Abstract
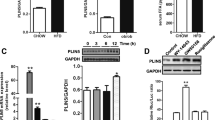
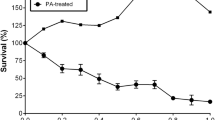
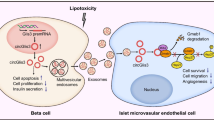
Lipoapoptosis plays an important role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta (PPARdelta), a vital regulator of glucose and lipid metabolism, may reduce fatty acid-induced pancreatic β cell lipotoxicity in diabetes. However, the detailed molecular mechanisms underlying this process are not fully understood. In this study, we investigated the effect of activation of PPARdelta on palmitate-induced β cell apoptosis, and we explored the potential mechanism of the antiapoptotic effect. The cell apoptosis was determined by DNA fragmentation analysis and Hoechst 33342 staining. The expressing of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) in INS-1 cells was assessed by Western blotting, quantification of PCR, and was further confirmed by immunofluorescence staining. The potential of PPARdelta to interact with homologous PPRE in the GLP-1R gene was determined by Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP). Our results showed that exposure of INS-1 cells to palmitate for 24 h caused a significant increase in cell apoptosis, which was inhibited by GW501516. PPARdelta exerted anti-apoptotic effects in pancreatic β cells via the PI3 K/PKB/FoxO1 signaling pathway. Moreover, PPARdelta upregulated the GLP-1R expression under lipotoxic conditions. The ChIP assay revealed a direct binding of PPARdelta to a noncanonical PPRE motif of the GLP-1R gene in INS-1 cells. Our study suggested that the anti-apoptotic action of PPARdelta may involve its transcriptional regulation of GLP-1R and PI3 K/PKB/FoxO1 signaling. GW501516 and possible other GW-based strategies may confer additional benefit beyond improved glycemic control.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- FFA:
-
Free fatty acids
- FoxO1:
-
Forkhead box O1
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GLP-1R:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor
- PAM:
-
Palmitate
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PKB:
-
Protein kinase B
- PPARdelta:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor delta
- RT-qPCR:
-
Real-time quantitative PCR
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
References
Unger RH, Zhou YT (2001) Lipotoxicity of beta-cells in obesity and in other causes of fatty acid spillover. Diabetes 50(Suppl 1):S118–S121
Wilding JP (2007) The importance of free fatty acids in the development of Type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 24(9):934–945
Laybutt DR, Preston AM, Akerfeldt MC, Kench JG, Busch AK, Biankin AV, Biden TJ (2007) Endoplasmic reticulum stress contributes to beta cell apoptosis in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 50(4):752–763
Shimabukuro M, Zhou YT, Levi M, Unger RH (1998) Fatty acid-induced beta cell apoptosis: a link between obesity and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(5):2498–2502
Lupi R, Dotta F, Marselli L, Del Guerra S, Masini M, Santangelo C, Patané G, Boggi U, Piro S, Anello M, Bergamini E, Mosca F, Di Mario U, Del Prato S, Marchetti P (2002) Prolonged exposure to free fatty acids has cytostatic and pro-apoptotic effects on human pancreatic islets: evidence that beta-cell death is caspase mediated, partially dependent on ceramide pathway, and Bcl-2 regulated. Diabetes 51(5):1437–1442
Vilsbøll T, Krarup T, Deacon CF, Madsbad S, Holst JJ (2001) Reduced postprandial concentrations of intact biologically active glucagon-like peptide 1 in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes 50(3):609–613
Thorens B (1992) Expression cloning of the pancreatic beta cell receptor for the gluco-incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(18):8641–8645
Thorens B, Porret A, Bühler L, Deng SP, Morel P, Widmann C (1993) Cloning and functional expression of the human islet GLP-1 receptor. Demonstration that exendin-4 is an agonist and exendin-(9–39) an antagonist of the receptor. Diabetes 42(11):1678–1682
Xu G, Kaneto H, Laybutt DR, Duvivier-Kali VF, Trivedi N, Suzuma K, King GL, Weir GC, Bonner-Weir S (2007) Downregulation of GLP-1 and GIP receptor expression by hyperglycemia: possible contribution to impaired incretin effects in diabetes. Diabetes 56(6):1551–1558
Farilla L, Bulotta A, Hirshberg B, Li Calzi S, Khoury N, Noushmehr H, Bertolotto C, Di Mario U, Harlan DM, Perfetti R (2003) Glucagon-like peptide 1 inhibits cell apoptosis and improves glucose responsiveness of freshly isolated human islets. Endocrinology 144(12):5149–5158
Meier JJ, Nauck MA (2005) Glucagon-like peptide 1(GLP-1) in biology and pathology. Diabete Metab Res Rev 21(2):91–117
Drucker DJ (2007) The role of gut hormones in glucose homeostasis. J Clin Invest 117(1):24–32
Ravnskjaer K, Frigerio F, Boergesen M, Nielsen T, Maechler P, Mandrup S (2010) PPARdelta is a fatty acid sensor that enhances mitochondrial oxidation in insulin-secreting cells and protects against fatty acid-induced dysfunction. J Lipid Res 51(6):1370–1379
Wan J, Jiang L, Lü Q, Ke L, Li X, Tong N (2010) Activation of PPARdelta up-regulates fatty acid oxidation and energy uncoupling genes of mitochondria and reduces palmitate-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 391(3):1567–1572
Kersten S, Desvergne B, Wahli W (2000) Roles of PPARs in health and disease. Nature 405(6785):421–424
Elghazi L, Balcazar N, Bernal-Mizrachi E (2006) Emerging role of protein kinaseB/Akt signaling in pancreatic β-cell mass and function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 38(2):157–163
Kharroubi I, Ladriere L, Cardozo AK, Dogusan Z, Cnop M, Eizirik DL (2004) Free fatty acids and cytokines induce pancreatic β-cell apoptosis by different mechanisms: role of nuclear factor-кB and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Endocrinology 145(11):5087–5096
McGarry JD, Dobbins RL (1999) Fatty acid, lipotoxicity and insulin secretion. Diabetologia 42(2):128–138
Franke TF, Hornik CP, Segev L, Shostak GA, Sugimoto C (2003) PI3 K/Akt and apoptosis: size matters. Oncogene 22(56):8983–8998
Wrede CE, Dickson LM, Lingohr MK, Briaud I, Rhodes CJ (2002) Protein kinase B/Akt prevents fatty acid-induced apoptosis in pancreatic beta-cells (INS-1). J Biol Chem 277(51):49676–49684
Hirabara SM, Curi R, Maechler P (2010) Saturated fatty acid-induced insulin resistance is associated with mitochondrial dysfunction in skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Physiol 222(1):187–194
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME (1999) Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96(6):857–868
Cypess AM, Zhang H, Schulz TJ, Huang TL, Espinoza DO, Kristiansen K, Unterman TG, Tseng YH (2011) Insulin/IGF-I regulation of necdin and brown adipocyte differentiation via CREB- and FoxO1-associated pathways. Endocrinology 152(10):3680–3689
Nakae J, Oki M, Cao Y (2008) The FoxO transcription factors and metabolic regulation. FEBS Lett 582(1):54–67
Zhang X, Yong W, Lv J, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Chen F, Zhang R, Yang T, Sun Y, Han X (2009) Inhibition of forkhead boxO1 protects pancreatic beta-cells against dexamethasone-induced dysfunction. Endocrinology 150(9):4065–4073
Wang Q, Li L, Xu E, Wong V, Rhodes C, Brubaker PL (2004) Glucagon-like peptide-1 regulates proliferation and apoptosis via activation of protein kinaseB in pancreatic INS-1 beta cells. Diabetologia 47(3):478–487
Buteau J, Spatz ML, Accili D (2006) Transcription factor FoxO1 mediates glucagon-like peptide-1 effects on pancreatic beta-cell mass. Diabetes 55(5):1190–1196
Wang HW, Mizuta M, Saitoh Y, Noma K, Ueno H, Nakazato M (2011) Glucagon-like peptide-1 and candesartan additively improve glucolipotoxicity in pancreatic β-cells. Metabolism 60(8):1081–1089
Shi Y, Hon M, Evans RM (2002) The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ, an integrator of transcriptional repression and nuclear receptor signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(5):2613–2618
Khozoie C, Borland MG, Zhu B, Baek S, John S, Hager GL, Shah YM, Gonzalez FJ, Peters JM (2012) Analysis of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor -β/δ (PPARβ/δ) cistrome reveals novel co-regulatory role of ATF4. BMC Genom 13:665
Biddie SC, Hager GL (2009) Glucocorticoid receptor dynamics and gene regulation. Stress 12(3):193–205
Biddie SC, John S, Hager GL (2010) Genome-wide mechanisms of nuclear receptor action. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2(1):3–9
Gupta D, Peshavaria M, Monga N, Jetton TL, Leahy JL (2010) Physiologic and pharmacologic modulation of glucose-dependent insulinotropicpolypeptide (GIP)receptor expression in beta-cells by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma signaling:possible mechanism for the GIP resistance in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 59(6):1445–1450
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81170777).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Ren, J., Tong, Y. et al. Protective Role of PPARdelta in Lipoapoptosis of Pancreatic β Cells. Lipids 51, 1259–1268 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4190-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-016-4190-5