Abstract
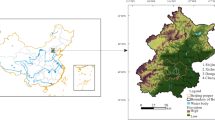
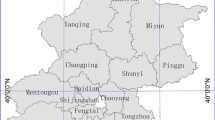
This study investigated and simulated land use patterns in Beijing for the year 2000 and the year 2005 from the actual land use data for the year 1995 and the year 2000, respectively, by combining spatial land allocation simulation using the CLUE-S model, and numerical land demand prediction using the Markov model. The simulations for 2000 and 2005 were confirmed to be generally accurate using Kappa indices. Then the land-use scenarios for Beijing in 2015 were simulated assuming two modes of development: 1) urban development following existing trends; and 2) under a strict farmland control. The simulations suggested that under either mode, urbanized areas would expand at the expense of land for other uses. This expansion was predicted to dominate the land-use conversions between 2005 and 2015, and was expected to be accompanied by an extensive loss of farmland. The key susceptible to land-use changes were found to be located at the central urban Beijing and the surrounding regions including Yanqing County, Changping District and Fangshan District. Also, the simulations predicted a considerable expansion of urban/suburban areas in the mountainous regions of Beijing, suggesting a need for priority monitoring and protection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics, 1996. Beijing Statistical Yearbook 1996. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics, 2001. Beijing Statistical Yearbook 2001. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
Beijing Municipal Bureau of Statistics, 2006. Beijing Statistical Yearbook 2006. Beijing: China Statistics Press.
Deng X Z, Huang J K, Rozelle S et al., 2008. Growth, population and industrialization, and urban land expansion of China. Journal of Urban Economics, 63(1): 96–115. doi: 10.1016/j.jue.2006.12.006
Han Fei, Cai Jianming, Liu Junping, 2010. Discussion on the spatial differentiation of Beijing’s urban agriculture. System Sciences and Comprehensive Studies in Agriculture, 26(3): 293–298. (in Chinese)
He Dan, Jin Fengjun, Zhou Jing, 2011. The changes of land use and landscape pattern based on Logistic-CA-Markov Model—A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei metropolitan region. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 31(8): 903–910. (in Chinese)
Huang Qingxu, He Chun Yang, Shi Peijun et al., 2009. Understanding multi-scale urban expansion driving forces: In the case study of Beijing. Economic Geography, 29(5): 714–721. (in Chinese)
Jiang Guanghui, Zhang Fengrong, Wu Jianzhai et al., 2006. Construction land expansion and its relationship with cultivated land in Beijing mountainous areas. Transactions of the CSA E, 22(10): 88–93. (in Chinese)
Liang Youjia, Xu Zhongmin, Zhong Fanglei, 2011. Land use scenario analyses by based on system dynamic model and CLUE-S model at regional scale: A case study of Ganzhou district of Zhangye city. Geographical Research, 30(3): 564–576. (in Chinese)
Lu Rucheng, Huang Xianjin, Zuo Tianhui et al., 2009. Land use scenarios simulation based on CLUE-S and markov composite model. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 29(4): 577–581. (in Chinese)
Overmars KP, Verburg PH, Veldkamp T, 2007. Comparison of a deductive and an inductive approach to specify land suitability in a spatially explicit land use model. Land Use Policy, 24: 584–599. doi: 10.1016/j.landusepol.2005.09.008
Pan Y, Roth A, Yu Z et al., 2010. The impact of variation in scale on the behavior of a cellular automata used for land use change modeling. Compute, Environment and Urban System, 34(5) 400–408. doi: 10.1016/j.compenvurbsys.2010.03.003
Pan Ying, Liu Yunhui, Wang Jing et al., 2011. Non-point pollution control for landscape conservation analysis on CLUE-S simulations in Miyun County. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(2): 529–537. (in Chinese)
Pontius R G, 2002. Statistical methods to partition effects of quantity and location comparison of categorical maps at multiple resolutions. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 68(10): 1041–1049.
Quan Quan, Tian Guangjin, Sha Moqua, 2011. Dynamic simulation of Shanghai urban expansion based on multi-agent system and cellular automata models. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(10): 2875–2887. (in Chinese)
Sheng Sheng, Liu Maosong, Xu Chi et al., 2008. The application of the CLUE-S model in Nanjing’s land use change research. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 27(2): 235–239. (in Chinese)
Sohl TL, Sayler KL, Drummond MA et al., 2007. The FORE-SCE model: A practical approach for projecting land cover change using scenario-based modeling. Land Use Science, 2: 103–126. doi: 10.1080/17474230701218202
Sun Yongguang, Li Xiuzhen, Guo Wenyong et al., 2011. Contribution rates of landscape driving factors in coastal reclamation zone based on CLUE-S model validation. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology, 22(9): 2391–2398. (in Chinese)
Verburg P H, Veldkamp W, Limpiada R et al., 2002. Modeling the spatial dynamics of regional land use: The CLUE-S model. Environmental Management, 30(3): 391–405. doi: 10.1007/s00267-002-2630-x
Wang Jian, Tian Guangjin, Quan Quan et al., 2010. Dynamic simulation of land use pattern in Guangzhou based on CLUE-S model. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 29(6): 1257–1262. (in Chinese)
Wang Jianying, Li Jiangfeng, Zhang Liqin et al., 2012. Prediction of land use structure based on biodiversity conservation. Transactions of the CSAE, 28(4): 221–226. (in Chinese)
Wu Guiping, Zeng Yongnian, Feng Xuezhi et al., 2010. Dynamic simulation of land use change based on the improved CLUE-S model: A case study of Yongding County, Zhangjiajie. Geographical Research, 29(3): 460–470. (in Chinese)
Wu Jiansheng, Feng Zhe, Gao Yang et al., 2012. Application progress and improvement research of CLUE-S model. Progress of Geography, 31(1): 460–470. (in Chinese)
Wu Jiansheng, Feng Zhe, Huang Li et al., 2011. The scenarios predict of sustainable land use based on framework of CLUE-S model: A case study of Yongquan’s suburb. Resources Science, 33(9): 1699–1707. (in Chinese)
Xia Jing, 2010. Evaluating Land Use Type Change and Ecosystem Services in Mountainous Region of Beijing. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University.
Zhang Ping, Liu Yunhui, Pan Ying et al., 2011. Land use pattern optimization based on CLUE-S and SWAT models for agricultural non-point source pollution control. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, Online. doi: 10.1016/j.mcm.2011.10.061
Zhou Rui, Su Hailong, Wang Xinjun et al., 2011. Simulation of land use change in Xinzhuang Town under different scenarios based on the CLUE-S model and Markov Model. Resources Science, 33(12): 2262–2270. (in Chinese)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Foundation item: Under the auspices of National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 70903061, 41171440), National Public Benefit (Land) Research Foundation of China (No. 201111014), Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2011YXL055)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Y., Zheng, Y. & Zheng, X. Simulation of land-use scenarios for Beijing using CLUE-S and Markov composite models. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 23, 92–100 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0594-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11769-013-0594-9