Abstract
Aim
Surfing is increasing in popularity in Ireland. Exostoses of the external auditory canal are a common finding in those who surf in cold water. The aim of this study was to examine the prevalence of external canal exostoses in a population of Irish surfers.
Methods
A cross-sectional study of Irish surfers was carried out. Patients were examined and questioned on their knowledge of exostoses, surfing routine, use of barrier protection and symptoms experienced.
Results
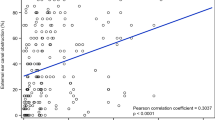
119 surfers were analysed. 66 % of the surfers examined exhibited exostoses and 88 % were unaware of their diagnosis. Those that developed exostoses had surfed for a mean of 5,028 h, those that did not had surfed for a significantly shorter mean of 1,909 h (p = 0.0002).
Conclusions
This is first study of this nature in the UK or Ireland. With a 5- to 6-year lag phase for exostoses to develop, these patients are likely to become an increasing part of Otolaryngologist’s workload.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Van Gilse P (1938) Des observations ulterieures sur la genese exostoses du conduit externe par l’iritatio d’eau froid. Acta Otolaryngol 26:343–352
Ito M, Ikeda M (1998) Does cold water truly promote diver’s ear? Undersea Hyperb Med 25:59–62
Fabiani M, Barbara M, Filipo R (1984) External ear canal exostosis and aquatic sports. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 46:159–164
Karegeannes JC (1995) Incidence of bony outgrowths of the external ear canal in US Navy divers. Undersea Hyperb Med 22:301–306
Timofeev I, Notkina N, Smith IM (2004) Exostoses of the external auditory canal: a long-term follow-up study of surgical treatment. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 29:588–594
Cooper A, Tong R, Neil R, Owens D, Tomkinson A (2010) External auditory canal exostoses in white water kayakers. Br J Sports Med 44:144–147
History See http://www.isasurf.ie/history/ for further details. Accessed 31 Oct 2012
Sea Temperatures See http://www.met.ie/marine/marine_climatology.asp for further details. Accessed 31 Oct 12
Kroon DF, Lawson ML, Derkay CS, Hoffmann K, McCook J (2002) Surfer’s ear: external auditory exostoses are more prevalent in cold water surfers. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 126:499–504
Chaplin JM, Stewart IA (1998) The prevalence of exostoses in the external auditory meatus of surfers. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci 23:326–330
Nakanishi H, Tono T, Kawano H (2011) Incidence of external auditory canal exostoses in competitive surfers in Japan. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 145:80–85
Wong BJ, Cervantes W, Doyle KJ et al (1999) Prevalence of external auditory canal exostoses in surfers. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:969–972
Altuna Mariezkurrena X, Gomez Suarez J, Luqui Albisua I, Vea Orte JC, Algaba Guimera J (2004) Prevalence of exostoses among surfers of the Basque Coast. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp 55:364–368
Hurst W, Bailey M, Hurst B (2004) Prevalence of external auditory canal exostoses in Australian surfboard riders. J Laryngol Otol 118:348–351
DiBartolomeo JR (1979) Exostoses of the external auditory canal. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl 88:2–20
King JF, Kinney AC, Iacobellis SF 2nd et al (2010) Laterality of exostosis in surfers due to evaporative cooling effect. Otol Neurotol 31:345–351
Umeda Y, Nakajima M, Yoshioka H (1989) Surfer’s ear in Japan. Laryngoscope 99:639–641
Kennedy GE (1986) The relationship between auditory exostoses and cold water: a latitudinal analysis. Am J Phys Anthropol 71:401–415
Sheard PW, Doherty M (2008) Prevalence and severity of external auditory exostoses in breath-hold divers. J Laryngol Otol 122:1162–1167
Deleyiannis FW, Cockcroft BD, Pinczower EF (1996) Exostoses of the external auditory canal in Oregon surfers. Am J Otolaryngol 17:303–307
Reddy VM, Abdelrahman T, Lau A, Flanagan PM (2011) Surfers’ awareness of the preventability of ‘surfer’s ear’ and use of water precautions. J Laryngol Otol. doi:10.1017/S0022215111000041
Moore RD, Schuman TA, Scott TA, Mann SE, Davidson MA, Labadie RF (2010) Exostoses of the external auditory canal in white-water kayakers. Laryngoscope 120(3):582–590. doi:10.1002/lary.20781
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lennon, P., Murphy, C., Fennessy, B. et al. Auditory canal exostoses in Irish surfers. Ir J Med Sci 185, 183–187 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1265-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-015-1265-x