Abstract
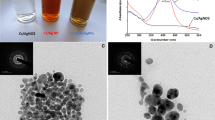
The cellulose-based textiles currently used in hospitals are good conducive materials for cross-infection or transmission of diseases caused by microorganisms. Thus, great interest has been recently found in the antibacterial finishing of fabrics for practical applications to prevent the infection incidence. In this work, we developed novel SnO2/ZnO/chitosan bionanocomposites by one-step simultaneous sonochemical/sol–gel deposition to prepare an antibacterial textile as a model for combating bacterial infections. The different prepared samples were characterized using transmission electron microscope, X-ray diffraction, and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) indicating the embedded SnO2 and ZnO nanoparticles in treated fabrics. The treated fabrics were used to evaluate antibacterial activities against Escherichia coli and Streptococcus aureus as a model for Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria, respectively, using disk diffusion method in dark conditions as an in vitro model for treatment of bacterial wound infection. The procedure was more developed in terms of SnO2/ZnO molar ratio and using chitosan and citric acid to improve the antibacterial properties of the fabrics and their wash durability, respectively. The highest antibacterial activity of the fabrics was attained in a 50 min sonochemical coating process using SnO2/ZnO 1:2 molar ratio in initial sol and simultaneously deposited chitosan and citric acid. The presence of chitosan as complexing agent, citric acid as crosslink agent, and SnO2–ZnO heterojunction as important influencing parameters synergistically enhanced both the antimicrobial efficiency and maintenance of modified cotton durability after performing several washing cycles.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fijan, S, TurkInt, SŠ, “Hospital Textiles, Are They a Possible Vehicle for Healthcare-Associated Infections?” J. Environ. Res. Public. Health., 9 3330–3343 (2012)
Hota, B, “Contamination, Disinfection, Cross-colonization: Are Hospital Surfaces Reservoirs for Nosocomial Infection?” Clin. Infect. Dis., 39 1182–1189 (2004)
Nguyen QV. Hospital-acquired infections. 2006, http://www.emedicine.com/ped/topic1691.htm.
Hospital-acquired infections-trends across Europe., Frost Sullivan.,/http://www.reportlinker.com/p0249335-summary/Hospital-acquired-infections-trends-across-Europe.htmlS. June 2010, Accessed 01 Nov 2012.
Bidet, P, Metais, A, Mahjoub-Messai, F, et al., “Detection Identification by PCR of a Highly Virulent Phylogenetic Subgroup Among Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli B2 Strains.” Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 73 2373–2377 (2007)
Stoimenov, P, Klinger, R, Marchin, G, et al., “Metal Oxide Nanoparticles as Bactericidal Agents.” Langmuir, 18 6679–6686 (2002)
El Shafei, A, Abou-Okeil, A, “ZnO/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Bionano-Composite to Impart Antibacterial UV Protection for Cotton Fabric.” Carbohyd. Polym., 83 920–925 (2011)
Ashraf, M, Champagne, P, Perwuelz, A, et al., “Photocatalytic Solution Discoloration and Self-Cleaning by Polyester Fabric Functionalized with ZnO Nanorods.” J. Ind. Text., 19 (6) 34–41 (2014)
Ostrovsky, S, Kazimirsky, G, Gedanken, A, et al., “Selective Cytotoxic Effect of ZnO Nanoparticles on Glioma Cells.” Nano. Res., 2 882–890 (2009)
Poulios, I, Makri, D, Prohaska, X, “Photocatalytic Treatment of Olive Milling Wastewater, Oxidation of Protocatechuic Acid.” Global NEST, 1 55–62 (1999)
Carraway, ER, Hoffman, AJ, Hoffmann, MR, “Photocatalytic Production of H2O2 Organic Acids on Quantum-Sized Semi-conductor Colloids.” Environ. Sci. Technol., 28 786–793 (1994)
Talebian, N, Amininezhad, SM, Doudi, M, “Controllable Synthesis of ZnO Nanoparticles Their Morphology-Dependent Antibacterial Optical Properties.” Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 120 66–73 (2013)
Niinomi, M, “Recent Metallic Materials for Biomedical Applications.” Metall. Mater. Trans. A., 33 477–486 (2002)
Cremasco, A, Messias, AD, Esposito, AR, et al., “Effects of Alloying Elements on the Cytotoxic Response of Titanium Alloys.” Mater. Sci. Eng. C., 31 833–839 (2011)
Mei, S, Zhao, L, Wang, W, et al., “Biomimetic Titanium Alloy with Sparsely Distributed Nanotubes Could Enhance Osteoblast Functions.” Adv. Eng. Mater., 14 B166–B174 (2012)
Acevedo-Morantes, CY, Irizarry-Ortiz, RA, Caceres-Valencia, PG, et al., “Combinatorial Growth of Oxide Nanoscaffolds and Its Influence in Osteoblast Cell Adhesion.” J. Appl. Phys., 111 102810-1 (2012)
Vidhu, VK, Philip, D, “Phytosynthesis and Applications of Bioactive SnO2 Nanoparticles.” Mater. Charact., 101 97–105 (2015)
Vidhu, VK, Philip, D, “Biogenic Synthesis of SnO2 Nanoparticles, Evaluation of Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities.” Spectrochim. Acta. Part A, 134 372–379 (2015)
Peller, J, Wiest, O, Kamat, PV, “Synergy of Combining Sonolysis and Photocatalysis in the Degradation and Mineralization of Chlorinated Aromatic Compounds.” Environ. Sci. Technol.
Meena Kumari, M, Philip, D, “Synthesis of Biogenic SnO2 Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Thermal, Rheological, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activities.” Powder Tech., 270 312–319 (2015)
Kongsong, P, Sikong, L, Niyomwas, S, et al., “Photocatalytic Antibacterial Performance of Glass Fibers Thin Film Coated with N-Doped SnO2/TiO2.” Sci. World J., 2014 869706 (2014)
Talebian, N, Nilforoushan, MR, Badri Zargar, E, “Enhanced Antibacterial Performance of Hybrid Semiconductor Nanomaterials, ZnO/SnO2 Nanocomposite Thin Films.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 258 (1) 547–555 (2011)
Talebian, N, Sadeghi Haddad Zavvare, H, “Enhanced Bactericidal Action of SnO2 Nanostructures Having Different Morphologies Under Visible Light, Influence of Surfactant.” J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 130 132–139 (2014)
Phukan, A, Bhattacharjee, RP, Kumar Dutta, D, Stabilization of SnO 2 Nanoparticles into the Nanopores of Modified Montmorillonite and Their Antibacterial Activity. Adv. Powder Tech., Available Online (2016)
Fakhri, A, Behrouz, S, Pourm, M, “Synthesis, Photocatalytic and Antimicrobial Properties of SnO2, SnS2 SnO2/SnS2 Nanostructure.” J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 149 45–50 (2015)
Nasir, Z, Shakir, M, Wahab, R, et al., “Co-precipitation Synthesis and Characterization of Co Doped SnO2 NPs, HSA Interaction Via Various Spectroscopic Techniques and Their Antimicrobial and Photocatalytic Activities.” Int. J. Biol. Macromol. Part A, 94 554–565 (2017)
Chávez-Calderón, A, Paraguay-Delgado, F, Orrantia-Borunda, E, et al., “Size Effect of SnO2 Nanoparticles on Bacteria Toxicity Their Membrane Damage.” Chemosphere, 165 33–40 (2016)
Tammina, SK, Mandal, BK, Ranjan, S, et al., “Cytotoxicity Study of Piper Nigrum Seed Mediated Synthesized SnO2 Nanoparticles Towards Colorectal (HCT116) and Lung Cancer (A549) Cell Lines.” J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 166 158–168 (2017)
Fakhri, A, Naji, M, Afshar Nejad, P, “Adsorption and Photocatalysis Efficiency of Magnetite Quantum Dots Anchored Tin Dioxide Nanofibers for Removal of Mutagenic Compound: Toxicity Evaluation and Antibacterial Activity.” J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol., 173 204–209 (2017)
Roopan, SM, Kumar, SHS, Madhumitha, G, et al., “Biogenic-Production of SnO2 Nanoparticles and Its Cytotoxic Effect Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line (HepG2).” Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 175 1567–1575 (2015)
Mohana Roopan, S, Hari Subbish Kumar, S, Madhumitha, G, et al., “Biogenic-Production of SnO2 Nanoparticles and Its Cytotoxic Effect Against Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line (HepG2).” Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol., 175 1567–1575 (2015)
http://www.who.int/pcs/, World Health Organization, International Programme on Chemical Safety, 1211 Geneva 27 (2005) and references therein.
Westrum, B, Thomassen, Y, “The Nordic Expert Group for Criteria Documentation of Health Risks from Chemicals and the Dutch Expert Committee on Occupational Standards: 130. Tin and Inorganic Tin Compounds.” Arbete och Hälsa, 10 1–48 (2002), and references therein
Drader, M, Ara, P, Ruiz-Hitzky, E, “Bionanocomposites, A New Concept of Ecological, Bioinspired, and Functional Hybrid Materials.” Adv. Mater., 19 1309–1316 (2007)
Mangiacapra, P, Gorrasi, G, Sorrentino, A, et al., “Biodegradable Nanocomposites Obtained by Ball Milling of Pectin and Montmorillonites.” Carbohyd. Polym., 64 516–523 (2006)
Jayakumar, R, Prabaharan, M, Sudheesh Kumar, PT, et al., “Biomaterials Based on Chitin/Chitosan in Wound Dressing Applications.” Biotechnol. Adv., 29 322–337 (2011)
Lim, S-H, Hudson, SM, “Synthesis Antimicrobial Activity of Water Soluble Chitosan Derivative with a Fibre-Reactive Group.” Carbohydr. Res., 339 313–319 (2004)
Sford, P, Skjak-Braek, G, Anthonsen, T, et al. (eds.), Chitin and Chitosan: Sources, Chemistry, Biochemistry, Physical Properties and Application, pp. 51–69. Elsevier Applied Science, London/New York (1989)
Petkova, P, Francesko, A, Fernes, MM, et al., “Sonochemical Coating of Textiles with Hybrid ZnO/Chitosan Antimicrobial Nanoparticles.” Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 6 1164–1172 (2014)
Kong, M, Chen, XG, Liu, CS, et al., “Antibacterial Mechanism of Chitosan Microspheres in a Solid Dispersing System Against E. coli.” Colloid Surf. B, 65 197–202 (2008)
Wang, X, Du, Y, Liu, H, “Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan–Zn Complex.” Carbohyd. Polym., 56 21–26 (2004)
Rajendran, K, Sivalingam, T, “Industrial Method of Cotton Fabric Finishing with Chitosan–ZnO Composite for Anti-bacterial and Thermal Stability.” Ind. Crops Prod., 47 160–167 (2013)
Farouk, A, Moussa, S, Ulbricht, M, et al., “ZnO Nanoparticles-Chitosan Composite as Antibacterial Finish for Textiles.” Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem., 2012 e693629 (2012)
Abd Elhady, MM, “Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles for Imparting Antimicrobial and UV Protection to Cotton Fabric.” Int. J. Carbohydr. Chem., 2012 e840591 (2012)
Jin, C, Jiang, Y, Niu, T, et al., “Cellulose-Based Material with Amphiphobicity to Inhibit Bacterial Adhesion by Surface Modification.” Mater. Chem., 22 2562–12567 (2012)
Alonso, D, Gimeno, M, Olayo, R, et al., “Cross Linking Chitosan into UV-Irradiated Cellulose Fibers for Preparation Antibacterial-Finished Textiles.” Carbohydr. Polym., 77 (3) 536–543 (2009)
Cheng, Q, Li, C, Pavlinek, V, et al., “Surface-Modified Antibacterial TiO2/Ag Nanoparticles, Preparation Properties.” Appl. Surf. Sci., 252 4154–4160 (2006)
Abdel-Mohsen, AM, Aly, AS, Hrdina, R, et al., “Antibacterial Activity and Cell Viability of Hyaluronan Fiber with Silver Nanoparticles.” J. Polym. Environ., 20 104–116 (2012)
Huang, J, Gu, Y, “Self-Assembly of Various Guest Substrates in Natural Cellulose Substances to Functional Nanostructured Materials.” Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface. Sci., 16 470–481 (2011)
Alongi, J, Ciobanu, M, Malucelli, G, “Thermal Stability, Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Cotton Fabrics Treated with Inorganic Coatings Synthesized Through Sol–Gel Processes.” Carbohydr. Polym., 87 2093–2099 (2012)
Harifi, T, Montazer, MA, “Review on Textile Sonoprocessing, A Special Focus on Sonosynthesis of Nanomaterials on Textile Substrates.” Ultrason. Sonochem., 23 1–10 (2015)
Rezapour, M, Talebian, N, “Comparison of Structural, Optical Properties and Photocatalytic Activity of ZnO with Different Morphologies: Effect of Synthesis Methods and Reaction Media.” Mater. Chem. Phys., 129 249–255 (2011)
Mathew, AP, Oksman, K, Sain, M, “Mechanical Properties of Biodegradable Composites from Poly Lactic Acid (PLA) and Microcrystalline Cellulose (MCC).” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 97 (5) 2014–2025 (2005)
Mridha, S, Basak, D, “Effect of Thickness on the Structural, Electrical and Optical Properties of ZnO Films.” Mater. Res. Bull., 42 875–882 (2007)
Ganesh, EP, Dnyaneshwar, DK, Gaikwad, VB, et al., “Preparation and Characterization of SnO2 Nanoparticles by Hydrothermal Route.” Int. Nano Lett., 2 (17) 1–5 (2012)
Perelshtein, I, Applerot, G, Perkas, N, et al., “A One-Step Process for the Antimicrobial Finishing of Textiles with Crystalline TiO2 Nanoparticles.” Chem. Eur. J., 18 4575–4582 (2012)
Perelshtein, I, Ruderman, E, Perkas, N, et al., “Chitosan and Chitosan–ZnO-Based Complex Nanoparticles, Formation, Characterization, and Antibacterial Activity.” J. Mater. Chem. B, 1 1968–1976 (2013)
Hirota, K, Sugimoto, M, Kato, M, et al., “Preparation of Zinc Oxide Ceramics with a Sustainable Antibacterial Activity Under Dark Conditions.” Ceram. Int., 36 497–506 (2010)
Song, W, Zhang, J, Guo, J, et al., “Role of the Dissolved Zinc Ion and Reactive Oxygen Species in Cytotoxicity of ZnO Nanoparticles.” Toxicol. Lett., 199 389–397 (2010)
Ma, H, Williams, PL, Diamond, SA, “Ecotoxicity of Manufactured ZnO Nanoparticles.” Environ. Pollut., 172 76–85 (2013)
Sasidharan, A, Parwathy, C, Menon, D, et al., “Rapid Dissolution of ZnO Nanocrystals in Acidic Cancer Microenvironment Leading to Preferential Apoptosis.” Nanoscale, 3 3657–3669 (2011)
Fukui, H, Horie, M, Endoh, S, et al., “Association of Zinc Ion Release and Oxidative Stress Induced by Intratracheal Instillation of ZnO Nanoparticles to Rat Lung.” Chem. Biol. Interact., 198 29–37 (2012)
Ding, F, Nie, Z, Deng, H, et al., “Antibacterial Hydrogel Coating by Electrophoretic Co-deposition of Chitosan/Alkynyl Chitosan.” Carbohydr. Polym., 98 1547–1552 (2013)
Wang, X, Du, Y, Liu, H, “Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activity of Chitosan–Zn Complex.” Carbohydr. Polym., 56 21–26 (2004)
Sanpui, P, Murugadoss, A, Prasad, PVD, et al., “Chattopadhyay, The Antibacterial Properties of a Novel Chitosan–Ag-Nanoparticle Composite.” Int. J. Food Microbiol., 124 142–146 (2008)
Wang, C, Lv, J, Ren, Y, et al., “Cotton Fabric with Plasma Pretreatment and ZnO/Carboxymethyl Chitosan Composite Finishing for Durable UV Resistance and Antibacterial Property.” Carbohydr. Polym., 138 106–113 (2016)
Rabea, EI, Badawy, MET, Stevens, CV, et al., “Chitosan as Antimicrobial Agent, Applications Mode of Action.” Biomacromolecules, 4 1457–1465 (2003)
Krishnaveni, R, Thambidurai, S, “Industrial Method of Cotton Fabric Finishing with Chitosan–ZnO Composite for Anti-bacterial and Thermal Stability.” Ind. Crops Prod., 47 160–167 (2013)
Li, L-H, Deng, J-C, Deng, HR, et al., “Preparation, Characterization and Antimicrobial Activities of Chitosan/Ag/ZnO Blend Films.” Chem. Eng. J., 160 378–382 (2010)
Orhan, M, Kut, D, Gunesoglu, C, “Improving the Antibacterial Activity of Cotton Fabrics Finished with Triclosan by the Use of 1,2,3,4-Butanetetracarboxylic Acid and Citric Acid.” J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 111 1344–1352 (2009)
Zhang, Y, Shao, CL, Li, XH, “Electrospun Nanofibers of ZnO–SnO2 Heterojunction with High Photocatalytic Activity.” J. Phys. Chem. C, 114 7920–7925 (2010)
Zhu, H-Y, Xiao, L, Jiang, R, et al., “Efficient Decolorization of Azo Dye Solution by Visible Light-Induced Photocatalytic Process Using SnO2/ZnO Heterojunction Immobilized in Chitosan Matrix.” Chem. Eng. J., 172 746–753 (2011)
Talebian, N, Doudi, M, Mogoei, H, “Antibacterial Activities of Sol–Gel Derived ZnO-Multilayered Thin Films, p-NiO Heterojunction Layer Effect.” J. Sol-Gel. Sci. Technol., 74 650–660 (2015)
Hans, M, Erbe, A, Mathews, S, et al., “Role of Copper Oxides in Contact Killing of Bacteria.” Langmuir, 29 (52) 16160–16166 (2013)
Gao, Y, Cranston, R, “Recent Advances in Antimicrobial Treatments of Textiles.” Text. Res. J., 78 (1) 60–72 (2008)
Suslick, KS, Price, GJ, “Applications of Ultrasound to Materials Chemistry.” Annu. Rev. Mater. Sci., 29 295–326 (1999)
Perelshtein, I, Ruderman, Y, Perkas, N, et al., “Enzymatic Pre-treatment as a Means of Enhancing the Antibacterial Activity and Stability of ZnO Nanoparticles Sonochemically Coated on Cotton Fabrics.” J. Mater. Chem., 22 10736–10742 (2012)
Yuranova, T, Laub, D, Kiwi, J, “Synthesis, Activity and Characterization of Textiles Showing Self-Cleaning Activity Under Daylight Irradiation.” Catal. Today, 122 109–117 (2007)
Nazari, A, Montazer, M, Yazdanshenas, ME, et al., “Nano TiO2 Photo-catalyst and Sodium Hypophosphite for Cross-linking Cotton with Poly Carboxylic Acids Under UV High Temperature.” Appl. Catal. A Gen., 371 10–16 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Islamic Azad University, Shahreza Branch, for financial support to carry out this project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamali, P., Talebian, N. Sonochemically sol–gel derived coating of textiles using heterojunction SnO2/ZnO/chitosan bionanocomposites: in vitro antibacterial evaluation. J Coat Technol Res 15, 1133–1144 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-018-0057-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11998-018-0057-4