Abstract
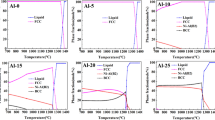
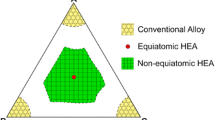
The proposal of configurational entropy maximization to produce massive solid-solution (SS)-strengthened, single-phase high-entropy alloy (HEA) systems has gained much scientific interest. Although most of this interest focuses on the basic role of configurational entropy in SS formability, setting future research directions also requires the overall property benefits of massive SS strengthening to be carefully investigated. To this end, taking the most promising CoCrFeMnNi HEA system as the starting point, we investigate SS formability, deformation mechanisms, and the achievable mechanical property ranges of different compositions and microstructural states. A comparative assessment of the results with respect to room temperature behavior of binary Fe-Mn alloys reveals only limited benefits of massive SS formation. Nevertheless, the results also clarify that the compositional requirements in this alloy system to stabilize the face-centered cubic (fcc) SS are sufficiently relaxed to allow considering nonequiatomic compositions and exploring improved strength–ductility combinations at reduced alloying costs.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A total of 25 indentation experiments carried out at different processing states reveal an increase in the as-cast Vickers hardness value (under1 kg. load) of 130 ± 3 to 200 ± 10 in the hot-rolled state (during which only partial recrystallization is observed), while the hardness of the homogenized state drops down to the as cast state level at 139 ± 9.
References
J.W. Yeh, S.K. Chen, S.J. Lin, J.-Y. Gan, T.-S. Chin, T.-T. Shun, C.-H. Tsau, and S.-Y. Chang, Adv. Eng. Mater. 6, 299 (2004).
Y. Zhang, Y.J. Zhou, J.P. Lin, G.L. Chen, and P.K. Liaw, Adv. Eng. Mater. 10, 534 (2008).
Y. Zhang, X. Yang, and P.K. Liaw, JOM 64, 830 (2012).
S. Guo, C. Ng, J. Lu, and C.T. Liu, J. Appl. Phys. 109, 103505 (2011).
S. Guo and C. Liu, Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 21, 433 (2011).
B. Cantor, I.T.H. Chang, P. Knight, and A.J.B. Vincent, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 375, 213 (2004).
O.N. Senkov, G.B. Wilks, J.M. Scott, and D.B. Miracle, Intermetallics 19, 698 (2011).
O.N. Senkov, J.M. Scott, S.V. Senkova, D.B. Miracle, and C.F. Woodward, J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 6043 (2011).
F. Otto, Y. Yang, H. Bei, and E.P. George, Acta Mater. 61, 2628 (2013).
M.J. Yao, K.G. Pradeep, C.C. Tasan, and D. Raabe, Scripta Mater. 72, 5 (2014).
K.G. Pradeep, N. Wanderka, P. Choi, J. Banhart, B.S. Murty, and D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 61, 4696 (2013).
F. Otto, A. Dlouhy, C. Somsen, H. Bei, G. Eggeler, and E.P. George, Acta Mater. 61, 5743 (2013).
Z. Wu, H. Bei, F. Otto, G.M. Pharr, and E.P. George, Intermetallics 46, 131 (2014).
P.P. Bhattacharjee, G.D. Sathiaraj, M. Zaid, J.R. Gatti, C. Lee, C.-W. Tsai, and J.-W. Yeh, J. Alloy. Compd. 587, 544 (2014).
K.-Y. Tsai, M.-H. Tsai, and J.-W. Yeh, Acta Mater. 61, 4887 (2013).
W.H. Liu, Y. Wu, J.Y. He, T.G. Nieh, and Z.P. Lu, Scripta Mater. 68, 526 (2013).
A. Gali and E.P. George, Intermetallics 39, 74 (2013).
C. Zhu, Z.P. Lu, and T.G. Nieh, Acta Mater. 61, 2993 (2013).
G.A. Salishchev, M.A. Tikhonovsky, D.G. Shaysultanov, N.D. Stepanov, A.V. Kuznetsov, I.V. Kolodiy, A.S. Tortika, and O.N. Senkov, J. Alloy. Compd. 591, 11 (2014).
M.S. Rashid, Ann. Rev. Mater. Sci. 11, 245 (1981).
S. Sadagopan and D. Urban, AISI/DOE Technology Roadmap Program (Oak Ridge, TN: Office of Scientific and Technical Information, 2003).
M. Calcagnotto, Y. Adachi, D. Ponge, and D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 59, 658 (2011).
T. Dursun and C. Soutis, Mater. Des. 56, 862 (2014).
H. Springer and D. Raabe, Acta Mater. 60, 4950 (2012).
I. Gutierrez-Urrutia, S. Zaefferer, and D. Raabe, Scripta Mater. 61, 737 (2009).
S. Mandal, K.G. Pradeep, S. Zaefferer, and D. Raabe, Scripta Mater. 81, 16 (2014).
C.C. Tasan, J.P.M. Hoefnagels, and M.G.D. Geers, Scripta Mater. 62, 835 (2010).
A. Holden, J.D. Bolton, and E.R. Petty, J. Iron Steel I, 721 (1971).
Y. Tomota, M. Strum, and J.W. Morris Jr., Metall. Trans. A 17A, 537 (1986).
A.L. Schaeffler, Metal Progr. 56, 680 (1949).
U. Brüx, G. Frommeyer, O. Grässel, L.W. Meyer, and A. Weise, Steel Res. 73, 294 (2002).
H. Ding, H. Ding, D. Song, Z. Tang, and P. Yang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 528, 868 (2011).
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to gratefully acknowledge the financial support by the European Union via the ERC Advanced Grant “SMARTMET” and the contributions of Michael Kulse, Frank Schlüter, Frank Rütters, Michael Adamek, Jiali Zhang, and Motomichi Koyama.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tasan, C.C., Deng, Y., Pradeep, K.G. et al. Composition Dependence of Phase Stability, Deformation Mechanisms, and Mechanical Properties of the CoCrFeMnNi High-Entropy Alloy System. JOM 66, 1993–2001 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1133-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-014-1133-6