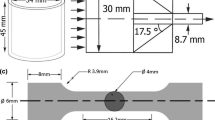
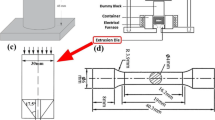
Abstract
A powder-processed hot-extruded high-performance Mg-0.5 wt.% Cu alloy has been developed by solid-state diffusion of elemental copper into commercially pure magnesium powder. Copper, in nanoparticle form, was blended to form a dry-coat layer on micrometer-size magnesium particles, which subsequently homogeneously diffused, forming a single-phase solid solution during the sintering process. Copper as a solute atom did not act as a grain refiner. Investigation of the mechanical properties revealed that the strength properties of commercially pure magnesium were significantly improved (macrohardness by 32.5%, microhardness by 42.7%, tensile yield strength by 114%, tensile strength by 69%, compressive yield strength by 46%, and compressive strength by 48%) due to the dissolution of copper as solute atoms. The ductility of the magnesium suffered marginal loss despite the fracture mode being ductile, which was due to decohesion at the magnesium interparticle boundaries induced by the relatively higher copper concentration.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.K. Kulekci, Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 39, 851 (2008).
I. Ostrovsky and Y. Henn, in International Conference on New Challenges in Aeronautics, Moscow (2007), p. 1.
J. Deetz, JOM 57, 51 (2005).
G. Manoj and G. Shwetabh, JOJ Mater. Sci. 2, 002–555598 (2017).
X. Chen, L. Liu, F. Pan, J. Mao, X. Xu, and T. Yan, Mater. Sci. Eng., B 197, 67 (2015).
X. Chen, J. Liu, and F. Pan, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 74, 872 (2013).
S.K. Oh, H.W. Kim, M.J. Kim, K.S. Eom, J.S. Kyung, D.H. Kim, E.A. Cho, and H.S. Kwon, J. Alloys Compd. 741, 590 (2018).
S. Oh, M. Kim, K. Eom, J. Kyung, D. Kim, E. Cho, and H. Kwon, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 5296 (2016).
S. Oh, T. Jo, M. Kim, J. Lim, K. Eom, D. Kim, E. Cho, and H. Kwon, Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 42, 7761 (2017).
M.P. Staiger, A.M. Pietak, J. Huadmai, and G. Dias, Biomaterials 27, 1728 (2006).
Y. Zhao, M.I. Jamesh, W.K. Li, G. Wu, C. Wang, Y. Zheng, K.W.K. Yeung, and P.K. Chu, Acta Biomater. 10, 544 (2014).
A.M. Kumar, S.F. Hassan, A.A. Sorour, M. Paramsothy, and M. Gupta, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 27, 3419 (2018).
C. Liu, X. Fu, H. Pan, P. Wan, L. Wang, L. Tan, K. Wang, Y. Zhao, K. Yang, and P.K. Chu, Sci. Rep. 6, 27374 (2016).
M. Lotfpour, M. Emamy, C. Dehghanian, and K. Tavighi, J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 26, 2136 (2017).
M.O. Pekguleryuz and A.A. Kaya, Adv. Eng. Mater. 5, 866 (2003).
J.H. Jun, J.M. Kim, B.K. Park, K.T. Kim, and W.J. Jung, J. Mater. Sci. 40, 2659 (2005).
S. Golmakaniyoon and R. Mahmudi, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 5228 (2011).
J. Buha, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 489, 127 (2008).
S. Zhu, T. Luo, T. Zhang, Y. Li, and Y. Yang, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 689, 203 (2017).
J. Wang, R. Liu, T. Luo, and Y. Yang, Mater. Des. 47, 746 (2013).
Z. Zhang, A. Couture, and A. Luo, Scr. Mater. 39, 45 (1998).
J. Zhang, Z.X. Guo, F.S. Pan, Z.S. Li, and X.D. Luo, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 456, 43 (2007).
H.M. Zhu, G. Sha, J.W. Liu, C.L. Wu, C.P. Luo, Z.W. Liu, R.K. Zheng, and S.P. Ringer, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3526 (2011).
M.L. He, T.J. Luo, Y.T. Liu, T. Lin, J.X. Zhou, and Y.S. Yang, J. Alloys Compd. 767, 1216 (2018).
H.M. Zhu, C.P. Luo, J.W. Liu, and D.L. Jiao, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 24, 605 (2014).
H.M. Zhu, C.P. Luo, J.W. Liu, and D.L. Jiao, Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 24, 316 (2014).
M. Hansen, J. Inst. Met. 37, 93 (1927).
N.I. Stepanov and I.I. Kornilov, Izv. Inst. Fiz.-Khim. Analisa 7, 89 (1935).
A.A. Nayeb-Hashemi and J.B. Clark, Bull. Alloy Phase Diagr. 5, 36 (1984).
S.F. Hassan and M. Gupta, Mater. Sci. Technol. 19, 253 (2003).
J. Dai, B. Jiang, J. Zhang, Q. Yang, Z. Jiang, H. Dong, and F. Pan, J. Phase Equilib. Diffus. 36, 613 (2015).
S.F. Hassan, M.T. Islam, S. Nouari, N. Al-Aqeeli, M.M.A. Baig, and F. Patel, J. Alloys Compd. 787, 1015 (2019).
S. Fida Hassan, O. Siddiqui, M.F. Ahmed, and A.I. AlNawwah, J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 141, 021007 (2018).
Powder Diffraction File (International Center for Diffraction Data. Swarthmore, USA, 1991).
W.D. Callister and D.G. Rethwisch, Materials Science and Engineering: An Introduction, 8th ed. (New York: Wiley, 2011), pp. 226–227.
P. Burke, G.J. Kipouros, D. Fancelli, and V. Laverdiere, Can. Metall. Q. 48, 123 (2009).
P. Burke, C. Petit, V. Vuaroqueaux, A. Doyle, and G.J. Kipouros, Can. Metall. Q. 50, 240 (2011).
Y.Q. Zhang, S.M. Du, and J. Hu, MATEC Web of Conference 67, 03035 (2016).
S.F. Hassan, O.O. Nasirudeen, N. Al-Aqeeli, N. Saheb, M.M.A. Baig, and F. Patel, J. Mater. Res. 33, 130 (2018).
A.C. Hänzi, A. Sologubenko, P. Gunde, M. Schinhammer, and P.J. Uggowitzer, Philos. Mag. Lett. 92, 417 (2012).
M.R. Barnett, C.H.J. Davies, and X. Ma, Scr. Mater. 52, 627 (2005).
R.E. Reed-Hill, Physical Metallurgy Principles, 2nd ed. (New York: D. Van Nostrand Company, 1964), pp. 192–194.
W.F. Hosford, The Mechanics of Crystals and Textures Polycrystals (New York: Oxford University Press, 1993).
G.S. KIM, Small Volume Investigation of Slip and Twinning in Magnesium Single Crystals (Doctoral Thesis, Université Grenoble, 2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the support provided by the Deanship of Scientific Research (DSR) at King Fahd University of Petroleum and Minerals (KFUPM) for funding this work through Project No. IN151019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassan, S.F., Islam, M.T., Nouari, S. et al. Extraordinary Strengthening of Magnesium by Solid-State Diffusion of Copper in Mg-0.5Cu Alloy. JOM 72, 1597–1606 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04023-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-020-04023-9