Abstract
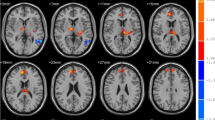
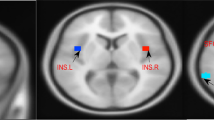
Primary insomnia (PI) is strongly associated with emotional dysregulation. However, the neurobiological pathology of the association between PI and emotional dysregulation is limited. Previous studies have indicated an impact of PI on the emotional regulatory system, but the specificity of this finding remains to be confirmed. A sample of 27 primary insomnia patients (PIs) and 32 matched healthy controls (HCs) was recruited for this study. The functional connectivity density (FCD) was used to assess the spontaneous functional brain organization in PIs. Then, we identified whether the local (lFCD) and global FCD (gFCD) abnormalities can be the potential biomarker for emotion level in PIs. Our findings suggested that PIs exhibited higher levels of anxiety and depression, and the levels of anxiety and depression is associated with the insomnia severity. We also found that PIs showed both lower lFCD and gFCD in several regions (i.e. thalamus, anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), insula). Furthermore, the lower gFCD values of left ACC and right insula were associated with their anxiety level in PIs, which demonstrated their potential biomarker for anxiety in PIs. Our results demonstrated that the relationship between the insomnia severity and the anxiety level could be partially mediated by gFCD of the ACC and insula. The current study improved our understanding of the anxiety in PIs and provided helpful information for future therapeutic development for PIs.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ancoli-Israel, S., & Roth, T. (1999). Characteristics of insomnia in the United States: results of the 1991 National Sleep Foundation survey I. Sleep, 22, S347–S353.
BøRge, S., Paula, S., Arnstein, M., Mari, H., StåLe, P., Steinar, K., et al. (2012). The bidirectional association between depression and insomnia: the HUNT study. Psychosomatic Medicine, 74(7), 758–765.
Bruno, R. M., & Sakmann, B. (2006). Cortex is driven by weak but synchronously active thalamocortical synapses. Science, 312(5780), 1622–1627.
Buysse, D. J., Jules, A., Alex, G., Vladeta, A., Dominique, E., & Wulf, R. S. (2008). Prevalence, course, and comorbidity of insomnia and depression in young adults. Sleep, 31(4), 473–480.
Cano, G., Mochizuki, T., & Saper, C. B. (2008). Neural circuitry of stress-induced insomnia in rats. Journal of Neuroscience, 28(40), 10167–10184.
Caparelli, E. C., Tomasi, D., & Ernst, T. (2005). The effect of small rotations on R 2 * measured with echo planar imaging. Neuroimage, 24(4), 1164–1169.
Chen, M. C., Chang, C., Glover, G. H., & Gotlib, I. H. (2014). Increased insula coactivation with salience networks in insomnia. Biological Psychology, 97, 1–8.
Chen, P. J., Huang, C. L., Weng, S. F., Wu, M. P., Ho, C. H., Wang, J. J., et al. (2017). Relapse insomnia increases greater risk of anxiety and depression: evidence from a population-based 4-year cohort study. Sleep Medicine, 38, 122.
Cooper, J. (2001). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th edn, text revision)(DsM-IV-TR). RCP.
Cordes, D., ., Haughton, V. M., Arfanakis, K., ., Carew, J. D., Turski, P. A., Moritz, C. H., Quigley M.A., Meyerand M.E. (2001). Frequencies contributing to functional connectivity in the cerebral cortex in “resting-state” data. AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology, 22(7), 1326–1333.
Del Felice, A., Formaggio, E., Storti, S. F., Fiaschi, A., & Manganotti, P. (2012). The gating role of the thalamus to protect sleep: An f-MRI report. Sleep Medicine, 13(4), 447–449.
Desseilles, M., Dang-Vu, T., Schabus, M., Sterpenich, V., Maquet, P., & Schwartz, S. (2008). Neuroimaging insights into the pathophysiology of sleep disorders. Sleep, 31(6), 777–794.
Eklund, A., Nichols, T. E., & Knutsson, H. (2016). Cluster failure: Why fMRI inferences for spatial extent have inflated false-positive rates. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 113(28), 7900–7905.
Evans, K. C., Simon, N. M., Dougherty, D. D., Hoge, E. A., Worthington, J. J., Chow, C., Kaufman, R. E., Gold, A. L., Fischman, A. J., Pollack, M. H., & Rauch, S. L. (2009). A PET study of tiagabine treatment implicates ventral medial prefrontal cortex in generalized social anxiety disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology, 34(2), 390–398.
Foerster, B. U., Dardo, T., & Caparelli, E. C. (2010). Magnetic field shift due to mechanical vibration in functional magnetic resonance imaging. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 54(5), 1261–1267.
Ford, D. E., & Kamerow, D. B. (2016). Epidemiologic study of sleep disturbances and psychiatric disorders: an opportunity for prevention? Jama, 262(11), 1479–1484.
Frewen, P. A., Dozois, D. J., & Lanius, R. A. (2008). Neuroimaging studies of psychological interventions for mood and anxiety disorders: empirical and methodological review. Clinical Psychology Review, 28(2), 228–246.
Gentili, C., Gobbini, M. I., Ricciardi, E., Vanello, N., Pietrini, P., Haxby, J. V., & Guazzelli, M. (2008). Differential modulation of neural activity throughout the distributed neural system for face perception in patients with social phobia and healthy subjects. Brain Research Bulletin, 77(5), 286–292.
Hoehn-Saric, R., Schlund, M. W., & Wong, S. H. (2004). Effects of citalopram on worry and brain activation in patients with generalized anxiety disorder. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging, 131(1), 11–21.
Holzschneider, K., & Mulert, C. (2011). Neuroimaging in anxiety disorders. Dialogues in Clinical Neuroscience, 13(4), 453–461.
Huang, Z., Liang, P., Jia, X., Zhan, S., Li, N., Ding, Y., Lu, J., Wang, Y., & Li, K. (2012). Abnormal amygdala connectivity in patients with primary insomnia: evidence from resting state fMRI. European Journal of Radiology, 81(6), 1288–1295.
Kyle, S. D., Espie, C. A., & Morgan, K. (2010). “ … Not just a minor thing, it is something major, which stops you from functioning daily”: quality of life and daytime functioning in insomnia. Behavioral Sleep Medicine, 8(3), 123–140.
Leppänen, J. M. (2006). Emotional information processing in mood disorders: a review of behavioral and neuroimaging findings. Current Opinion in Psychiatry, 19(1), 34–39.
Levin, B., & Duchowny, M. (1991). Childhood obsessive-compulsive disorder and cingulate epilepsy. Biological Psychiatry, 30(10), 1049–1055.
Liu, C.-H., Liu, C.-Z., Zhang, J., Yuan, Z., Tang, L.-R., Tie, C.-L., Fan, J., & Liu, Q. Q. (2016). Reduced spontaneous neuronal activity in the insular cortex and thalamus in healthy adults with insomnia symptoms. Brain Research, 1648, 317–324.
Mayberg, H. S., Liotti, M., Brannan, S. K., McGinnis, S., Mahurin, R. K., Jerabek, P. A., et al. (1999). Reciprocal limbic-cortical function and negative mood: converging PET findings in depression and normal sadness. American Journal of Psychiatry, 156(5), 675–682.
Min, L., Wang, R., Meng, Z., Zhai, J., Bo, L., Yu, D., et al. (2018). Abnormalities of thalamus volume and resting state functional connectivity in primary insomnia patients. Brain Imaging & Behavior, 1–9.
Monti, J. M., & Monti, D. (2000). Sleep disturbance in generalized anxiety disorder and its treatment. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 4(3), 263–276.
Nofzinger, E. A., Buysse, D. J., Miewald, J. M., Meltzer, C. C., Price, J. C., Sembrat, R. C., et al. (2002). Human regional cerebral glucose metabolism during non-rapid eye movement sleep in relation to waking. Brain, 125(5), 1105–1115.
Nofzinger, E. A., Buysse, D. J., Germain, A., Price, J. C., Miewald, J. M., & Kupfer, D. J. (2004). Functional neuroimaging evidence for hyperarousal in insomnia. American Journal of Psychiatry, 161(11), 2126–2128.
Nofzinger, E. A., Nissen, C., Germain, A., Moul, D., Hall, M., Price, J. C., Miewald, J. M., & Buysse, D. J. (2006). Regional cerebral metabolic correlates of WASO during NREM sleep in insomnia. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 2(3), 316–322.
Paulus, M. P., & Stein, M. B. (2006). An insular view of anxiety. Biological Psychiatry, 60(4), 383–387.
Paulus, M. P., & Stein, M. B. (2010). Interoception in anxiety and depression. Brain Structure and Function, 214(5–6), 451–463.
Périco, C. A.-M., Skaf, C. R., Yamada, A., Duran, F., Buchpiguel, C. A., Castro, C. C., et al. (2005). Relationship between regional cerebral blood flow and separate symptom clusters of major depression: a single photon emission computed tomography study using statistical parametric mapping. Neuroscience letters, 384(3), 265-270.
Plante, D. T., Jensen, J. E., Schoerning, L., & Winkelman, J. W. (2012). Reduced γ-aminobutyric acid in occipital and anterior cingulate cortices in primary insomnia: a link to major depressive disorder? Neuropsychopharmacology, 37(6), 1548–1557.
Riemann, D., Spiegelhalder, K., Feige, B., Voderholzer, U., Berger, M., Perlis, M., & Nissen, C. (2010). The hyperarousal model of insomnia: a review of the concept and its evidence. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 14(1), 19–31.
Rive, M. M., van Rooijen, G., Veltman, D. J., Phillips, M. L., Schene, A. H., & Ruhé, H. G. (2013). Neural correlates of dysfunctional emotion regulation in major depressive disorder. A systematic review of neuroimaging studies. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 37(10), 2529–2553.
Shin, L. M., Dougherty, D. D., Orr, S. P., Pitman, R. K., Lasko, M., Macklin, M. L., Alpert, N. M., Fischman, A. J., & Rauch, S. L. (2000). Activation of anterior paralimbic structures during guilt-related script-driven imagery. Biological Psychiatry, 48(1), 43–50.
Stoffers, D., Moens, S., Benjamins, J. S., Van Tol, M., Penninx, B. W. J. H., Veltman, D. J., et al. (2012). Orbitofrontal gray matter relates to early morning awakening: a neural correlate of insomnia complaints? Frontiers in Neurology, 3, 105–105.
Tomasi, D., & Volkow, N. D. (2010). Functional connectivity density mapping. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 107(21), 9885–9890.
Wang, T., Li, S., Jiang, G., Lin, C., Li, M., Ma, X., Zhan, W., Fang, J., Li, L., Li, C., & Tian, J. (2016). Regional homogeneity changes in patients with primary insomnia. European Radiology, 26(5), 1292–1300.
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by the academic capability and leaders training program supported by Hebei province Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical statements
Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Y., Zhao, X., Yin, H. et al. Functional connectivity density abnormalities and anxiety in primary insomnia patients. Brain Imaging and Behavior 15, 114–121 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00238-w
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11682-019-00238-w