Abstract
Objective
To observe the effect of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on liver X receptor alpha (LXRα) in rabbits with atherosclerosis.
Methods
Thirty-six male New Zealand rabbits were randomly divided into a normal group, a model group, a herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group and a simvastatin group according to the random number table method, with 9 rabbits in each group. Rabbits in the model group, the herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group and the simvastatin group were modeled by high fat feeding method which took 12 weeks. After verification of the successful model, rabbits in the normal group were not treated, in the model group were bundled, in the herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group were treated with herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion, and those in the simvastatin group were treated with simvastatin, all for a total of 4 weeks. At the end of the experiment, the aorta and liver were observed for pathological changes; serum and liver were used to detect lipid levels; Western blot (WB) and real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) were used to detect LXRα protein and mRNA expression levels, respectively.
Results
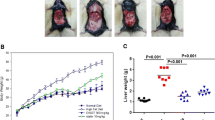
Compared with the normal group, the structure of aorta was disordered, the wall was rough and thick, the intima was unsmooth, and the vascular smooth muscle cells were arranged closely and disorderly in the model group, which was consistent with the characteristics of the rabbit model of aortic atherosclerosis. Compared with the model group, the aortic structure was clear, the degree of hepatocyte degeneration was reduced, the serum total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein levels were significantly decreased (all P<0.01), the high-density lipoprotein level was elevated (P<0.01), and the total liver cholesterol was decreased significantly (P<0.01) in the rabbits of the herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group and the simvastatin group; compared with the model group, the protein (P<0.01 or P<0.05) and mRNA (P<0.01) expressions of rabbit LXRα in the herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion group and the simvastatin group were increased.
Conclusion
Herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion can improve the aortic and hepatic lesions, regulate blood lipid and liver lipid levels, increase the expression of liver cholesterol reverse transport nuclear receptor LXRα, promote reverse cholesterol transport in the rabbits with aortic atherosclerosis, therefore produces an antiatherogenic effect.
概要
目的
观察隔药饼灸对动脉粥样硬化兔胆固醇逆转运肝X受体α (LXRα)的影响。
方法
将36只雄性新西兰 兔按随机数字表法随机分为正常组、模型组、隔药饼灸组和辛伐他汀组, 每组9只。模型组、隔药饼灸组和辛伐 他汀组采用高脂饲养法造模, 共12周。验证造模成功后, 正常组不予治疗, 模型组予以捆绑, 隔药饼灸组予以隔 药饼灸治疗, 辛伐他汀组予以辛伐他汀治疗, 共治疗4周。实验结束后取主动脉及肝脏观察其病理形态变化, 取血 清及肝脏检测脂质水平, 以蛋白质印迹法(WB)和实时荧光定量聚合酶链反应(RT-qPCR)法分别检测LXRα蛋白及 mRNA表达水平。
结果
与正常组比较, 模型组主动脉结构紊乱, 管壁粗糙增厚, 内膜不光滑, 血管平滑肌细胞排 列紧密无序, 符合主动脉粥样硬化兔模型的特点。与模型组比较, 隔药饼灸组和辛伐他汀组兔主动脉结构清晰, 肝细胞变性程度减轻, 血清总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白明显降低(均P<0.01), 高密度脂蛋白升高(P<0.01), 肝脏总 胆固醇明显降低(P<0.01); 隔药饼灸组和辛伐他汀组兔与模型组比较, LXRα蛋白(P<0.01或P<0.05)及 LXRα mRNA (P<0.01)表达增加。
结论
隔药饼灸可改善主动脉粥样硬化兔主动脉及肝脏的病变情况, 调节血脂和 肝脏脂质水平, 提高肝脏胆固醇逆转运核受体LXRα的表达, 促进胆固醇逆转运从而发挥抗动脉粥样硬化的作用。
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Professional Group of Lipid and Atherosclerosis, Cardiovascular Disease Committee of Chinese Association of the Integration of Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine. Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of atherosclerosis by combination of traditional Chinese and Western medicine. Zhongguo Quanke Yixue, 2017, 20(5): 507–511.
Wang YF, Song XS, Bai R, Liang B, Liu GZ, Lou XP, Er L, Hou YY, Zhang YL, Bian YF, Xiao CS. Effect of NgBR on reverse cholesterol transport of macrophage derived foam cells. Zhongguo Dongmai Yinghua Zazhi, 2016, 24(9): 893–898.
Yin K, Liao DF, Tang CK. ATP–binding membrane cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1): a possible link between inflammation and reverse cholesterol transport. Mol Med, 2015, 16(9–10): 438–449.
Xu XL, Li Q, Pang LW, Huang GQ, Huang JC, Shi M, Sun XT, Wang YQ. Arctigenin promotes cholesterol efflux from THP–1 macrophages through PPAR–?/LXR–a signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2013, 441(2): 321–326.
Chang XR, Yan J, Yi SX, Yue ZH, Lin YP. Clinical research on cake–seperated moxibustion treating patients with hyperlipernia. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2010, 28(1): 8–10.
Ai K, Ai X, Liu M, Chang XR, Zhang L, Fu L, Li JS, Xie H. Influence of moxibustion with herbal cake on total cholesterol and triglyceride in atherosclerotic rabbits. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2013, 31(9): 1857–1859.
Li PC, Tan DQ, Yin KK, Lu LL, Tan F, Ren ZR. Effects of Shuxin Wenban granules on blood lipids and ICAM–1 in rabbits with atherosclerosis. Hunan Zhongyi Zazhi, 2014, 30(4): 151–154.
Li ZR. Experimental Acupuncture Science. Beijing: China Press of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2007: 242–244.
Ma XY, Lin CR, Wang M, Liu JX. Effect of Rongban Tongmai granules on experimental hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis in rabbits. Zhongchengyao, 2006, 28(8): 1167–1170.
Chang XR, Zhang L, Yu BS, Fu L, Yue ZH, He XQ. Effect of cake–separated moxibustion on the expression of PPAR–? mRNA in aortic endothelial cells of atheroscierotic rabbits. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Xuekan, 2011, 29(6): 1197–1199.
Liu CX, Ding HJ, Lü T, Chen SL, Xu CH. The correlation between carotid atherosclerosis and serum lipid level. Zhongguo Linchuang Baojian Zazhi, 2014, 17(1): 48–50.
Baigent C, Keech A, Kearney PM, Blackwell L, Buck G, Pollicino C, Kirby A, Sourjina T, Peto R, Collins R, Simes R; Cholesterol Treatment Trialists (CTT) Collaborators. Efficacy and safety of cholesterol–lowering treatment: prospective meta–analysis of data from 90 056 participants in 14 randomised trials of statins. Lancet, 2005, 366(9493): 1267–1278.
Joint Committee for the Revision of Guidelines for Prevention and Treatment of Dyslipidemia in Chinese Adults. Guidelines for the prevention and treatment of dyslipidemia in Chinese adults (revised edition 2016). Zhongguo Xunhuan Zazhi, 2016, 16(10): 15–35.
Liao DF, Qin L. Caveolae and caveolin: a possible platform of reverse cholesterol transport and inflammation in atherosclerosis. Zhongguo Dongmai Yinghua Zazhi, 2012, 20(5): 385–392.
Cuchel M, Rader DJ. Macrophage reverse cholesterol transport: key to the regression of atherosclerosis? Circulation, 2006, 113(21): 2548–2555.
Ni ZL, Gao CY, Zhao SP. Probucol promotes reverse cholesterol transport from macrophage to feces in mice in vivo. Linchuang Xinxueguanbing Zazhi, 2014, 30(1): 49–52.
Lo Sasso G, Murzilli S, Salvatore L, D'Errico I, Petruzzelli M, Conca P, Jiang ZY, Calabresi L, Parini P, Moschetta A. Intestinal specific LXR activation stimulates reverse cholesterol transport and protects from atherosclerosis. Cell Metab, 2010, 12(2): 187–193.
Bischoff ED, Daige CL, Petrowski M, Dedman H, Pattison J, Li AC, Schulman IG. Non–redundant roles for LXR alpha and LXR beta in atherosclerosis susceptibility in low density lipoprotein receptor knockout mice. J Lipid Res, 2010, 51(5): 900–906.
Naik SU, Wang X, Da SJ, Jaye M, Macphee CH, Reilly MP, Billheimer JT, Rothblat GH, Rader DJ. Pharmacological activation of liver X receptors promotes reverse cholesterol transport in vivo. Circulation, 2006, 113(1): 90–97.
Zhao C, Dahlman–Wright K. Liver X receptor in cholesterol metabolism. J Endocrinol, 2010, 204(3): 233–240.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China ( 国家自然科学基金项目, No. 81874509, No. 81704182, No. 81403486); Graduate Student Research Innovation Project of Hunan Province (湖南省研究生科研创新项目, No. CX2017B430); Yifang Graduate Student Research Innovation Project of Hunan University of Chinese Medicine (湖南中医药大学一方研 究生科研创新课题项目, No. YF201716); Hunan Provincial Natural Science Youth Fund (湖南省自然科学 青年基金, No. 2018JJ3397).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Liu, Ml., Wang, Hl. et al. Regulatory effect of herbal cake-partitioned moxibustion on cholesterol reverse transport nuclear receptor LXRα in rabbits with atherosclerosis. J. Acupunct. Tuina. Sci. 17, 1–8 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1087-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11726-019-1087-x
Keywords
- Moxibustion Therapy
- Indirect Moxibustion
- Medicinal Cake-partitioned Moxibustion
- Atherosclerosis
- Cholesterol
- Liver X Receptors
- Rabbits