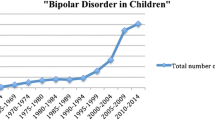
Abstract
Pediatric onset bipolar disorder (BD) is a challenging diagnosis with potentially debilitating outcomes. This review aims to critically evaluate recently published literature relevant to the diagnosis of BD in youth, emphasizing interesting and important new findings characterizing pediatric BD and reporting updates in the diagnostic and statistical manual relevant to this disorder in youth. Challenges regarding the diagnosis of BD will be discussed, in addition to important distinctions with other childhood disorders, including other bipolar spectrum disorders; major depressive disorder; dysthymia; disruptive mood dysregulation disorder (DMDD); attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and other disruptive behavioral disorders; anxiety disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD); psychotic disorders; autism spectrum disorders; substance use disorders; and borderline personality disorder. The review concludes with a comment on past research limitations and future directions in the field.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance
Perlis RH, Dennehy EB, Miklowitz DJ, Delbello MP, Ostacher M, Calabrese JR, et al. Retrospective age at onset of bipolar disorder and outcome during 2-year follow-up: results from the STEP-BD study. Bipolar Disord. 2009;11(4):391–400. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2009.00686.x.
McClellan J, Kowatch R, Findling RL. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with bipolar disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(1):107–25.
Singh MK, Chang K. The impact of bipolar disorder on selected areas of pediatric development: a research update. Pediatr Health. 2007;1(2):199–215.
Rocha TB, Zeni CP, Caetano SC, Kieling C. Mood disorders in childhood and adolescence. Rev Bras Psiquiatr. 2013;35 Suppl 1:S22–31. doi:10.1590/1516-4446-2013-S106.
Chang K, Steiner H, Ketter T. Studies of offspring of parents with bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet C: Semin Med Genet. 2003;123C(1):26–35. doi:10.1002/ajmg.c.20011.
Singh MK, DelBello MP, Stanford KE, Soutullo C, McDonough-Ryan P, McElroy SL, et al. Psychopathology in children of bipolar parents. J Affect Disord. 2007;102(1–3):131–6. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2007.01.004.
Axelson DA, Birmaher B, Strober MA, Goldstein BI, Ha W, Gill MK, et al. Course of subthreshold bipolar disorder in youth: diagnostic progression from bipolar disorder not otherwise specified. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;50(10):1001–16 e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.07.005.
Chang K. Challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of pediatric bipolar depression. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2009;11(1):73–80.
Chang KD. Diagnosing bipolar disorder in children and adolescents. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70(11):e41. doi:10.4088/JCP.8125tx6c.
Chang KD. Course and impact of bipolar disorder in young patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(2):e05. doi:10.4088/JCP.8125tx7c.
Cosgrove VE, Roybal D, Chang KD. Bipolar depression in pediatric populations: epidemiology and management. Paediatr Drugs. 2013;15(2):83–91. doi:10.1007/s40272-013-0022-8.
Ketter TA. Handbook of diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder. Washington: American Psychiatric Publishing, Inc.; 2010.
Van Meter AR, Moreira AL, Youngstrom EA. Meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies of pediatric bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2011;72(9):1250–6. doi:10.4088/JCP.10m06290.
Merikangas KR, Lamers F. The ‘true’ prevalence of bipolar II disorder. Curr Opin Psychiatry. 2012;25(1):19–23. doi:10.1097/YCO.0b013e32834de3de.
Merikangas KR, Cui L, Kattan G, Carlson GA, Youngstrom EA, Angst J. Mania with and without depression in a community sample of US adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2012;69(9):943–51. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2012.38.
Moreno C, Laje G, Blanco C, Jiang H, Schmidt AB, Olfson M. National trends in the outpatient diagnosis and treatment of bipolar disorder in youth. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2007;64(9):1032–9.
Weintraub M, Youngstrom EA, Marvin SE, Podell JL, Walshaw PD, Kim EY, et al. Diagnostic profiles and clinical characteristics of youth referred to a pediatric mood disorders clinic. J Psychiatr Pract. 2014;20(2):154–62. doi:10.1097/01.pra.0000445251.20875.47.
Post RM, Leverich GS, Kupka R, Keck Jr P, McElroy S, Altshuler L, et al. Increased parental history of bipolar disorder in the United States: association with early age of onset. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 2014;129(5):375–82. doi:10.1111/acps.12208.
Post RM, Altshuler L, Kupka R, McElroy S, Frye MA, Rowe M, et al. More pernicious course of bipolar disorder in the United States than in many European countries: implications for policy and treatment. J Affect Disord. 2014;160:27–33. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2014.02.006.
James A, Hoang U, Seagroatt V, Clacey J, Goldacre M, Leibenluft E. A comparison of American and English hospital discharge rates for pediatric bipolar disorder, 2000–2010. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;53(6):614–24. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2014.02.008.
Weissman MM, Bland RC, Canino GJ, Faravelli C, Greenwald S, Hwu HG, et al. Cross-national epidemiology of major depression and bipolar disorder. JAMA. 1996;276(4):293–9.
Soutullo CA, Escamilla-Canales I, Wozniak J, Gamazo-Garran P, Figueroa-Quintana A, Biederman J. Pediatric bipolar disorder in a Spanish sample: features before and at the time of diagnosis. J Affect Disord. 2009;118(1–3):39–47. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2009.02.010.
Soutullo CA, Chang KD, Diez-Suarez A, Figueroa-Quintana A, Escamilla-Canales I, Rapado-Castro M, et al. Bipolar disorder in children and adolescents: international perspective on epidemiology and phenomenology. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(6):497–506.
Reichart CG, Nolen WA. Earlier onset of bipolar disorder in children by antidepressants or stimulants? An hypothesis. J Affect Disord. 2004;78(1):81–4.
Goldsmith M, Singh M, Chang K. Antidepressants and psychostimulants in pediatric populations: is there an association with mania? Paediatr Drugs. 2011;13(4):225–43. doi:10.2165/11591660-000000000-00000.
Kim EY, Miklowitz DJ. Childhood mania, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and conduct disorder: a critical review of diagnostic dilemmas. Bipolar Disord. 2002;4(4):215–25.
Freeman AJ, Youngstrom EA, Freeman MJ, Youngstrom JK, Findling RL. Is caregiver-adolescent disagreement due to differences in thresholds for reporting manic symptoms? J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2011;21(5):425–32. doi:10.1089/cap.2011.0033.
Bhargava Raman RP, Sheshadri SP, Janardhan Reddy YC, Girimaji SC, Srinath S, Raghunandan VN. Is bipolar II disorder misdiagnosed as major depressive disorder in children? J Affect Disord. 2007;98(3):263–6. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2006.08.006.
Singh MK, DelBello MP, Kowatch RA, Strakowski SM. Co-occurrence of bipolar and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorders in children. Bipolar Disord. 2006;8(6):710–20. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2006.00391.x.
Chang KD. The bipolar spectrum in children and adolescents: developmental issues. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008;69(3):e9.
Correll CU, Hauser M, Penzner JB, Auther AM, Kafantaris V, Saito E, et al. Type and duration of subsyndromal symptoms in youth with bipolar I disorder prior to their first manic episode. Bipolar Disord. 2014. doi:10.1111/bdi.12194. Among a sample of 52 youth with BD-I, a long, slow-onset mania prodrome that included both subthreshold manic and depressive symptoms was found to be common.
Correll CU, Olvet DM, Auther AM, Hauser M, Kishimoto T, Carrion RE, et al. The bipolar prodrome symptom interview and scale-prospective (BPSS-P): description and validation in a psychiatric sample and healthy controls. Bipolar Disord. 2014. doi:10.1111/bdi.12209.
Youngstrom E, Youngstrom JK, Starr M. Bipolar diagnoses in community mental health: Achenbach child behavior checklist profiles and patterns of comorbidity. Biol Psychiatry. 2005;58(7):569–75. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2005.04.004.
American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, fifth edition (DSM-5). Washington: American Psychiatric Association; 2013.
Towbin K, Axelson D, Leibenluft E, Birmaher B. Differentiating bipolar disorder-not otherwise specified and severe mood dysregulation. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;52(5):466–81. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.02.006.
Leibenluft E. Severe mood dysregulation, irritability, and the diagnostic boundaries of bipolar disorder in youths. Am J Psychiatry. 2011;168(2):129–42. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2010.10050766.
Axelson D, Findling RL, Fristad MA, Kowatch RA, Youngstrom EA, Horwitz SM, et al. Examining the proposed disruptive mood dysregulation disorder diagnosis in children in the longitudinal assessment of manic symptoms study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2012;73(10):1342–50. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07674. Using data from the LAMS study, DMDD was found to be diagnostically unstable, unassociated with parental history, current, or future-onset mood or anxiety disorders, and unable to be delimited from oppositional defiant disorder or conduct disorder.
Youngstrom EA, Birmaher B, Findling RL. Pediatric bipolar disorder: validity, phenomenology, and recommendations for diagnosis. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(1 Pt 2):194–214. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2007.00563.x.
Akiskal HS, Pinto O. The evolving bipolar spectrum. Prototypes I, II, III, and IV. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 1999;22(3):517–34.
Parens E, Johnston J, Carlson GA. Pediatric mental health care dysfunction disorder? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(20):1853–5. doi:10.1056/NEJMp1003175.
Bebko G, Bertocci MA, Fournier JC, Hinze AK, Bonar L, Almeida JR, et al. Parsing dimensional vs diagnostic category-related patterns of reward circuitry function in behaviorally and emotionally dysregulated youth in the longitudinal assessment of manic symptoms study. JAMA Psychiatry. 2014;71(1):71–80. doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2013.2870. Reward-related neurophysiologic features in behaviorally and emotionally dysregulated youth from the LAMS study support a dimensional approach of study.
Findling RL, Jo B, Frazier TW, Youngstrom EA, Demeter CA, Fristad MA, et al. The 24-month course of manic symptoms in children. Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(6):669–79. doi:10.1111/bdi.12100.
Wozniak J, Petty CR, Schreck M, Moses A, Faraone SV, Biederman J. High level of persistence of pediatric bipolar-I disorder from childhood onto adolescent years: a 4 year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Psychiatr Res. 2011;45(10):1273–82. doi:10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.10.006.
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Goldstein B, Strober M, Gill MK, Hunt J, et al. Four-year longitudinal course of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders: the course and outcome of bipolar youth (COBY) study. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(7):795–804. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.08101569.
Birmaher B, Gill MK, Axelson DA, Goldstein BI, Goldstein TR, Yu H, et al. Longitudinal trajectories and associated baseline predictors in youths with bipolar spectrum disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 2014. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.13121577. In this study of 367 youths with BD, a significant proportion was found to be euthymic over extended periods of time.
Safer DJ, Magno Zito J, Safer AM. Age-grouped differences in bipolar mania. Compr Psychiatry. 2012;53(8):1110–7. doi:10.1016/j.comppsych.2012.04.011.
Demeter CA, Youngstrom EA, Carlson GA, Frazier TW, Rowles BM, Lingler J, et al. Age differences in the phenomenology of pediatric bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 2013;147(1–3):295–303. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2012.11.021.
Wozniak J, Biederman J, Martelon MK, Hernandez M, Woodworth KY, Faraone SV. Does sex moderate the clinical correlates of pediatric bipolar-I disorder? Results from a large controlled family-genetic study. J Affect Disord. 2013;149(1–3):269–76. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.01.040.
Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, Bolhofner K, Craney JL, Delbello MP, et al. Diagnostic characteristics of 93 cases of a prepubertal and early adolescent bipolar disorder phenotype by gender, puberty and comorbid attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2000;10(3):157–64. doi:10.1089/10445460050167269.
Goldstein BI. Recent progress in understanding pediatric bipolar disorder. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2012;166(4):362–71. doi:10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.832.
Hunt JI, Case BG, Birmaher B, Stout RL, Dickstein DP, Yen S, et al. Irritability and elation in a large bipolar youth sample: relative symptom severity and clinical outcomes over 4 years. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(1):e110–7. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07874.
Biederman J, Petty CR, Wozniak J, Wilens TE, Fried R, Doyle A, et al. Impact of executive function deficits in youth with bipolar I disorder: a controlled study. Psychiatry Res. 2011;186(1):58–64. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2010.08.029.
Lera-Miguel S, Andres-Perpina S, Calvo R, Fatjo-Vilas M, Fananas L, Lazaro L. Early-onset bipolar disorder: how about visual-spatial skills and executive functions? Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2011;261(3):195–203. doi:10.1007/s00406-010-0169-z.
Jacobs RH, Pavuluri MN, Schenkel LS, Palmer A, Shah K, Vemuri D, et al. Negative emotion impacts memory for verbal discourse in pediatric bipolar disorder. Bipolar Disord. 2011;13(3):287–93. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2011.00922.x.
Schenkel LS, Passarotti AM, Sweeney JA, Pavuluri MN. Negative emotion impairs working memory in pediatric patients with bipolar disorder type I. Psychol Med. 2012;42(12):2567–77. doi:10.1017/S0033291712000797.
Schenkel LS, West AE, Jacobs R, Sweeney JA, Pavuluri MN. Cognitive dysfunction is worse among pediatric patients with bipolar disorder type I than type II. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2012;53(7):775–81. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2011.02519.x. BD-I youth were found to have worse performance than BD-II youth on all domains of cognitive functioning except for working memory. BD-II youth performed more poorly compared to healthy controls only on memory and verbal learning, which may act as a cognitive endophenotype for BD.
Van Meter A, Youngstrom EA, Youngstrom JK, Feeny NC, Findling RL. Examining the validity of cyclothymic disorder in a youth sample. J Affect Disord. 2011;132(1–2):55–63. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2011.02.004.
Van Meter A, Youngstrom EA, Demeter C, Findling RL. Examining the validity of cyclothymic disorder in a youth sample: replication and extension. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2013;41(3):367–78. doi:10.1007/s10802-012-9680-1.
Akiskal HS, Djenderedjian AM, Rosenthal RH, Khani MK. Cyclothymic disorder: validating criteria for inclusion in the bipolar affective group. Am J Psychiatry. 1977;134(11):1227–33.
Dunner DL, Russek FD, Russek B, Fieve RR. Classification of bipolar affective disorder subtypes. Compr Psychiatry. 1982;23(2):186–9.
Howes OD, Lim S, Theologos G, Yung AR, Goodwin GM, McGuire P. A comprehensive review and model of putative prodromal features of bipolar affective disorder. Psychol Med. 2011;41(8):1567–77. doi:10.1017/S0033291710001790.
Youngstrom E, Van Meter A. Validating cyclothymic disorder in youth. Nice: International Review of Bipolar Disorders; 2012.
Kessler RC, Avenevoli S, Ries MK. Mood disorders in children and adolescents: an epidemiologic perspective. Biol Psychiatry. 2001;49(12):1002–14.
Howland RH, Thase ME. A comprehensive review of cyclothymic disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis. 1993;181(8):485–93.
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Strober M, Gill MK, Valeri S, Chiappetta L, et al. Clinical course of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(2):175–83. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.2.175.
Schraufnagel CD, Brumback RA, Harper CR, Weinberg WA. Affective illness in children and adolescents: patterns of presentation in relation to pubertal maturation and family history. J Child Neurol. 2001;16(8):553–61.
McElroy SL, Strakowski SM, West SA, Keck Jr PE, McConville BJ. Phenomenology of adolescent and adult mania in hospitalized patients with bipolar disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 1997;154(1):44–9.
Van Meter AR, Youngstrom EA. Cyclothymic disorder in youth: why is it overlooked, what do we know and where is the field headed? Neuropsychiatry (London). 2012;2(6):509–19. doi:10.2217/npy.12.64.
Axelson D, Birmaher B, Strober M, Gill MK, Valeri S, Chiappetta L, et al. Phenomenology of children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2006;63(10):1139–48. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.10.1139.
Hafeman D, Axelson D, Demeter C, Findling RL, Fristad MA, Kowatch RA, et al. Phenomenology of bipolar disorder not otherwise specified in youth: a comparison of clinical characteristics across the spectrum of manic symptoms. Bipolar Disord. 2013;15(3):240–52. doi:10.1111/bdi.12054.
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Monk K, Kalas C, Goldstein B, Hickey MB, et al. Lifetime psychiatric disorders in school-aged offspring of parents with bipolar disorder: the Pittsburgh bipolar offspring study. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2009;66(3):287–96. doi:10.1001/archgenpsychiatry.2008.546.
Ladouceur CD, Farchione T, Diwadkar V, Pruitt P, Radwan J, Axelson DA, et al. Differential patterns of abnormal activity and connectivity in the amygdala-prefrontal circuitry in bipolar-I and bipolar-NOS youth. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2011;50(12):1275–89 e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2011.09.023.
Geller B, Zimerman B, Williams M, Bolhofner K, Craney JL. Bipolar disorder at prospective follow-up of adults who had prepubertal major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2001;158(1):125–7.
Birmaher B, Brent D, Issues AWGoQ, Bernet W, Bukstein O, Walter H, et al. Practice parameter for the assessment and treatment of children and adolescents with depressive disorders. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007;46(11):1503–26. doi:10.1097/chi.0b013e318145ae1c.
Van Meter AR, Henry DB, West AE. What goes up must come down: the burden of bipolar depression in youth. J Affect Disord. 2013;150(3):1048–54. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.05.039. Findings suggest that depression in youth with bipolar spectrum disorders is more detrimental to functioning and quality of life than mania.
Birmaher B, Axelson D, Strober M, Gill MK, Yang M, Ryan N, et al. Comparison of manic and depressive symptoms between children and adolescents with bipolar spectrum disorders. Bipolar Disord. 2009;11(1):52–62. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2008.00659.x.
Lish JD, Dime-Meenan S, Whybrow PC, Price RA, Hirschfeld RM. The national depressive and manic-depressive association (DMDA) survey of bipolar members. J Affect Disord. 1994;31(4):281–94.
Hirschfeld RM, Lewis L, Vornik LA. Perceptions and impact of bipolar disorder: how far have we really come? Results of the national depressive and manic-depressive association 2,000 survey of individuals with bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychiatry. 2003;64(2):161–74.
Bowden CL. Strategies to reduce misdiagnosis of bipolar depression. Psychiatr Serv. 2001;52(1):51–5.
Wozniak J, Spencer T, Biederman J, Kwon A, Monuteaux M, Rettew J, et al. The clinical characteristics of unipolar vs. bipolar major depression in ADHD youth. J Affect Disord. 2004;82 Suppl 1:S59–69. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2004.05.013.
Mitchell PB, Goodwin GM, Johnson GF, Hirschfeld RMA. Diagnostic guidelines for bipolar depression: a probabilistic approach. Bipolar Disord. 2008;10(1p2):144–52.
Diler RS, Pan LA, Segreti A, Ladouceur CD, Forbes E, Cela SR, et al. Differential anterior cingulate activity during response inhibition in depressed adolescents with bipolar and unipolar major depressive disorder. J Can Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2014;23(1):10–9.
Diler RS, de Almeida JR, Ladouceur C, Birmaher B, Axelson D, Phillips M. Neural activity to intense positive versus negative stimuli can help differentiate bipolar disorder from unipolar major depressive disorder in depressed adolescents: a pilot fMRI study. Psychiatry Res. 2013;214(3):277–84. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2013.06.013.
Copeland WE, Angold A, Costello EJ, Egger H. Prevalence, comorbidity, and correlates of DSM-5 proposed disruptive mood dysregulation disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(2):173–9. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2012.12010132. Prevalence, comorbidity, and correlates of DMDD were estimated using data from three community studies. Findings indicate that DMDD is uncommon after early childhood and is comorbid with other psychiatric disorders 62–92% of the time. DMDD was also found to meet common standards for psychiatric “caseness”.
Leibenluft E, Cohen P, Gorrindo T, Brook JS, Pine DS. Chronic versus episodic irritability in youth: a community-based, longitudinal study of clinical and diagnostic associations. J Child Adolesc Psychopharmacol. 2006;16(4):456–66. doi:10.1089/cap.2006.16.456.
Stringaris A, Cohen P, Pine DS, Leibenluft E. Adult outcomes of youth irritability: a 20-year prospective community-based study. Am J Psychiatry. 2009;166(9):1048–54. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.08121849.
Brotman MA, Schmajuk M, Rich BA, Dickstein DP, Guyer AE, Costello EJ, et al. Prevalence, clinical correlates, and longitudinal course of severe mood dysregulation in children. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(9):991–7. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.08.042.
Deveney CM, Connolly ME, Haring CT, Bones BL, Reynolds RC, Kim P, et al. Neural mechanisms of frustration in chronically irritable children. Am J Psychiatry. 2013;170(10):1186–94. doi:10.1176/appi.ajp.2013.12070917.
Kowatch RA, Youngstrom EA, Danielyan A, Findling RL. Review and meta-analysis of the phenomenology and clinical characteristics of mania in children and adolescents. Bipolar Disord. 2005;7(6):483–96. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2005.00261.x.
Seymour KE, Pescosolido MF, Reidy BL, Galvan T, Kim KL, Young M, et al. Emotional face identification in youths with primary bipolar disorder or primary attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2013;52(5):537–46 e3. doi:10.1016/j.jaac.2013.03.011. Emotional face identification was assessed in youth ages 7–17 years with pediatric BD, ADHD, and healthy controls. Results indicate that youths with BD have specific emotional face-identification alterations when identifying happy faces.
Arnold LE, Demeter C, Mount K, Frazier TW, Youngstrom EA, Fristad M, et al. Pediatric bipolar spectrum disorder and ADHD: comparison and comorbidity in the LAMS clinical sample. Bipolar Disord. 2011;13(5–6):509–21. doi:10.1111/j.1399-5618.2011.00948.x.
Doerfler LA, Connor DF, Toscano Jr PF. Aggression, ADHD symptoms, and dysphoria in children and adolescents diagnosed with bipolar disorder and ADHD. J Affect Disord. 2011;131(1–3):312–9. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2010.11.029.
Young ME, Galvan T, Reidy BL, Pescosolido MF, Kim KL, Seymour K, et al. Family functioning deficits in bipolar disorder and ADHD in youth. J Affect Disord. 2013;150(3):1096–102. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2013.04.027.
Rucklidge JJ. Impact of ADHD on the neurocognitive functioning of adolescents with bipolar disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(9):921–8. doi:10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.03.067.
Udal AH, Oygarden B, Egeland J, Malt UF, Groholt B. Memory in early onset bipolar disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: similarities and differences. J Abnorm Child Psychol. 2012;40(7):1179–92. doi:10.1007/s10802-012-9631-x.
Mattis S, Papolos D, Luck D, Cockerham M, Thode Jr HC. Neuropsychological factors differentiating treated children with pediatric bipolar disorder from those with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol. 2011;33(1):74–84. doi:10.1080/13803395.2010.493146.
Liu IY, Howe M, Garrett A, Karchemskiy A, Kelley R, Alegria D, et al. Striatal volumes in pediatric bipolar patients with and without comorbid ADHD. Psychiatry Res. 2011;194(1):14–20. doi:10.1016/j.pscychresns.2011.06.008.
Passarotti AM, Pavuluri MN. Brain functional domains inform therapeutic interventions in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and pediatric bipolar disorder. Expert Rev Neurother. 2011;11(6):897–914. doi:10.1586/ern.11.71.
Castilla-Puentes R, Sala R, Ng B, Galvez J, Camacho A. Anxiety disorders and rapid cycling: data from a cohort of 8,129 youths with bipolar disorder. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2013;201(12):1060–5. doi:10.1097/NMD.0000000000000052.
Biederman J, Wozniak J, Martelon MK, Spencer TJ, Woodworth Y, Joshi G, et al. Can pediatric bipolar-I disorder be diagnosed in the context of posttraumatic stress disorder? A familial risk analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2013;208(3):215–24. doi:10.1016/j.psychres.2013.05.011.
Pavuluri MN, Herbener ES, Sweeney JA. Psychotic symptoms in pediatric bipolar disorder. J Affect Disord. 2004;80(1):19–28. doi:10.1016/S0165-0327(03)00053-3.
Malaspina D, Owen MJ, Heckers S, Tandon R, Bustillo J, Schultz S, et al. Schizoaffective disorder in the DSM-5. Schizophr Res. 2013;150(1):21–5. doi:10.1016/j.schres.2013.04.026.
Nieto RG, Castellanos FX. A meta-analysis of neuropsychological functioning in patients with early onset schizophrenia and pediatric bipolar disorder. J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol. 2011;40(2):266–80. doi:10.1080/15374416.2011.546049.
Parellada M, Fraguas D, Bombin I, Otero S, Castro-Fornieles J, Baeza I, et al. Insight correlates in child- and adolescent-onset first episodes of psychosis: results from the CAFEPS study. Psychol Med. 2009;39(9):1433–45. doi:10.1017/S0033291708004868.
Joshi G, Biederman J, Petty C, Goldin RL, Furtak SL, Wozniak J. Examining the comorbidity of bipolar disorder and autism spectrum disorders: a large controlled analysis of phenotypic and familial correlates in a referred population of youth with bipolar I disorder with and without autism spectrum disorders. J Clin Psychiatry. 2013;74(6):578–86. doi:10.4088/JCP.12m07392.
Chiu S, Widjaja F, Bates ME, Voelbel GT, Pandina G, Marble J, et al. Anterior cingulate volume in pediatric bipolar disorder and autism. J Affect Disord. 2008;105(1–3):93–9. doi:10.1016/j.jad.2007.04.019.
Goldstein BI, Bukstein OG. Comorbid substance use disorders among youth with bipolar disorder: opportunities for early identification and prevention. J Clin Psychiatry. 2010;71(3):348–58. doi:10.4088/JCP.09r05222gry.
Ghaemi SN, Dalley S. The bipolar spectrum: conceptions and misconceptions. Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2014;48(4):314–24. doi:10.1177/0004867413504830.
Compliance with Ethics Guidelines
Conflict of Interest
Manpreet K. Singh declares no conflict of interest. Dr. Singh receives research support from Stanford Child Health Research Institute.
Kiki D. Chang receives research support from the National Institute of Mental Health and Stanford University. Dr. Chang is also an unpaid consultant for GlaxoSmithKline, Eli Lilly, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. He is on the Data Safety Monitoring Board for Sunovion. In the past two years, he has received research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Merck.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Bipolar Disorders
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, M.K., Ketter, T. & Chang, K.D. Distinguishing Bipolar Disorder From Other Psychiatric Disorders in Children. Curr Psychiatry Rep 16, 516 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-014-0516-2
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-014-0516-2