Abstract
Objective
To compare the therapeutic efficacy between warm needling moxibustion and electroacupuncture (EA) in the treatment of simple obesity due to yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney.
Methods
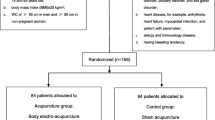
Seventy patients with simple obesity due to yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney were randomly divided into a warm needling moxibustion group and an EA group, with 35 subjects in each group. Same major acupoints were selected for the two groups, including Shuifen (CV 9), Guanyuan (CV 4), Daheng (SP 15), Shuidao (ST 28), Shousanli (LI 10), Zusanli (ST 36), Sanyinjiao (SP 6) and Taixi (KI 3). The warm needling moxibustion group received warm needling moxibustion, while the EA group received EA treatment. The interventions were performed once every other day, with 15 treatments as one course. The therapeutic efficacy, body weight and body mass index (BMI) were then observed and compared.
Results
The total effective rate in the warm needling moxibustion group was 85.7% versus 77.1% in the EA group, and the between-group difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The warm needling moxibustion was remarkably superior to the EA in weight loss and lowering BMI, both with statistical significance (P<0.05, P<0.01). At the three-month follow-up, the body weight and BMI further decreased in the warm needling moxibustion group (both P<0.05), and the levels were lower than those in the EA group (P<0.05, P<0.01).
Conclusion
Warm needling moxibustion can produce reliable and consistent efficacy in the treatment of simple obesity due to yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney. Compared with EA, warm needling moxibustion shows advantage in both short-term and long-term efficacies, and thus is worth promotion in clinical practice.
摘要
目的
比较温针灸与电针治疗脾肾阳虚型单纯性肥胖症的临床疗效。
方法
将70例脾肾阳虚型单纯性肥胖症患者随机分为温针灸组和电针组, 每组35例。 两组均取水分、 关元、 大横、 水道、 手三里、 足三里、 三阴交和太溪为主穴, 温针灸组接受温针灸治疗, 电针组接受电针治疗。 隔日治疗1次, 15次为1个疗程。 一个疗程结束后, 对其临床疗效、 体重及体质量指数(BMI)等指标进行观察和比较。
结果
温针灸组总有效率为85.7%, 电针组为77.1%, 两组差异有统计学意义(P<0.05); 温针灸组在降低体重和BMI方面优于电针组, 组间差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05, P<0.01)。 治疗后3个月随访, 温针灸组的体重和BMI均较治疗后进一步下降(均P<0.05), 且明显低于电针组(P<0.05, P<0.01)。
结论
温针灸治疗脾肾阳虚型单纯性肥胖症疗效确切、持久, 近期和远期疗效均优于电针治疗, 值得临床推广应用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V, Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, Elbourne D, Egger M, Altman DG; CONSORT. CONSORT 2010 explanation and elaboration: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. Int J Surg, 2012, 10(1): 28–55.
MacPherson H, Altman DG, Hammerschlag R, Li Y, Wu T, White A, Moher D; STRICTA Revision Group. Revised Standards for Reporting Interventions in Clinical Trials of Acupuncture (STRICTA): extending the CONSORT statement. Acupunct Med, 2010, 28(2): 83–93.
Wei BH, Jia BP. Criteria for diagnosis and therapeutic effect evaluation of simple obesity. Chin J Integr Trad West Med, 1998, 18(5): 317–319.
Wu J, Li Q, Chen L, Tian DH, Tian D. Clinical research on using acupuncture to treat female adult abdominal obesity with spleen deficiency and exuberant dampness. J Tradit Chin Med, 2014, 34(3): 274–278.
Yan LM, Liu ZC, Yuan JH, Xu B. Effects of electroacupuncture for visceral fat of simple obesity with stomach and intestinal heat. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2016, 36(9): 897–900.
He YZ, Tang HZ. Progress on the mechanism of hypothalamus participating in the weight loss by acupuncture and moxibustion. Henan Zhongyi, 2017, 37(12): 2197–2199.
Xing JM, Sheng XY, Xu X, Zhao ZT, Yan XH. Research progress of the central mechanism of acupuncture-moxibustion for simple obesity. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2016, 14(6): 438–442.
Wang JJ, Chen X, Huang W, Zhou ZY. Effect of acupoint thread embedding on the peripheral serum leptin and insulin levels in simple obesity patients. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(1): 55–59.
Ge BH, Wang XY, Zhang T, An BZ, Chen YZ, Liu Y. Effect of acupoint thread embedding on blood lipids and insulin in simple obesity. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2015, 34(2): 117–119.
Xu XK, Gao F, Wang LL, Wu ZQ, Liang YL, Sun XX, Du XY, Zhou XH, Sun LH. A comparative study of the effect of low-frequency electroacupuncture on blood lipids between men and women with simple obesity. J Acupunct Tuina Sci, 2017, 15(6): 415–419.
Yan RH, Liu XM, Bai J, Yu J, Gu JS. Influence of catgut implantation at acupoints on leptin and insulin resistance in simple obesity rats. J Tradit Chin Med, 2012, 32(3): 477–481.
Kong XJ, Gao L, Peng H, Shi X. Effects of electroacupuncture on expression of obestatin in hypothalamus of rats with simple obesity. Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xuebao, 2010, 8(5): 480–485.
Jie X, Li X, Song JQ, Wang D, Wang JH. Anti-inflammatory and autonomic effects of electroacupuncture in a rat model of diet-induced obesity. Acupunct Med, 2018, 36(2): 103–109.
Cai SK, Li YB, Yang F, Fan YZ, Dong JL, Wu Q, Cai Y. Effect of electroacupuncture on hypothalamic IRS-1 in a rat model of T2DM. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2018, 37(3): 330–334.
Tian L, Zhang SY, Gao F, Sun XX, Du XY, Sun LH, Liang YL. Effect of electroacupuncture on serum insulin and the fat content in male and female experimental obesity rats. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2017, 36(1): 94–97.
Pang TT, Liu ZC, Xu B. Clinical observation on obesity and hyperlipidemia of yang deficiency of spleen and kidney syndrome in female patients treated with warm acupuncture combined with auricular acupuncture. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu, 2015, 35(6): 529–533.
Darbandi M, Darbandi S, Owji AA, Mokarram P, Mobarhan MG, Fardaei M, Zhao B, Abdi H, Nematy M, Safarian M, Parizadeh MR, Dabbaghmanesh MH, Abbasi P, Ferns G. Auricular or body acupuncture: which one is more effective in reducing abdominal fat mass in Iranian men with obesity: a randomized clinical trial. J Diabetes Metab Disord, 2014, 13(1): 92.
Firouzjaei A, Li GC, Wang N, Liu WX, Zhu BM. Comparative evaluation of the therapeutic effect of metformin monotherapy with metformin and acupuncture combined therapy on weight loss and insulin sensitivity in diabetic patients. Nutr Diabetes, 2016, 6(5): e209.
Han YP, Li Y, Yang G, Wang LS. Efficacy observation of electroacupuncture on simple obesity of female patients with spleen dysfunction and dampness syndrome. J Clin Acupunct Moxib, 2015, 31(6): 25–27.
Wu YF, Huang XG, Zhao LH. Observations on the efficacy of electroacupuncture plus weak laser fat dissolution technique in treating female patients with simple obesity and overweight of stomach heat dampness stagnation type. Shanghai Zhenjiu Zazhi, 2015, 34(9): 852–855.
Pang TT, Liu ZC, Xu B. Effects of warming needle moxibustion combined with ear-acupuncture on blood lipid level in obesity patients with syndrome of yang deficiency of spleen and kidney complicated with hyperlipidemia. Chin J Tradit Chin Med Pharm, 2016, 31(6): 2133–2138.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Scientific Research Fund of Jiading District Science and Technology Commission, Shanghai (上海市嘉定区科委科研课题, No. 2015-KW-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declared that there was no potential conflict of interest in this article.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Ly., He, Tf., Chu, Xy. et al. Warm needling moxibustion versus electroacupuncture for simple obesity due to yang deficiency of the spleen and kidney: a controlled clinical trial. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 258–263 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1125-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1125-8
Keywords
- Acupuncture Therapy
- Warm Needling Therapy
- Electroacupuncture
- Points, Lower Extremities
- Points, Chest & Abdomen
- Obesity
- Yang Deficiency of the Spleen and Kidney