Abstract
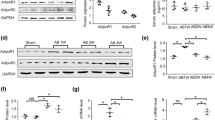
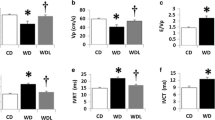
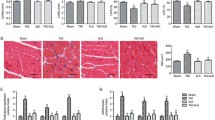
Adiponectin is a polypeptide known to inhibit cardiac fibrosis via the activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK). Statins can also activate AMPK, resulting in the secretion of adiponectin. We determined whether atorvastatin inhibits angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis (AICF) in the presence or absence of adiponectin. Adiponectin knockout (APN-KO, n = 44) and wild type (WT, n = 44) mice were received subcutaneous angiotensin II (1.5 mg/kg/day), and atorvastatin (10 mg/kg/day) was administered orally for 15 days. The mRNA expression levels of collagen type I and III, as well as AMPK phosphorylation levels in cardiac tissue were then measured. In the APN-KO mice, collagen type I (p < 0.001) and type III (p = 0.001) expression was significantly greater when treated with angiotensin II, while their expression was significantly reduced in the presence of angiotensin II and atorvastatin. Relative AMPK phosphorylation levels in APN-KO mice were also significantly higher in the angiotensin II + atorvastatin group when compared with angiotensin II group alone. We conclude that atorvastatin attenuates AICF independently from adiponectin by activating AMPK. These data suggest potential cardioprotection beyond lipid modulation potentially supporting statin pleiotropic hypothesis.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
13 October 2017
In the original published article, Victor Serebruany was designated as the corresponding author in error. The corresponding author is Jong Sung Park. Dr. Park can be reached by email at thinkmed@dau.ac.kr.
Abbreviations
- AMPK:
-
Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- APN-KO:
-
Adiponectin knockout
- AICF:
-
Angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis
- BW:
-
Body weight
- ERK:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- HW:
-
Heart weight
- TGF:
-
Transforming growth factor
References
Beauloye C, Bertrand L, Horman S, Hue L (2011) AMPK activation, a preventive therapeutic target in the transition from cardiac injury to heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 90(2):224–233
Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated/SNF1 protein kinases: conserved guardians of cellular energy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(10):774–785
Zhang P, Hu X, Xu X, Fassett J, Zhu G, Viollet B, Xu W, Wiczer B, Bernlohr DA, Bache RJ, Chen Y (2008) AMP activated protein kinase-alpha2 deficiency exacerbates pressure-overload-induced left ventricular hypertrophy and dysfunction in mice. Hypertension 52(5):918–924
Du J, Guan T, Zhang H, Xia Y, Liu F, Zhang Y (2008) Inhibitory crosstalk between ERK and AMPK in the growth and proliferation of cardiac fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368(2):402–407
Stuck BJ, Lenski M, Böhm M, Laufs U (2008) Metabolic switch and hypertrophy of cardiomyocytes following treatment with angiotensin II are prevented by AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem 283(47):32562–32569
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Minokoshi Y, Ito Y, Waki H, Uchida S, Yamashita S, Noda M, Kita S, Ueki K, Eto K, Akanuma Y, Froguel P, Foufelle F, Ferre P, Carling D, Kimura S, Nagai R, Kahn BB, Kadowaki T (2002) Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat Med 8(11):1288–1295
Xu A, Vanhoutte PM (2012) Adiponectin and adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 302(6):H1231–H1240
Fujita K, Maeda N, Sonoda M, Ohashi K, Hibuse T, Nishizawa H, Nishida M, Hiuge A, Kurata A, Kihara S, Shimomura I, Funahashi T (2008) Adiponectin protects against angiotensin II-induced cardiac fibrosis through activation of PPAR-alpha. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28(5):863–870
Konishi M, Haraguchi G, Ohigashi H, Ishihara T, Saito K, Nakano Y, Isobe M (2011) Adiponectin protects against doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathyby anti-apoptotic effects through AMPK up-regulation. Cardiovasc Res 89(2):309–319
Zhou Q, Liao JK (2010) Pleiotropic effects of statins-Basic research and clinical perspectives. Circ J 74(5):818–826
Yamamoto C, Fukuda N, Jumabay M, Saito K, Matsumoto T, Ueno T, Soma M, Matsumoto K, Shimosawa T (2011) Protective effects of statin on cardiac fibrosis and apoptosis in adrenomedullin-knockout mice treated with Ang II and high salt loading. Hypertens Res 34(3):348–353
An Z, Yang G, He YQ, Dong N, Ge LL, Li SM, Zhang WQ (2013) Atorvastatin reduces myocardial fibrosis in a rat model with post-myocardial infarction heart failure by increasing the matrix metalloproteinase-2/tissue matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor-2 ratio. Chin Med J (Engl) 126(11):2149–2156
Rodrigues Díez R, Rodrigues-Díez RR, Lavoz C, Rayego-Mateos S, Civantos E, Rodríguez-Vita J, Mezzano S, Ortiz A, Egido J, Ruiz-Ortega M (2010) Statins inhibit angiotensin II/Smad pathway and related vascular fibrosis, by a TGF-β-independent process. PLoS One 5(11):e14145
Rupérez M, Rodrigues-Díez R, Blanco-Colio LM, Sánchez-López E, Rodríguez-Vita J, Esteban V, Carvajal G, Plaza JJ, Egido J, Ruiz-Ortega M (2007) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors decrease angiotensin II-induced vascular fibrosis: role of RhoA/ROCK and MAPK pathways. Hypertension 50(2):377–383
Sun W, Lee TS, Zhu M, Gu C, Wang Y, Zhu Y, Shyy JY (2006) Statins activate AMP-activated protein kinase in vitro and in vivo. Circulation 114(24):2655–2662
Hermida N, Markl A, Hamelet J, Van Assche T, Vanderper A, Herijgers P, van Bilsen M, Hilfiker-Kleiner D, Noppe G, Beauloye C, Horman S, Balligand JL (2013) HMG CoA reductase inhibition reverses myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction through AMP-activated protein kinase activation in a mouse model of metabolic syndrome. Cardiovasc Res 99(1):44–54
Qu HY, Xiao YW, Jiang GH, Wang ZY, Zhang Y, Zhang M (2009) Effect of atorvastatin versus rosuvastatin on levels of serum lipids, inflammatory markers and adiponectin in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Pharm Res 26(4):958–964
Blanco-Colio L, Martín-Ventura JL, Gómez-Guerrero C, Masramon X, de Teresa E, Farsang C, Gaw A, Gensini G, Leiter LA, Langer A, Egido J (2008) Adiponectin plasma levels are increased by atorvastatin treatment in subjects at high cardiovascular risk. Eur J Pharmacol 586(1–3):259–265
Sugiyama S, Fukushima H, Kugiyama K, Maruyoshi H, Kojima S, Funahashi T, Sakamoto T, Horibata Y, Watanabe K, Koga H, Sugamura K, Otsuka F, Shimomura I, Ogawa H (2007) Pravastatin improved glucose metabolism associated with increasing plasma adiponectin in patients with impaired glucose tolerance and coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 194(2):e43–e51
Inami N, Nomura S, Shouzu A, Omoto S, Kimura Y, Takahashi N, Tanaka A, Nanba M, Shouda Y, Iwasaka T (2007) Effects of pitavastatin on adiponectin in patients with hyperlipidemia. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 36(1):1–8
Essick EE, Ouchi N, Wilson RM, Ohashi K, Ghobrial J, Shibata R, Pimentel DR, Sam F (2011) Adiponectin mediates cardioprotection in oxidative stress-induced cardiac myocyte remodeling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 301(3):H984–H993
Zhong J, Basu R, Guo D, Chow FL, Byrns S, Schuster M, Loibner H, Wang XH, Penninger JM, Kassiri Z, Oudit GY (2010) Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 suppresses pathological hypertrophy, myocardial fibrosis, and cardiac dysfunction. Circulation 122(7):717–728
Zadelaar S, Kleemann R, Verschuren L, de der Vries-Van Weij J, van der Hoom J, Princen HM, Kooistra T (2007) Mouse models for atherosclerosis and pharmaceutical modifiers. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27(8):1706–1721
Nie P, Li D, Hu L, Jin S, Yu Y, Cai Z, Shao Q, Shen J, Yi J, Xiao H, Shen L, He B (2014) Atorvastatin improves plaque stability in ApoE-knockout mice by regulating chemokines and chemokine receptors. PLoS One 9(5):e97009
Hunyady L, Catt KJ (2006) Pleiotropic AT1 receptor signaling pathways mediating physiological and pathogenic actions of angiotensin II. Mol Endocrinol 20(5):953–970
Serebruany VL, Miller M, Pokov AN, Malinin AI, Lowry DR, Tanguay JF, Hennekens CH (2006) Effect of statins on platelet PAR-1 thrombin receptor in patients with the metabolic syndrome (from the PAR-1 inhibition by statins [PARIS] study). Am J Cardiol 97(9):1332–1336
Han SH, Quon MJ, Kim JA, Koh KK (2007) Adiponectin and cardiovascular disease: response to therapeutic interventions. J Am Coll Cardiol 49(5):531–538
Acknowledgements
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. Part of this work was supported by the “Brain Pool” program funded by the Korea Ministry of Science and Technology to Dr. Serebruany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article is available at https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-017-4296-4.
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S.Y., Park, J.S., Roh, M.S. et al. Inhibition of Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiac Fibrosis by Atorvastatin in Adiponectin Knockout Mice. Lipids 52, 415–422 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-017-4246-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-017-4246-1