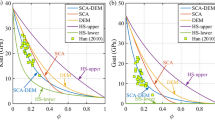
Abstract
Acoustic and electrical methods are commonly used to evaluate hydrate saturation based on P-wave velocity (Vp) and resistivity, respectively. We evaluate hydrate saturation using petrophysical parameters directly related to the presence of hydrates. Five petrophysical parameters sensitive to hydrate saturation were first analyzed using the equivalent medium rock physical model, logging intersection plots, and petrophysical parameter inversion. The simulated annealing global optimization method was then used to estimate the hydrate saturation profile in the Shenhu Area, China. The petrophysical parameters Vp, λρ, and λμ, which are associated with the rock elastic and shear moduli, are highly sensitive to hydrate saturation for an estimated saturation range of 0.1–0.44. This range is consistent with that obtained from the original well diameter curves. However, the parameters Vs and μρ, which are only related to the rock shear modulus, yield high hydrate saturation estimates of 0.22–0.43 and exhibit some deviations from the real-time data. Owing to its sensitivity, the Poisson’s ratio is least desired for hydrate evaluation among the studied parameters. The sensitivity of hydrate saturation depends on the petrophysical model used for studying hydrate physical properties and storage analysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archie G E, The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics[J]. Transactions of the AIME, 1942, 146(01): 54–62.
Dvorkin J, Nur A, 1996. Elasticity of high-porosity sandstones: Theory for two North Sea datasets. Geophysics, 61(5): 1363–1370.
Fu Shao Ying, Lu Jing An. The characteristics and origin of gas hydrate in shenhu area, south china sea [J]. Marine Geology Letters. 2010, 26(9): 6–10.
Lee M W, Waite W F. Estimating pore-space gas hydrate saturations from well log acoustics data. Geochem, Geophys, 2008, 9(7): Q07008.
Liang Jin, Wang MingJun, Wang HongBin, et al. Relationship between the Sonic Logging Velocity and Saturation of Gas Hydrate in Shenhu Area Northern Slope of South China Sea. Geoscience, 2009, 23(2): 217–222.
Lee M W, Collett T S, Lewis K A. Anisotropic models to account for large borehole washouts to estimate gas hydrate saturations in the gulf of Mexico gas hydrate joint industry project leg A laminos Canyon 21 B well[J]. Marine and Petroleum Geology, 2012, 34(1): 85–95
Lu Jingan, Yang Shengxiong, Wu Nengyou, et al. Well logging evaluation of gas hydrate in Shenhu area, South China Sea [J]. Geoscience. 2008, 22(3): 447- 451.
Lee M W. Hutchinson D R, Collett T S, et al. Seismic velocities for hydrate-bearing sediments using weighted equation [J], Joural of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth (1978-2012), 1996, 101(B9): 20347–20358.
Liu Jie, Zhang Jian Zhong, Sun Yun Bao, Zhao Tie Hu. Gas hydrate reservoir parameter evaluation using logging data in the Shenhu area, South China Sea. Natural Gas Geoscience. 2017, 28(1): 164–172.
Lin Lin, Liang Jin, Guo Yiqun, Lu Jingan, Liang Jinqiang. Estimating Saturation of Gas Hydrates Within Marine Sediments Using Sonic Log Data. WELL LOGGING TECHNOLOGY. 2014, 38(2): 235–238.
Ning Fulong, Liu Li, Li Shi, et al. Well loging assessment of natural gas hydrate reservoirs and relevant influential factors [J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2013, 34(3): 591–606.
Sloan E D, Fundamental principles and applications of natural gas hydrates[J]. Nature, 2003, 426(6964): 353–363.
Sun Chunyan, Zhang Mingyu, Niu Binhua, et al. Micromodels of gas hydrate and their velocity estimation methods[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2003, 10(1): 191–198.
Simandoux P. Dielectric measurements on porous media, application to the measurements of water saturation: study of Francais du Petrole, 1963, 18: 193–215
Wang Xiujuan, Wu Shiguo, Liu Xuewei, et al. Estimation of gas hydrate saturation based on resistivity logging and analysis of estimation error[J]. Geoscience, 2010, 24(5): 993–999.
Wang Xiu Juan. Seismic characters of gas hydrate-bearing sediments in the northern of south china sea. [Master's Thesis]. 2006.
Wang Lin Bing, Yao Zhen Xing, Ji Chen, Zhang Zhong Jie. Fast Simulated Annealing Algorithm and Its Application. Petroleum Geophysical Prospecting. 1997, 32(5): 654–660.
Wu N Y, Yang S X, Wang H B, et al. Gas-bearing fluis influx sub-system for gas hydrate geological system in Shenhu Area, Northern South China Sea. Geophys. 2009, 52(6): 1641–1650.
Yun T S, Francisca F M, Santamarina J C, et al. Compressional and shear wave velocities in uncemented sediment containing gas hydrate. Geophys, 2005, 32(10): L10609.
Zang Hui, Lu HaiLong, Liang JinQiang, Wu NengYou. The methane hydrate accumulation controlled compellingly by sediment grain at Shenhu, northern South China Sea. 2016, 61(3): 388–397.
Zhang weidong, Wang Ruihe, Ren Shaoran, et al. A study on physical models of gas hydrate reservoirs[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica, 2011, 32(5): 866–871.
Acknowledgements
The study is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.91958206, 41876053), the National Key Research and Development Plan (2017YFC0307401,2018YFC1405901), the Fund of Acoustics Science and Technology Laboratory (GK2050260214, GK2050260217, GK2050260218, KY10500180084, KY10500190031, 6142108200202), and Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (HEUCFJ180503, 201964016).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
About the first author
Liu Xue-Qin Ph.D. graduated from Ocean University of China (Qingdao) in 2014. Her main research interests are seismic processing and interpretation. Lecturer, Harbin Engineering University.
Xing Lei, male, born in 1984 in Laiwu City, Shandong Province; doctor; graduated from Ocean University of China. He is now interested in the study of marine science.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, XQ., Liu, HS., Xing, L. et al. Sensitivity Analysis of Petrophysical Parameters for Estimating Hydrate Saturation in the Shenhu Area. Appl. Geophys. 17, 649–659 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-018-0718-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11770-018-0718-1