Abstract
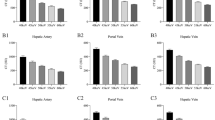
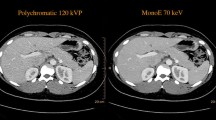
To assess the image quality of monochromatic imaging from spectral CT in patients with Budd-Chiari syndrome (BCS), fifty patients with BCS underwent spectral CT to generate conventional 140 kVp polychromatic images (group A) and monochromatic images, with energy levels from 40 to 80, 40 + 70, and 50 + 70 keV fusion images (group B) during the portal venous phase (PVP) and the hepatic venous phase (HVP). Two-sample t tests compared vessel-to-liver contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR) and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for the portal vein (PV), hepatic vein (HV), inferior vena cava. Readers’ subjective evaluations of the image quality were recorded. The highest SNR values in group B were distributed at 50 keV; the highest CNR values in group B were distributed at 40 keV. The higher CNR values and SNR values were obtained though PVP of PV (SNR 18.39 ± 6.13 vs. 10.56 ± 3.31, CNR 7.81 ± 3.40 vs. 3.58 ± 1.31) and HVP of HV (3.89 ± 2.08 vs. 1.27 ± 1.55) in the group B; the lower image noise for group B was at 70 keV and 50 + 70 keV (15.54 ± 8.39 vs. 18.40 ± 4.97, P = 0.0004 and 18.97 ± 7.61 vs. 18.40 ± 4.97, P = 0.0691); the results show that the 50 + 70 keV fusion image quality was better than that in group A. Monochromatic energy levels of 40–70, 40 + 70, and 50 + 70 keV fusion image can increase vascular contrast and that will be helpful for the diagnosis of BCS, we select the 50 + 70 keV fusion image to acquire the best BCS images.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Menon, K. V., Shah, V., & Kamath, P. S. (2004). The Budd-Chiari syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine, 350(6), 578–585.
Janssen, H. L., Garcia-Pagan, J. C., Elias, E., Mentha, G., Hadengue, A., & Valla, D. C. (2003). Budd-Chiari syndrome: A review by an expert panel. Journal of Hepatology, 38(3), 364–371.
Ludwig, J., Hashimoto, E., McGill, D. B., & van Heerden, J. A. (1990). Classification of hepatic venous outflow obstruction: Ambiguous terminology of the Budd-Chiari syndrome. Mayo Clinic Proceedings, 65(1), 51–55.
Wu, T., Wang, L., Xiao, Q., et al. (2002). Percutaneous balloon angioplasty of inferior vena cava in Budd-Chiari syndrome-R1. International Journal of Cardiology, 83(2), 175–178.
Xu, K., He, F. X., Zhang, H. G., et al. (1996). Budd-Chiari syndrome caused by obstruction of the hepatic inferior vena cava: Immediate and 2-year treatment results of transluminal angioplasty and metallic stent placement. Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiology, 19(1), 32–36.
Bhasin, D. K., & Malhi, N. J. (2002). Variceal bleeding and portal hypertension: Much to learn, much to explore. Endoscopy, 34(2), 119–128.
Matsumoto, A. (2008). Management of gastric fundal varices. Hepatology, 48(1), 343–344.
Meng, X. C., Zhu, K. S., Qin, J., et al. (2007). Clinical significance of multislice spiral CT scans in hepatic veins occlusion in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Chinese Medical Journal (English Edition), 120(2), 100–105.
Kang, H. K., Jeong, Y. Y., Choi, J. H., et al. (2002). Three-dimensional multi-detector row CT portal venography in the evaluation of portosystemic collateral vessels in liver cirrhosis. Radiographics, 22(5), 1053–1061.
Zhao, L. Q., He, W., & Chen, G. (2008). Characteristics of paraesophageal varices: A study with 64-row multidetector computed tomography portal venography. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 14(34), 5331–5335.
Zhao, L. Q., He, W., Li, J. Y., Chen, J. H., Wang, K. Y., & Tan, L. (2012). Improving image quality in portal venography with spectral CT imaging. European Journal of Radiology, 81(8), 1677–1681.
Awai, K., Hiraishi, K., & Hori, S. (2004). Effect of contrast material injection duration and rate on aortic peak time and peak enhancement at dynamic CT involving injection protocol with dose tailored to patient weight. Radiology, 230(1), 142–150.
Erturk, S. M., Ichikawa, T., Sou, H., Tsukamoto, T., Motosugi, U., & Araki, T. (2008). Effect of duration of contrast material injection on peak enhancement times and values of the aorta, main portal vein, and liver at dynamic MDCT with the dose of contrast medium tailored to patient weight. Clinical Radiology, 63(3), 263–271.
Lv, P., Lin, X. Z., Li, J., Li, W., & Chen, K. (2011). Differentiation of small hepatic hemangioma from small hepatocellular carcinoma: Recently introduced spectral CT method. Radiology, 259(3), 720–729.
Richter, G. M., Noeldge, G., Palmaz, J. C., et al. (1990). Transjugular intrahepatic portacaval stent shunt: Preliminary clinical results. Radiology, 174(3 Pt 2), 1027–1030.
Lv, P., Lin, X. Z., Chen, K., & Gao, J. (2012). Spectral CT in patients with small HCC: Investigation of image quality and diagnostic accuracy. European Radiology, 22(10), 2117–2124.
Yilmaz, S., Yekeler, E., Agayev, A., Pinarbasi, B., Bakkaloglu, H., & Acunas, B. (2008). A rapidly increasing abdominal girth in a young patient: MDCT findings of Budd-Chiari syndrome. Surgery, 144(1), 101–102.
Lupescu, I. G., Dobromir, C., Popa, G. A., Gheorghe, L., & Georgescu, S. A. (2008). Spiral computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography evaluation in Budd-Chiari syndrome. Journal of Gastrointestinal and Liver Diseases, 17(2), 223–226.
Watanabe, H., Kanematsu, M., Miyoshi, T., et al. (2010). Improvement of image quality of low radiation dose abdominal CT by increasing contrast enhancement. AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology, 195(4), 986–992.
Lin, X. Z., Wu, Z. Y., Tao, R., et al. (2012). Dual energy spectral CT imaging of insulinoma—value in preoperative diagnosis compared with conventional multi-detector CT. European Journal of Radiology, 81(10), 2487–2494.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Lei Su and Junqiang Dong contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, L., Dong, J., Sun, Q. et al. Spectral CT Imaging in Patients with Budd-Chiari Syndrome: Investigation of Image Quality. Cell Biochem Biophys 70, 1043–1049 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0021-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-014-0021-6