Abstract
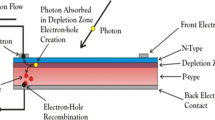
In modern years due to rising environmental issues such as energy cost and greenhouse gas emission have motivated new research into alternative methods of generation of electrical power. A vast deal of new research and enlargement for the renewable energy photovoltaic (PV) system. The PV module is conducted to search out non-polluting and renewable sources. New inventions are in development and exploring the perfection of solar cells to increase the efficiency and reduce the cost of power in per peak watt. The analysis of different kinds of control methods in PV system according to reviewed previous studies, shows that the most useful method is a hybrid technique as compared to other maximum power point tracking (MPPT) control methods. MPPT control method used to optimize the output of solar PV system with variable inputs such as solar radiations and temperature. The MPPT may include the use of a different DC–DC converter and also some different MPPT algorithms such as current based MPPT. Multi-input energy systems for the hybrid wind/solar energy systems need to be developed.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reisi AR, Moradi MH, Jamasb S (2013) Classification and comparison of maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic system: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 19:433–443
Ameli MT, Moslehpour S, Shamlo M (2008) Economical load distribution in power networks that include hybrid solar power plants. Electr Power Syst Res 78(7):1147–1152
Hua C, Shen C (May 1998) Study of maximum power tracking techniques and control of DC/DC converters for photovoltaic power system. In: 29th annual IEEE power electronics specialists conference, 1998. PESC 98 Record, vol 1. IEEE, pp 86–93
Lim YH, Hamill DC (2000) Simple maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic arrays. Electron Lett 36(11):1
Enrique JM, Andújar JM, Bohórquez MA (2010) A reliable, fast and low cost maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic applications. Sol Energy 84(1):79–89
Salas V, Olias E, Barrado A, Lazaro A (2006) Review of the maximum power point tracking algorithms for stand-alone photovoltaic systems. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 90(11):1555–1578
Iyasere E, Tatlicioglu E, Dawson DM (June 2010) Back stepping PWM control for maximum power tracking in photovoltaic array systems. In: American control conference (ACC). IEEE, pp 3561–3565
Chowdhury SR, Saha H (2010) Maximum power point tracking of partially shaded solar photovoltaic arrays. Sol Energy Mater Sol Cells 94(9):1441–1447
De Cesare G, Caputo D, Nascetti A (2006) Maximum power point tracker for portable photovoltaic systems with resistive-like load. Sol Energy 80(8):982–988
Chekired F, Mellit A, Kalogirou SA, Larbes C (2014) Intelligent maximum power point trackers for photovoltaic applications using FPGA chip: a comparative study. Sol Energy 101:83–99
Subudhi B, Pradhan R (2013) A comparative study on maximum power point tracking techniques for photovoltaic power systems. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 4(1):89–98
Stauth JT, Seeman MD, Kesarwani K (2013) Resonant switched-capacitor converters for sub-module distributed photovoltaic power management. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(3):1189–1198
Diallo D, Belkacem F, Berthelot E (May 2007) Design and control of a low power DC–DC converter fed by a photovoltaic array. In: IEEE international electric machines and drives conference, 2007. IEMDC’07, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1288–1293
Nordin AHM, Omar AM (June 2011) Modeling and simulation of photovoltaic (PV) array and maximum power point tracker (MPPT) for grid-connected PV system. In: 3rd International symposium & exhibition in sustainable energy & environment (ISESEE), 2011. IEEE, pp 114–119
Li S, Gao X, Wang L, Liu S (2013) A novel maximum power point tracking control method with variable weather parameters for photovoltaic systems. Sol Energy 97:529–536
Messai A, Mellit A, Guessoum A, Kalogirou SA (2011) Maximum power point tracking using a GA optimized fuzzy logic controller and its FPGA implementation. Sol Energy 85(2):265–277
Shaiek Y, Smida MB, Sakly A, Mimouni MF (2013) Comparison between conventional methods and GA approach for maximum power point tracking of shaded solar PV generators. Sol Energy 90:107–122
Kouchaki A, Iman-Eini H, Asaei B (2013) A new maximum power point tracking strategy for PV arrays under uniform and non-uniform insolation conditions. Sol Energy 91:221–232
Gao X, Li S, Gong R (2013) Maximum power point tracking control strategies with variable weather parameters for photovoltaic generation systems. Sol Energy 93:357–367
Moradi MH, Tousi SR, Nemati M, Basir NS, Shalavi N (2013) A robust hybrid method for maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic systems. Sol Energy 94:266–276
Raj JCM, Jeyakumar AE (2014) A two stage successive estimation based maximum power point tracking technique for photovoltaic modules. Sol Energy 103:43–61
Liu YH, Chen JH, Huang JW (2014) Global maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions using the segmentation search method. Sol Energy 103:350–363
Dounis AI, Kofinas P, Papadakis G, Alafodimos C (2015) A direct adaptive neural control for maximum power point tracking of photovoltaic system. Sol Energy 115:145–165
Liu YH, Chen JH, Huang JW (2015) A review of maximum power point tracking techniques for use in partially shaded conditions. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 41:436–453
Kuperman A, Averbukh M, Lineykin S (2013) Maximum power point matching versus maximum power point tracking for solar generators. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 19:11–17
Khan MJ, Chatterji S, Mathew L, Sharma A (2014) A survey of various maximum power point tracking techniques used in solar photovoltaic system, vol 283. Excel India Publishers, New Delhi, pp 283–288
Faranda R, Leva S, Maugeri V (July 2008) MPPT techniques for PV systems: energetic and cost comparison. In: Power and energy society general meeting-conversion and delivery of electrical energy in the 21st century, 2008 IEEE. IEEE, pp 1–6
Shenoy PS, Kim KA, Johnson BB, Krein PT (2013) Differential power processing for increased energy production and reliability of photovoltaic systems. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(6):2968–2979
Powell DM, Winkler MT, Goodrich A, Buonassisi T (2013) Modeling the cost and minimum sustainable price of crystalline silicon photovoltaic manufacturing in the United States. IEEE J Photo Voltai 3(2):662–668
Bodur M, Ermiş M (Apr 1994) Maximum power point tracking for low power photovoltaic solar panels. In: 1994. Proceedings, 7th Mediterranean electrotechnical conference. IEEE, pp 758–761
Kitano T, Matsui M, Xu DH (2001) Power sensor-less MPPT control scheme utilizing power balance at DC link-system design to ensure stability and response. In: Industrial electronics society, 2001. IECON’01. The 27th annual conference of the IEEE, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1309–1314
Bhide P, Bhat SR (June 1992) Modular power conditioning unit for photovoltaic applications. In: Power electronics specialists conference, 1992. PESC’92 record, 23rd annual IEEE. IEEE, pp 708–713
Sugimoto H, Dong H (Aug 1997) A new scheme for maximum photovoltaic power tracking control. In: Proceedings of the power conversion conference-Nagaoka 1997, vol 2. IEEE, pp 691–696
Chiang SJ, Chang KT, Yen CY (1998) Residential photovoltaic energy storage system. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 45(3):385–394
Bleijs JAM, Gow JA (2001) Fast maximum power point control of current-fed DC–DC converter for photovoltaic arrays. Electron Lett 37(1):5–6
Hou CL, Wu J, Zhang M, Yang JM, Li JP (Apr 2004) Application of adaptive algorithm of solar cell battery charger. In: Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE international conference on electric utility deregulation, restructuring and power technologies, 2004. (DRPT 2004), vol 2. IEEE, pp 810–813
Kim RY, Lai JS, York B, Koran A (2009) Analysis and design of maximum power point tracking scheme for thermoelectric battery energy storage system. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 56(9):3709–3716
El-Shibini MA, Rakha HH (Apr 1989) Maximum power point tracking technique. In: Electrotechnical conference, 1989. Proceedings. ‘Integrating research, industry and education in energy and communication engineering’, MELECON’89, Mediterranean. IEEE, pp 21–24
De Brito MA, Junior LG, Sampaio LP, Canesin CA (Sept 2011) Main maximum power point tracking strategies intended for photovoltaics. In: Power electronics conference (COBEP), 2011 Brazilian. IEEE, pp 524–530
De Brito MA, Sampaio LP, Junior LG, Canesin CA (June 2011) Evaluation of MPPT techniques for photovoltaic applications. In: 2011 IEEE international symposium on industrial electronics (ISIE). IEEE, pp 1039–1044
Khaehintung N, Pramotung K, Tuvirat B, Sirisuk P (Nov 2004) RISC-microcontroller built-in fuzzy logic controller of maximum power point tracking for solar-powered light-flasher applications. In: 30th annual conference of IEEE industrial electronics society, 2004. IECON 2004, vol 3. IEEE, pp 2673–2678
Veerachary M, Senjyu T, Uezato K (2003) Neural-network-based maximum-power-point tracking of coupled-inductor interleaved-boost-converter-supplied PV system using fuzzy controller. IEEE Trans Industr Electron 50(4):749–758
Mahmoud AMA, Mashaly HM, Kandil SA, El Khashab H, Nashed MNF (2000) Fuzzy logic implementation for photovoltaic maximum power tracking. In: Industrial electronics society, 2000. IECON 2000. 26th annual conference of the IEEE, vol 1. IEEE, pp 735–740
Patcharaprakiti N, Premrudeep-Reechacharn S (2002) Maximum power point tracking using adaptive fuzzy logic control for grid-connected photovoltaic system. In: Power engineering society winter meeting, 2002. IEEE, vol 1. IEEE, pp 372–377
Won CY, Kim DH, Kim SC, Kim WS, Kim HS (June 1994) A new maximum power point tracker of photovoltaic arrays using fuzzy controller. In: Power electronics specialists conference, PESC’94 record, 25th annual IEEE. IEEE, pp 396–403
Hiyama T, Kouzuma S, Imakubo T (1995) Identification of optimal operating point of PV modules using neural network for real time maximum power tracking control. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 10(2):360–367
Ho BM, Chung HS, Lo WL (2004) Use of system oscillation to locate the MPP of PV panels. IEEE Power Electron Lett 2(1):1–5
Ishaque K, Salam Z, Amjad M, Mekhilef S (2012) An improved particle swarm optimization (PSO)–based MPPT for PV with reduced steady-state oscillation. IEEE Trans Power Electron 27(8):3627–3638
Miyatake M, Veerachary M, Toriumi F, Fujii N, Ko H (2011) Maximum power point tracking of multiple photovoltaic arrays: a PSO approach. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 47(1):367–380
Liu YH, Huang SC, Huang JW, Liang WC (2012) A particle swarm optimization-based maximum power point tracking algorithm for PV systems operating under partially shaded conditions. IEEE Trans Energy Convers 27(4):1027–1035
Jiang LL, Maskell DL, Patra JC (2013) A novel ant colony optimization-based maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic systems under partially shaded conditions. Energy Build 58:227–236
Chai-Ead N, Aungkulanon P, Luangpaiboon P (Mar 2011) Bees and firefly algorithms for noisy non-linear optimisation problems. In: Proceedings of the international multi conference of engineering and computer scientists, vol 2
Logeswaran T, SenthilKumar A (2014) A review of maximum power point tracking algorithms for photovoltaic systems under uniform and non-uniform irradiances. Energy Proc 54:228–235
Tilahun SL, Ong HC (2012) Modified firefly algorithm. J Appl Math 2012:12
Younis MA, Khatib T, Najeeb M, Ariffin AM (2012) An improved maximum power point tracking controller for PV systems using artificial neural network. Przegląd Elektrotech 88(3b):116–121
Kobayashi K, Takano I, Sawada Y (2005) A study of a two-stage maximum power point tracking control of a photovoltaic system under partially shaded insolation conditions. Electr Eng Jpn 153(4):39–49
D’Souza NS, Lopes LA, Liu X (June 2005) An intelligent maximum power point tracker using peak current control. In: Power electronics specialists conference, 2005. PESC’05. IEEE 36th. IEEE, p 172
D’Souza NS, Lopes LA, Liu X (2010) Comparative study of variable size perturbation and observation maximum power point trackers for PV systems. Electr Power Syst Res 80(3):296–305
Koizumi H, Kurokawa K (June 2005) A novel maximum power point tracking method for PV module integrated converter. In: Power electronics specialists conference, 2005. PESC’05. IEEE 36th. IEEE, pp 2081–2086
Jain S, Agarwal V (2004) A new algorithm for rapid tracking of approximate maximum power point in photovoltaic systems. IEEE Power Electron Lett 2(1):16–19
Tafticht T, Agbossou K (May 2004) Development of a MPPT method for photovoltaic systems. In: Canadian conference on electrical and computer engineering, 2004, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1123–1126
Yang CY, Hsieh CY, Feng FK, Chen KH (2012) Highly efficient analog maximum power point tracking (AMPPT) in a photovoltaic system. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 59(7):1546–1556
Krstić M (2000) Performance improvement and limitations in extremum seeking control. Syst Control Lett 39(5):313–326
Krstić M, Wang HH (2000) Stability of extremum seeking feedback for general nonlinear dynamic systems. Automatica 36(4):595–601
Yu H, Ozguner U (2002) Extremum-seeking control strategy for ABS system with time delay. In: American control conference, 2002. Proceedings of the 2002, vol 5. IEEE, pp 3753–3758
Wang HH, Yeung S, Krstić M (2000) Experimental application of extremum seeking on an axial-flow compressor. IEEE Trans Control Syst Technol 8(2):300–309
Killingsworth NJ, KrstiĆ M (2006) PID tuning using extremum seeking: online, model-free performance optimization. IEEE Control Syst 26(1):70–79
Leyva R, Alonso C, Queinnec I, Cid-Pastor A, Lagrange D, Martinez-Salamero L (2006) MPPT of photovoltaic systems using extremum-seeking control. IEEE Trans Aerosp Electron Syst 42(1):249–258
Brunton SL, Rowley CW, Kulkarni SR, Clarkson C (2010) Maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic optimization using ripple-based extremum seeking control. IEEE Trans Power Electron 25(10):2531–2540
Lei P, Li Y, Seem JE (2011) Sequential ESC-based global MPPT control for photovoltaic array with variable shading. IEEE Trans Sustain Energy 2(3):348–358
Bazzi AM, Krein PT (2011) Concerning “maximum power point tracking for photovoltaic optimization using ripple-based extremum seeking control”. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26(6):1611–1612
Midya P, Krein PT, Turnbull J, Reppa R, Kimball J (June 1996) Dynamic maximum power point tracker for photovoltaic applications. In: Power electronics specialists conference, 1996. PESC’96 record, 27th annual IEEE, vol 2. IEEE, pp 1710–1716
Hohm DP, Ropp ME (2003) Comparative study of maximum power point tracking algorithms. Prog Photovoltaics Res Appl 11(1):47–62
http://powerelectronics.com/power_semiconductors/power_microinverters.computer.controlled_improve_04 09/. Powerelectronics.com. Retrieved 2011-06-10
Chu CC, Chen CL (2009) Robust maximum power point tracking method for photovoltaic cells: a sliding mode control approach. Sol Energy 83(8):1370–1378
Ardani K, Seif D, Davidson C, Morris J, Truitt S, Torbert R, Margolis R (June 2013) Preliminary non-hardware (“soft”) cost-reduction Roadmap for residential and small commercial solar photovoltaics, 2013–2020. In: 2013 IEEE 39th photovoltaic specialists conference (PVSC). IEEE, pp 3463–3468
Khan BH (2009) Non-conventional energy resources, 4th edn. Tata McGraw-Hill Publishing Co Ltd, New Delhi, pp 1–214
Olalla C, Deline C, Maksimovic D (2014) Performance of mismatched PV systems with submodule integrated converters. IEEE J Photovolt 4(1):396–404
Hu H, Harb S, Kutkut NH, Shen ZJ, Batarseh I (2013) A single-stage microinverter without using eletrolytic capacitors. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(6):2677–2687
Schaef C, Kesarwani K, Stauth JT (Mar 2013) A coupled-inductor multi-level ladder converter for sub-module PV power management. In: Applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC), 2013 28th annual IEEE. IEEE, pp 732–737
Ferdous SM, Mohammad MA, Nasrullah F, Saleque AM, Muttalib AZM (Dec 2012) Design and simulation of an open voltage algorithm based maximum power point tracker for battery charging PV system. In: 2012 7th international conference on electrical & computer engineering (ICECE). IEEE, pp 908–911
Rodriguez C, Amaratunga GA (2007) Analytic solution to the photovoltaic maximum power point problem. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I Regul Pap 54(9):2054–2060
Amrouche B, Belhamel M, Guessoum A (2007) Artificial intelligence based P&O MPPT method for photovoltaic systems. In: Revue des Energies Renouvelables ICRESD-07 Tlemcen, pp 11–16
Ramaprabha R, Mathur BL (2011) Intelligent controller based maximum power point tracking for solar PV system. Int J Comput Appl 12(10):37–41
Larbes C, Cheikh SA, Obeidi T, Zerguerras A (2009) Genetic algorithms optimized fuzzy logic control for the maximum power point tracking in photovoltaic system. Renew Energy 34(10):2093–2100
Iqbal A, Abu-Rub H, Ahmed SM (Dec 2010) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system based maximum power point tracking of a solar PV module. In: 2010 IEEE international energy conference and exhibition (EnergyCon). IEEE, pp 51–56
Qin S, Pilawa-Podgurski RC (Mar 2013) Sub-module differential power processing for photovoltaic applications. In: 2013 28th annual IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC). IEEE, pp 101–108
Poshtkouhi S, Biswas A, Trescases O (Feb 2012) DC–DC converter for high granularity, sub-string MPPT in photovoltaic applications using a virtual-parallel connection. In: 2012 27th annual IEEE applied power electronics conference and exposition (APEC). IEEE, pp 86–92
Esram T, Chapman PL (2007) Comparison of photovoltaic array maximum power point tracking techniques. IEEE Trans Energy Convers EC 22(2):439
Abdelsalam AK, Massoud AM, Ahmed S, Enjeti P (2011) High-performance adaptive perturb and observe MPPT technique for photovoltaic-based microgrids. IEEE Trans Power Electron 26(4):1010–1021
Esram T, Krein PT, Kuhn BT, Balog RS, Chapman PL (Nov 2008) Power electronics needs for achieving grid-parity solar energy costs. In: Energy 2030 conference, 2008. ENERGY 2008. IEEE. IEEE, pp 1–5
Koutroulis E, Blaabjerg F (2013) Design optimization of transformer less grid-connected PV inverters including reliability. IEEE Trans Power Electron 28(1):325–335
Matsui M, Kitano T, Xu DH, Yang ZQ (1999) A new maximum photovoltaic power tracking control scheme based on power equilibrium at DC link. In: Industry applications conference, 1999. 34th IAS annual meeting. Conference record of the 1999 IEEE, vol 2. IEEE, pp 804–809
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, M.J., Mathew, L. Different Kinds of Maximum Power Point Tracking Control Method for Photovoltaic Systems: A Review. Arch Computat Methods Eng 24, 855–867 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-016-9192-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11831-016-9192-1