuki, K., Marson, L., & Pedersen, C. (2013). Immunohistochemical localization of oxytocin receptors in human brain. Neuroscience, 253, 155–164.
Cai, Q., Feng, L., & Yap, K. Z. (2018). Systematic review and meta-analysis of reported adverse events of long-term intranasal oxytocin treatment for autism spectrum disorder. Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences, 72(3), 140–151.
Chen, A., Xiong, L.-J., Tong, Y., & Mao, M. (2013). The neuroprotective roles of BDNF in hypoxic ischemic brain injury. Biomedical Reports, 1(2), 167–176.
Dayi, A., Cetin, F., Sisman, A. R., Aksu, I., Tas, A., Gönenc, S., et al. (2015). The effects of oxytocin on cognitive defect caused by chronic restraint stress applied to adolescent rats and on hippocampal VEGF and BDNF levels. Medical Science Monitor: International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research, 21, 69.
Düşünceli, F., İşeri, S. Ö., Ercan, F., Gedik, N., Yeğen, C., & Yeğen, B. Ç. (2008). Oxytocin alleviates hepatic ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Peptides, 29(7), 1216–1222.
Filippidis, A., Carozza, R., & Rekate, H. (2016). Aquaporins in brain edema and neuropathological conditions. International journal of molecular sciences, 18(1), 55.
Gimpl, G., Reitz, J., Brauer, S., & Trossen, C. (2008). Oxytocin receptors: Ligand binding, signalling and cholesterol dependence. Progress in Brain Research, 170, 193–204.
Greenberg, M. E., Xu, B., Lu, B., & Hempstead, B. L. (2009). New insights in the biology of BDNF synthesis and release: implications in CNS function. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(41), 12764–12767.
Gutkowska, J., & Jankowski, M. (2009). Oxytocin: Old hormone, new drug. Pharmaceuticals, 2(3), 168–183.
Houlton, J., Abumaria, N., Hinkley, S. F., & Clarkson, A. N. (2019). Therapeutic potential of neurotrophins for repair after brain injury: A helping hand from Biomaterials. Frontiers in neuroscience, 13, 790.
Işeri, S. Ö., Şener, G., Saǧlam, B., Gedik, N., Ercan, F., & Yeǧen, B. Ç. (2005). Oxytocin protects against sepsis-induced multiple organ damage: Role of neutrophils. Journal of Surgical Research, 126(1), 73–81.
Jankowski, M., Bissonauth, V., Gao, L., Gangal, M., Wang, D., Danalache, B., et al. (2010). Anti-inflammatory effect of oxytocin in rat myocardial infarction. Basic Research in Cardiology, 105(2), 205–218.
Jin, K., Mao, X., Batteur, S., McEachron, E., Leahy, A., & Greenberg, D. (2001). Caspase-3 and the regulation of hypoxic neuronal death by vascular endothelial growth factor. Neuroscience, 108(2), 351–358.
Kaneko, Y., Pappas, C., Tajiri, N., & Borlongan, C. V. (2016). Oxytocin modulates GABA A R subunits to confer neuroprotection in stroke in vitro. Scientific Reports, 6, 35659.
Karelina, K., Stuller, K. A., Jarrett, B., Zhang, N., Wells, J., Norman, G. J., et al. (2011). Oxytocin mediates social neuroprotection after cerebral ischemia. Stroke, 42(12), 3606–3611.
Khori, V., Alizadeh, A. M., Khalighfard, S., Heidarian, Y., & Khodayari, H. (2018). Oxytocin effects on the inhibition of the NF-κB/miR195 pathway in mice breast cancer. Peptides, 107, 54–60.
Knobloch, H. S., Charlet, A., Hoffmann, L. C., Eliava, M., Khrulev, S., Cetin, A. H., et al. (2012). Evoked axonal oxytocin release in the central amygdala attenuates fear response. Neuron, 73(3), 553–566.
Lee, S.-Y., Park, S.-H., Chung, C., Kim, J. J., Choi, S.-Y., & Han, J.-S. (2015). Oxytocin protects hippocampal memory and plasticity from uncontrollable stress. Scientific Reports, 5, 18540.
Lin, Y.-T., & Hsu, K.-S. (2018). Oxytocin receptor signaling in the hippocampus: Role in regulating neuronal excitability, network oscillatory activity, synaptic plasticity and social memory. Progress in Neurobiology.
Liu, E., Sun, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, A., & Yan, J. (2020). Aquaporin4 knockout aggravates early brain injury following subarachnoid hemorrhage through impairment of the glymphatic system in rat brain. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (pp. 59–64). Berlin: Springer.
Macdonald, K., & Feifel, D. (2013). Helping oxytocin deliver: Considerations in the development of oxytocin-based therapeutics for brain disorders. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 7, 35.
Melville, K., & Varma, D. (1961). Synthetic oxytocin as an antagonist of experimental cardiac anoxic changes in rabbits. British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy, 17(2), 218–223.
Moghadam, S. E., Tameh, A. A., Vahidinia, Z., Atlasi, M. A., Bafrani, H. H., & Naderian, H. (2018). Neuroprotective effects of oxytocin hormone after an experimental stroke model and the possible role of calpain-1. Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases, 27(3), 724–732.
Neumann, I. D., Maloumby, R., Beiderbeck, D. I., Lukas, M., & Landgraf, R. (2013). Increased brain and plasma oxytocin after nasal and peripheral administration in rats and mice. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 38(10), 1985–1993.
Nowacka, M., & Obuchowicz, E. (2013). BDNF and VEGF in the pathogenesis of stress-induced affective diseases: An insight from experimental studies. Pharmacological Reports, 65(3), 535–546.
Oeckinghaus, A., & Ghosh, S. (2009). The NF-κB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology, 1(4), a000034.
Ondrejcakova, M., Ravingerova, T., Bakos, J., Pancza, D., & Jezova, D. (2009). Oxytocin exerts protective effects on in vitro myocardial injury induced by ischemia and reperfusion. Canadian journal of physiology and pharmacology, 87(2), 137–142.
Park, M. H., & Hong, J. T. (2016). Roles of NF-κB in cancer and inflammatory diseases and their therapeutic approaches. Cells, 5(2), 15.
Park, S.-H., Kim, Y.-J., Park, J.-C., Han, J.-S., & Choi, S.-Y. (2017). Intranasal oxytocin following uncontrollable stress blocks impairments in hippocampal plasticity and recognition memory in stressed rats. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 20(10), 861–866.
Rahmati, H., Momenabadi, S., Vafaei, A. A., Bandegi, A. R., Mazaheri, Z., & Vakili, A. (2019). Probiotic supplementation attenuates hippocampus injury and spatial learning and memory impairments in a cerebral hypoperfusion mouse model. Molecular biology reports, 1–11.
Shen, F., Walker, E. J., Jiang, L., Degos, V., Li, J., Sun, B., et al. (2011). Coexpression of angiopoietin-1 with VEGF increases the structural integrity of the blood–brain barrier and reduces atrophy volume. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 31(12), 2343–2351.
Stokum, J. A., Gerzanich, V., & Simard, J. M. (2016). Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral edema. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow & Metabolism, 36(3), 513–538.
Sun, Y., Jin, K., Xie, L., Childs, J., Mao, X. O., Logvinova, A., et al. (2003). VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 111(12), 1843–1851.
Tanaka, A., Furubayashi, T., Arai, M., Inoue, D., Kimura, S., Kiriyama, A., et al. (2018). Delivery of oxytocin to the brain for the treatment of autism spectrum disorder by nasal application. Molecular Pharmaceutics, 15(3), 1105–1111.
Vaidyanathan, R., & Hammock, E. A. (2017). Oxytocin receptor dynamics in the brain across development and species. Developmental Neurobiology, 77(2), 143–157.
Vakili, A., & Zahedi-Khorasani, M. (2008). Effect of aminoguanidine on post-ischemic damage in rodent model of stroke. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 21(1), 24–28.
Wang, H., Chen, H., Jin, J., Liu, Q., Zhong, D., & Li, G. (2020). Inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome reduces brain edema and regulates the distribution of aquaporin-4 after cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion. Life Sciences, 117638.
Wigton, R., Radua, J., Allen, P., Averbeck, B., Meyer-Lindenberg, A., McGuire, P., et al. (2015). Neurophysiological effects of acute oxytocin administration: Systematic review and meta-analysis of placebo-controlled imaging studies. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience.
Yeniel, A. Ö., Erbas, O., Ergenoglu, A. M., Aktug, H., Taskiran, D., Yildirim, N., et al. (2014). Effect of oxytocin treatment on explant size, plasma and peritoneal levels of MCP-1, VEGF, TNF-α and histopathological parameters in a rat endometriosis model. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology, 175, 134–139.
Yuan, L., Liu, S., Bai, X., Gao, Y., Liu, G., Wang, X., et al. (2016). Oxytocin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in microglial cells and attenuates microglial activation in lipopolysaccharide-treated mice. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 13(1), 77.
Zhang, W., Zhang, J., Xu, M., & Zhang, Y. (2007). Effect of oxytocin on gastric ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. Frontiers of Medicine in China, 1(4), 433–437.
Zhang, Z., & Chopp, M. (2002). Vascular endothelial growth factor and angiopoietins in focal cerebral ischemia. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine, 12(2), 62–66.
Zhao, H., Chen, Z., Xie, L.-J., & Liu, G.-F. (2018). Suppression of TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway improves cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Molecular Neurobiology, 55(5), 4311–4319.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by a research grant from Vice Chancellor for Research of the Semnan University of Medical Sciences (Grant Number: 1355). We thanks from Prof. Ali Rashidy-Pour for valuable comments and correction of manuscript and Mehrnoush Rahmani for help in doing of spatial memory evaluation. We also thank for some technical assistance provided by Reza Nasr form the Department of Biotechnology, Semnan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
All of procedures performed in this studies involving animals were in accordance with institutional animal care committee for animal surgery and ethical international guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals. Research procedure and protocols were approved by the SUMS institutional Committee of Research Ethics (Ethical Code Number: IR.SUMUMS.REC. 1396.241).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Momenabadi, S., Vafaei, A.A., Bandegi, A.R. et al. Oxytocin Reduces Brain Injury and Maintains Blood–Brain Barrier Integrity After Ischemic Stroke in Mice. Neuromol Med 22, 557–571 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08613-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-020-08613-3