Abstract
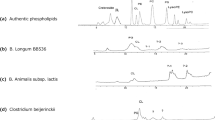
Ethanolamine plasmalogen (PlsEtn), which is present at high levels in brains, is believed to be involved in neuronal protection. The present study was performed to search for PlsEtn resources in foodstuffs. The foodstuffs examined showed a wide range of PlsEtn contents from 5 to 549 μmol/100 g wet wt. The marine invertebrates, blue mussel, and ascidian had high PlsEtn contents (over 200 μmol/100 g wet wt). Profiling of the molecular species showed that the predominant fatty acids of PlsEtn species were 20:5 (EPA) and 22:6 (DHA) at the sn-2 position of the glycerol moiety in marine foodstuffs, whereas major PlsEtn species in land foodstuffs were 20:4. Following quantitative analysis by multiple reaction monitoring, the ascidian viscera were shown to contain the highest levels of 18:0/20:5-PlsEtn and 18:0/22:6-PlsEtn (86 and 68 μmol/100 g wet wt, respectively). In order to evaluate a neuronal antiapoptotic effect of these PlsEtn species, human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were treated with ethanolamine glycerophospholipid (EtnGpl), purified from the ascidian viscera, under serum starvation conditions. Extrinsic EtnGpl from ascidian viscera showed stronger suppression of cell death induced by serum starvation than with bovine brain EtnGpl. The EtnGpl from ascidian viscera strongly suppressed the activation of caspase 3. These results suggest that PlsEtn, especially that containing EPA and DHA, from marine foodstuffs is potentially useful for a therapeutic dietary supplement preventing neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD).




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-β
- DHA:
-
Docosahexaenoic acid (22:6)
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium
- EPA:
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid (20:5)
- EtnGpl:
-
Ethanolamine glycerophospholipid
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- HPLC:
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- PakEtn:
-
1-O-Alkyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
- PlsEtn:
-
1-O-Alkenyl-2-acyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine or ethanolamine plasmalogen
- PtdEtn:
-
1,2-Diacyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine
- PUFA:
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids
- TLC:
-
Thin-layer chromatography
References
Dembitsky VM (1988) Quantification of plasmalogen, alkylacyl and diacyl glycerophospholipids by micro-thin-layer chromatography. J Chromatogr 436:467–473
Yang HC, Farooqui AA, Horrocks LA (1996) Plasmalogen-selective phospholipase A2 and its role in signal transduction. J Lipid Mediator Cell Signal 14:9–13
Farooqui AA, Horrocks LA (2006) Phospholipase A2-generated lipid mediators in the brain: the good, the bad, and the ugly. Neuroscientist 12:245–260
Hack MH, Helmy FM (1977) Thin-layer chromatographic resolution of molecular species of ethanolamine plasmalogen quantitatively unique to myelin. J Chromatogr 135:229–234
Glaser PE, Gross RW (1994) Plasmenylethanolamine facilitates rapid membrane fusion: a stopped-flow kinetic investigation correlating the propensity of a major plasma membrane constituent to adopt an HII phase with its ability to promote membrane fusion. Biochemistry 33:5805–5812
Wallner S, Schimtz G (2011) Plasmalogens the neglected regulatory and scavenging lipid species. Chem Phys Lipids 164:573–589
Broniec A, Klosinski R, Pawlak A, Wrona-Krol M, Thompson D, Sarna T (2011) Interactions of plasmalogens and their diacyl analogs with singlet oxygen in selected model systems. Free Radical Biol Med 50:892–898
Luoma AM, Kuo F, Cakici O, Inouye H, Crowther MN, Denninger AR, Avila RL, Brites P, Kirschner DA (2015) Plasmalogen phospholipids protect internal myelin form oxidative damage. Free Radical Biol Med 84:296–310
Busciglio J, Yankner BA (1995) Apoptosis and increased generation of reactive oxygen species in Down’s syndrome neurons in vitro. Nature 378:776–779
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462
Yamatsuji T, Matsui T, Okamoto T, Komatsuzaki K, Takeda S, Fukumoto H, Iwatsubo T, Suzuki N, Asami-Odaka A, Ireland S, Kinane TB, Giambarella U, Nishimoto I (1996) G protein-mediated neuronal DNA fragmentation induced by familial Alzheimer’s disease-associated mutants of APP. Science 272:1349–1352
Ginsberg L, Rafique S, Xuereb JH, Rapoport SI, Gershfeld NL (1995) Disease and anatomic specificity of ethanolamine plasmalogen deficiency in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain Res 698:223–226
Wells K, Farooqui AA, Liss L, Horrocks LA (1995) Neural membrane phospholipids in Alzheimer disease. Neurochem Res 20:1329–1333
Guan Z, Wang Y, Cairns NJ, Lantos PL, Dallner G, Sindelar PJ (1999) Decrease and structural modifications of phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen in the brain with Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:740–747
Miyazawa T, Kanno S, Eitsuka T, Nakagawa K (2006) Plasmalogen: a short review and newly-discovered functions. In: Knapp HR, Huang YS, Yanagita Y (eds) Dietary Fats and Risk of Chronic Disease. AOCS, Urbana
Yamashita S, Kanno S, Nakagawa K, Kinoshita M, Miyazawa T (2015) Extrinsic plasmalogen suppresses neuronal apoptosis in mouse neuroblastoma Neuro-2A cells: importance of plasmalogen molecular species. RSC Adv 5:61012–61020
Yamashita S, Abe A, Nakagawa K, Kinoshita M, Miyazawa T (2014) Separation and detection of plasmalogen in marine invertebrates by high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light-scattering detection. Lipids 49:1261–1273
Yamashita S, Honjo A, Aruga M, Nakagawa K, Miyazawa T (2014) Preparation of marine plasmalogen and selective identification of molecular species by LC-MS/MS. J Oleo Sci 63:423–430
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Rouser G, Kritchevsky G, Simon G, Nelson GJ (1967) Quantitative analysis of brain and spinach leaf lipids employing silicic acid column chromatography and acetone for elution of glycolipids. Lipids 2:37–40
Higuchi O, Nakagawa K, Tsuzuki T, Suzuki T, Oikawa S, Miyazawa T (2006) Aminophospholipid glycation and its inhibitor screening system: a new role of pyridoxal 5′-phosphate as the inhibitor. J Lipid Res 47:964–974
Viswanathan CV, Phillips F, Lundberg WO (1968) Two-dimensional reaction thin-layer chromatography in the analysis of phosphatide plasmalogens. J Chromatogr 35:66–71
Ishiyama M, Tominaga H, Shiga M, Sasamoto K, Ohkura Y, Ueno K (1996) A combined assay of cell viability and in vitro cytotoxicity with a highly water-soluble tetrazolium salt, neutral red and crystal violet. Biol Pharm Bull 19:1518–1520
Thornberry NA, Rano TA, Peterson EP, Rasper DM, Timkey T, Garcia-Calvo M, Houtzager VM, Nordstrom PA, Roy S, Vaillancourt JP, Chapman KT, Nicholson DW (1997) A combinatorial approach defines specificities of members of the caspase family and granzyme B. Functional relationships established for key mediators of apoptosis. J Biol Chem 272:17907–17911
Wolf BB, Schuler M, Echeverri F, Green DR (1999) Caspase-3 is the primary activator of apoptotic DNA fragmentation via DNA fragmentation factor-45/inhibitor of caspase-activated DNase inactivation. J Biol Chem 274:30651–30656
Maeba R, Ueta N (2003) Ethanolamine plasmalogens prevent the oxidation of cholesterol by reducing the oxidizability of cholesterol in phospholipid bilayers. J Lipid Res 44:164–171
Maeba R, Ueta N (2003) Ethanolamine plasmalogen and cholesterol reduce the total membrane oxidizability measured by the oxygen uptake method. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 302:265–270
Nishimukai M, Wakisaka T, Hara H (2003) Ingestion of plasmalogen markedly increased plasmalogen levels of blood plasma in rats. Lipids 38:1227–1235
Kraffe E, Soudant P, Marty Y (2004) Fatty acids of serine, ethanolamine, and choline plasmalogens in some marine bivalves. Lipids 39:59–66
Scott TW, Ashes JR, Fleck E, Gulati SK (1993) Effect of fish oil supplementation on the composition of molecular species of choline and ethanolamine glycerophospholipids in ruminant muscle. J Lipid Res 34:827–835
Ohshima T, Wada S, Koizumi C (1989) 1-O-Alk-1′-enyl-2-acyl and 1-O-alkyl-2-acyl glycerophospholipids in white muscle of bonito Euthynnus pelamis (Linnaeus). Lipids 24:363–370
Medina I, Aubourg SP, Martin RP (1995) Composition of phospholipids of white muscle of 6 tuna species. Lipids 30:1127–1135
Berry KAZ, Murphy RC (2004) Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry of glycerophosphoethanolamine plasmalogen phospholipids. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 15:1499–1508
Yunoki K, Kukino O, Nadachi Y, Fujino T, Ohnishi M (2008) Separation and determination of functional complex lipids from chicken skin. J Am Oil Chem Soc 85:427–433
Jeong BY, Ohshima T, Koizumi C (1996) Hydrocarbon chain distribution of ether phospholipids of the ascidian Halocynthia roretzi and the sea urchin Strongylocentrotus intermedius. Lipids 31:9–18
Hanuša LO, Dmitri OL, Shkrobc I, Dembitsky VM (2009) Plasmalogens, fatty acids and alkyl glyceryl ethers of marine and freshwater clams and mussels. Food Chem 116:491–498
Tomaz ACD, de Miranda GEC, de Souza MDV, de Cunha EVL (2012) Analysis and characterization of methyl esters of fatty acids of some Gracilaria species. Biochem Syst Ecol 44:303–306
Budihardjo I, Oliver H, Lutter M, Luo X, Wang X (1999) Biochemical pathways of caspase activation during apoptosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:269–290
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM (1998) Death receptors: signaling and modulation. Science 281:1305–1308
Hossain MS, Ifuku M, Take S, Kawamura J, Miake K, Katafuchi T (2013) Plasmalogens rescue neuronal cell death through an activation of AKT and ERK survival signaling. PLoS One 8:e83508
Mattson MP, Barger SW, Furukawa K, Bruce AJ, Wyss-Coray T, Mark RJ, Mucke L (1997) Cellular signaling roles of TGF beta, TNF alpha and beta APP in brain injury responss disease. Brain Res Rev J 23:47–61
Hara H, Wakisaka T, Aoyama Y (2003) Lymphatic absorption of plasmalogen in rats. Br J Nutr 90:29–32
Yan SD, Chen X, Fu J, Chen M, Zhu H, Roher A, Slattery T, Zhao L, Nagashima M, Morser J, Migheli A, Nawroth P, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1996) RAGE and amyloid-β peptide neurotoxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 382:685–691
Pratico D, Delanty N (2000) Oxidative injury in diseases of the central nervous system: focus on Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Med 109:577–585
Sutcliffe JG, Hedlund PB, Thomas EA, Bloom FE, Hilbush BS (2011) Peripheral reduction of β-amyloid is sufficient to reduce brain β-amyloid: implications for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci Res 89:808–814
Skerrett R, Pellegrino MP, Casali BT, Taraboanta L, Landreth GE (2015) Combined liver X receptor/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist treatment reduces amyloid β levels and improves behavior in amyloid precursor protein/presenilin 1 mice. J Biol Chem 290:21591–21602
Ifuku M, Katafuchi T, Mawatari S, Noda M, Miake K, Sugiyama M, Fujino T (2012) Anti-inflammatory/anti-amyloidogenic effects of plasmalogens in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation in adult mice. J Neuroinflammation 9:197
Yamashita S, Kiko T, Fujiwara H, Hashimoto M, Nakagawa K, Kinoshita M, Furukawa K, Arai H, Miyazawa T (2015) Alterations in the levels of amyloid-β, phospholipid hydroperoxide, and plasmalogen in the blood of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: Possible interactions between amyloid-β and these lipids. J Alzheimers Dis. doi:10.3233/JAD-150640
Onodera T, Futai E, Kan E, Abe N, Uchida T, Kamio Y, Kaneko J (2015) Phosphatidylethanolamine plasmalogen enhances the inhibiting effect of phosphatidylethanolamine on γ-secretase activity. J Biochem 157:301–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, S., Kanno, S., Honjo, A. et al. Analysis of Plasmalogen Species in Foodstuffs. Lipids 51, 199–210 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4112-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11745-015-4112-y