Abstract
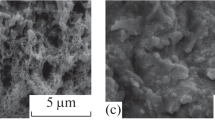
A highly sensitive, selective, reversible, and reusable glucose sensor is developed by using molecularly imprinted polymer-based artificial receptors onto interdigital transducer. Sensor receptors were synthesized through bulk imprinting technology by using styrene as monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate (EGDMA) as cross-linker, and AIBN as free radical initiator. Topography of the synthesized receptors was investigated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Fabricated sensor showed concentration-dependent linear and reversible response with lower limit of detection of 30 ppb and upper limit of detection ~ 500 ppm. Furthermore, newly fabricated sensor is highly selective towards its analyte of interest in the presence of other competing agents, and the regeneration of sensor response has been assessed with the percentage error of less than 2% under the period of 1 year at room temperature and pressure conditions. The reported sensor may have potential technological applications in the field of medical diagnostics, food, and pharmaceutical industry.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vargas, E., Ruiz, M. A., Campuzano, S., Reviejo, A. J., & Pingarrón, J. M. (2016). Noninvasive determination of glucose directly in raw fruits using a continuous flow system based on microdialysis sampling and amperometric detection at an integrated enzymatic biosensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 914, 53–61.
Galant, A. L., Kaufman, R. C., & Wilson, J. D. (2015). Glucose: Detection and analysis. Food Chemistry, 188, 149–160.
Hong, X., Wang, J., & Qiu, S. (2014). Authenticating cherry tomato juices-discussion of different data standardization and fusion approaches based on electronic nose and tongue. Food Research International, 60, 173–179.
Vargas, E., Ruiz, M. A., Campuzano, S., Reviejo, A. J., & Pingarrón, J. M. (2016). Non-invasive determination of glucose directly in raw fruits using a continuous flow system based on microdialysis sampling and amperometric detection at an integrated enzymatic biosensor. Analytica Chimica Acta, 914, 53–61.
Shen, W., Sun, J., Seah, J. Y. H., Shi, L., Tang, S., & Lee, H. K. (2018). Needle-based sampling coupled with colorimetric reaction catalyzed by layered double hydroxide peroxidase mimic for rapid detection of the change of d-glucose levels with time in bananas. Analytica Chimica Acta, 1001, 32–39.
Surareungchai, W., Deepunya, W., & Tasakorn, P. (2001). Quadruple-pulsed amperometric detection for simultaneous flow injection determination of glucose and fructose. Analytica Chimica Acta, 448(1–2), 215–220.
Wu, Y., Wang, Q., Chen, M., Dong, C., Zhang, X., & Wang, S. (2016). An enzyme free potentiometric detection of reducing sugars based on a poly (3-hydroxyphenylboronic acid-co-phenol) molecularly imprinted polymer modified electrode. American Journal of Biomedical Sciences, 8.
Chen, X., Chen, J., Wang, F., Xiang, X., Luo, M., Ji, X., & He, Z. (2012). Determination of glucose and uric acid with bienzyme colorimetry on microfluidic paper-based analysis devices. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 35(1), 363–368.
Gao, F., Luo, F., Chen, X., Yao, W., Yin, J., Yao, Z., & Wang, L. (2009). A novel nonenzymatic fluorescent sensor for glucose based on silica nanoparticles doped with europium coordination compound. Talanta, 80(1), 202–206.
Emran, M. Y., Mekawy, M., Akhtar, N., Shenashen, M. A., EL-Sewify, I. M., Faheem, A., & El-Safty, S. A. (2018). Broccoli-shaped biosensor hierarchy for electrochemical screening of noradrenaline in living cells. Biosens Bioelectrons, 100, 122–131.
Wahjudi, P. N., Patterson, M. E., Lim, S., Yee, J. K., Mao, C. S., & Lee, W.-N. P. (2010). Measurement of glucose and fructose in clinical samples using gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Clinical Biochemistry, 43(1-2), 198–207.
Ma, C., Sun, Z., Chen, C., Zhang, L., & Zhu, S. (2014). Simultaneous separation and determination of fructose, sorbitol, glucose and sucrose in fruits by HPLC-ELSD. Food Chemistry, 145, 784–788.
Akhtar, N., El-Safty, S. A., Abdelsalam, M. E., Shenashen, M. A., & Kawarada, H. (2016). Radially oriented nanostrand electrodes to boost glucose sensing in mammalian blood. Biosens Bioelectrons, 77, 656–665.
Emran, M. Y., Khalifa, H., Gomaa, H., Shenashen, M. A., Akhtar, N., Mekawy, M., Faheem, A., & El-Safty, S. A. (2017). Hierarchical CN doped NiO with dual-head echinop flowers for ultrasensitive monitoring of epinephrine in human blood serum. Microchimica Acta, 184(11), 4553–4562.
Liao, S.-H., Lu, S.-Y., Bao, S.-J., Yu, Y.-N., & Wang, M.-Q. (2016). NiMoO4 nanofibres designed by electrospining technique for glucose electrocatalytic oxidation. Analytica Chimica Acta, 905, 72–78.
Cao, X., & Wang, N. (2011). A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor modified with Fe2O3 nanowire arrays. Analyst, 136(20), 4241–4246.
Lu, W., Qin, X., Asiri, A. M., Al-Youbi, A. O., & Sun, X. (2013). Ni foam: a novel three dimensional porous sensing platform for sensitive and selective non enzymatic glucose detection. Analyst, 138(2), 417–420.
Choi, T., Kim, S. H., Lee, C. W., Kim, H., Choi, S.-K., Kim, S.-H., Kim, E., Park, J., & Kim, H. (2015). Synthesis of carbon nanotube-nickel nanocomposites using atomic layer deposition for high performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 63, 325–330.
Fischer, C., Fraiwan, A., & Choi, S. (2016). A 3D paper-based enzymatic fuel cell for self-powered, low-cost glucose monitoring. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 79, 193–197.
Fathollahzadeh, M., Hosseini, M., Haghighi, B., Kolahdouz, M., & Fathipour, M. (2016). Fabrication of a liquid-gated enzyme field effect device for sensitive glucose detection. Analytica Chimica Acta, 924, 99–105.
Li, N., Hao, X., Kang, B. H., Xu, Z., Shi, Y., Li, N. B., & Luo, H. Q. (2016). Enzyme-free fluorescent biosensor for the detection of DNA based on core-shell Fe3O4 polydopamine nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 77, 525–529.
Kan, X., Li, C., Zhou, H., Zhu, A., Xing, Z., Zhao, Z., & Xu, G. (2012). Three dimensional ordered macroporous electrochemical sensor for dopamine recognition and detection. American Journal of Biomedical Sciences, 4, 184–193.
Hu, W., Fu, G., Kong, J., Zhou, S., Scafa, N., & Zhang, X. (2015). Advancement of nucleic acid biosensors based on Morpholino. American Journal of Biomedical Sciences, 7.
Kim, D.-M., Cho, S. J., Cho, C.-H., Kim, K. B., Kim, M.-Y., & Shim, Y.-B. (2016). Disposable allsolid state pH and glucose sensors based on conductive polymer covered hierarchical AuZn oxide. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 79, 165–172.
Miao, F., Lu, X., Tao, B., Li, R., & Chu, P. K. (2016). Glucose oxidase immobilization platform based on ZnO nanowires supported by silicon nanowires for glucose biosensing. Microelectronic Engineering, 149, 153–158.
Myung, N., Kim, S., Lee, C., Kim, T., Rajeshwar, K. (2016). Facile synthesis of Pt-CuO Socie. 163, 180–184.
Thanh, T. D., Balamurugan, J., Hwang, J. Y., Kim, N. H., & Lee, J. H. (2016). In situ synthesis of graphene-encapsulated gold nanoparticle hybrid electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Carbon, 98, 90–98.
Shackery, I., Patil, U., Pezeshki, A., Shinde, N. M., Kang, S., Im, S., & Jun, S. C. (2016). Copper hydroxide nanorods decorated porous graphene foam electrodes for non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Electrochimica Acta, 191, 954–961.
Wei, C., Cheng, C., Zhao, J., Wang, Z., Wu, H., Gu, K., Du, W., & Pang, H. (2015). Mesoporous ZnSNiS nanocomposites for nonenzymatic electrochemical glucose sensors. Chemistry Open, 4, 32–38.
Saraf, M., Natarajan, K., & Mobin, S. M. (2016). Non-enzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose by employing sucrose templated microspheres of copper oxide (CuO). Dalton Transactions, 45(13), 5833–5840.
Yang, T., Xu, J., Lu, L., Zhu, X., Gao, Y., Xing, H., Yu, Y., Ding, W., & Liu, Z. (2016). Copper nanoparticle/graphene oxide/single wall carbon nanotube hybrid materials as electrochemical sensing platform for nonenzymatic glucose detection. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 761, 118–124.
Syshchyk, O., Skryshevsky, V. A., Soldatkin, O. O., & Soldatkin, A. P. (2015). Enzyme biosensor systems based on porous silicon photoluminescence for detection of glucose, urea and heavy metals. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 66, 89–94.
Joshi, N., Rawat, K., Solanki, P. R., & Bohidar, H. (2015). Enzyme-free and biocompatible nanocomposite based cholesterol sensor. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 102, 69–73.
Malitesta, C., Losito, I., & Zambonin, G. P. (1999). Molecularly imprinted electrosynthesized polymers: new materials for biomimetic sensors. Analytical Chemistry, 71(7), 13661370.
Farid, M. M., Goudini, L., Piri, F., Zamani, A., & Saadati, F. (2016). Molecular imprinting method for fabricating novel glucose sensor: Polyvinyl acetate electrode reinforced by MnO2/CuO loaded on graphene oxide nanoparticles. Food Chemistry, 194, 61–67.
Wu, G., & Zaman, M. H. (2015). Amperometric measurements of ethanol on paper with a glucometer. Talanta, 134, 194–199.
Zhuang, X., Tian, C., Luan, F., Wu, X., & Chen, L. (2016). One-step electrochemical fabrication of a nickel oxide nanoparticle/polyaniline nanowire/graphene oxide hybrid on a glassy carbon electrode for use as a non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. RSC Advances, 6, 9254192546.
Emran, M. Y., Shenashen, M. A., Morita, H., El-Safty, S. A. (2018). 3D-ridge stocked layers of nitrogen-doped mesoporous carbon nanosheets for ultrasensitive monitoring of dopamine released from PC12 cells under K+ stimulation. Advanced Healthcare Materials 1701459.
Kim, D. M., Moon, J. M., Lee, W. C., Yoon, J. H., Choi, C. S., & Shim, Y. B. (2017). A potentiometric non-enzymatic glucose sensor using a molecularly imprinted layer bonded on a conducting polymer. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 91, 276–283.
Gupta, V. K., Yola, M. L., Özaltın, N., Atar, N., Üstündağ, Z., & Uzun, L. (2013). Molecular imprinted polypyrrole modified glassy carbon electrode for the determination of tobramycin. Electrochimica Acta, 112, 37–43.
Wen, T., Zhu, W., Xue, C., Wu, J., Han, Q., Wang, X., Zhou, X., & Jiang, H. (2014). Novel electrochemical sensing platform based on magnetic field-induced self-assembly of Fe3O4@ polyaniline nanoparticles for clinical detection of creatinine. Biosensors & Bioelectronics, 56, 180–185.
Zhu, W., Jiang, G., Xu, L., Li, B., Cai, Q., Jiang, H., & Zhou, X. (2015). Facile and controllable onestep fabrication of molecularly imprinted polymer membrane by magnetic field directed selfassembly for electrochemical sensing of glutathione. Analytica Chimica Acta, 886, 37–47.
Carrasco, S., Benito-Peña, E., Navarro-Villoslada, F., Langer, J., Sanz-Ortiz, M. N., Reguera, J., Liz-Marzán, L. M., & Moreno-Bondi, M. C. (2016). Multi-branched gold-mesoporous silica nanoparticles coated with molecularly imprinted polymer for label-free antibiotic SERS analysis. Chemistry of Materials, 28(21), 7947–7954.
Kupis-Rozmysłowicz, J., Wagner, M., Bobacka, J., Lewenstam, A., & Migdalski, J. (2016). Biomimetic membranes based on molecularly imprinted conducting polymers as a sensing element for determination of taurine. Electrochimica Acta, 188, 537–544.
Uzun, L., & Turner, A. P. (2016). Molecularly-imprinted polymer sensors: realising their potential. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 76, 131–144.
Zhu, W., Xu, L., Zhu, C., Li, B., Xiao, H., Jiang, H., & Zhou, X. (2016). Magnetically controlled electrochemical sensing membrane based on multifunctional molecularly imprinted polymers for detection of insulin. Electrochimica Acta, 218, 91–100.
Ghani, N. T. A., El Nashar, R. M., Abdel-Haleem, F. M., Madbouly, A. (2016). Computational Design, Synthesis and application of a new selective molecularly imprinted polymer for electrochemical detection. Electroanalysis.
Cernat, A., Tertiș, M., Fritea, L., & Cristea, C. (2016). Graphene in sensors design. In Advanced 2D Materials (pp. 387-432). Scrivener Publishing and co-published with John Wiley & Sons USA.
Iqbal, N., Mustafa, G., & Lieberzeit, P. A. (2013). Mass sensitive multi-sensor platform for receptor screening and quantification purposes. Journal of the Chinese Advanced Materials Society, 1(3), 200–209.
Latif, U., Mujahid, A., Afzal, A., Sikorski, R., Lieberzeit, P. A., & Dickert, F. L. (2011). Dual and tetraelectrode QCMs using imprinted polymers as receptors for ions and neutral analytes. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 400(8), 2507–2515.
Cheng, Z., Wang, E., & Yang, X. (2001). Capacitive detection of glucose using molecularly imprinted polymers. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 16(3), 179–185.
Yang, Y., Yi, C., Luo, J., Liu, R., Liu, J., Jiang, J., & Liu, X. (2011). Glucose sensors based on electrodeposition of molecularly imprinted polymeric micelles: a novel strategy for MIP sensors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 26(5), 2607–2612.
Acknowledgments
Authors are thankful to Higher Education Commission of Pakistan, School of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Jinan (West Campus) Jinan, China and the Department of Chemistry, Al al-Bayt University Al-Mafraq, Jordan for their support in material testing.
Funding Statement
This work was supported financially by Higher Education Commission Pakistan, International Islamic University, Islamabad, Pakistan and OeAD Austria.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asghar, N., Mustafa, G., Yasinzai, M. et al. Real-Time and Online Monitoring of Glucose Contents by Using Molecular Imprinted Polymer-Based IDEs Sensor. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 189, 1156–1166 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03049-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-019-03049-3