Abstract
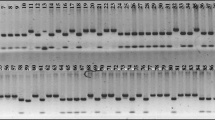
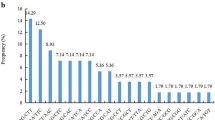
Because there are thousands of peach cultivars, cultivar classification is a critical step before starting a breeding project. Various molecular markers such as simple sequence repeats (SSRs) can be used. In this study, 67 polymorphic primers produced 302 bands. Higher values for SI index (1.903) suggested higher genetic variability in the genotype under investigation. Mean values for observed alleles (Na), expected heterozygosity (He), effective alleles (Ne), Nei’s information index (h), and polymorphic information content (PIC) were 4.5, 0.83, 5.45, 0.83, and 0.81, respectively. The dendrogram constructed based on Jaccard’s similarity coefficients outlined four distinct clusters in the entire germplasm. In addition, an analysis of molecular variance (AMOVA) showed that 70.68% of the total variation was due to within-population variation, while 29.32% was due to variation among populations. According to this research, all primers were successfully used for the peach accessions. The EST-SSR markers should be useful in peach breeding programs and other research.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PIC:
-
Polymorphic information content
- UPGMA:
-
Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic average
- AMOVA:
-
Analysis of molecular variance
- EST:
-
Expressed sequenced tags
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeats
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- SI:
-
Shannon’s information index
- h :
-
Nei’s information index
- He:
-
Expected heterozygosity
- Ho:
-
Observed hetrozygosity
- Ne:
-
Effective alleles
- Na:
-
Observed number of alleles
- MCMC:
-
Markov chain Monte Carlo,
- MAS:
-
Marker-assisted selection
References
Amirbakhtiar N, Shiran B, Moradi H, Sayed-Tabatabaei BE (2006) Molecular characterization of almond cultivars using microsatellite markers. Acta Hort 726:51–56
Andersen JR, Lubberstedt T (2003) Functional markers in plants. Trends Plant Sci 8:554–560
Anderson JA, Churchill GA, Autrique JE, Tanksley SD, Sorrells ME (1993) Optimizing parental selection for genetic linkage maps. Genome 36:181–186
Aranzana MJ, Garcia-Mas J, Carbo´ J, Aru´s P (2002) Development and variability analysis of microsatellite markers in peach. Plant Breed 121:87–92
Aranzana MJ, Pineda A, Cosson P, Dirlewanger E, Ascasibar J, Cipriani G, Ryder CD, Testolin R, Abbott A, King GJ, Iezzoni AF, Aru´s P (2003) A set of simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor Appl Genet 106:819–825
Arolu IW, Rafii MY, Hanafi MM, Mahmud TMM, Latif MA (2012) Molecular characterization of Jatropha curcas germplasm using inter simple sequence repeat (ISSR) markers in Peninsular Malaysia. Aust J Crop Sci 6:1666–1673
Benson LL, Lamboy WF, Zimmerman RH (2001) Molecular identification of Malus hupehensis (tea crabapple) accessions using simple sequence repeats. Hortic Sci 36:961–966
Blair MW, Gonza´lez LF, Kimani PM, Butare L (2010) Genetic diversity, inter-gene pool introgression and nutritional quality of common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) from Central Africa. Theor Appl Genet 121:237–248
Cantini C, Iezzoni AF, Lamboy WF, Boritzki M, Struss D (2001) DNA fingerprinting of tetraploid cherry germplasm using SSR. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 126:205–209
Chen CX, Zhou P, Choi YA, Huang S, Gmitter FG (2006) Mining and characterizing microsatellites from Citrus ESTs. Theor Appl Genet 112:1248–1257
Chen CX, Bock CH, Okie WR, Gmitter FG, Jung S, Main D, Beckman TG, Wood BW (2014) Genome-wide characterization and selection of expressed sequence tag simple sequence repeat primers for optimized marker distribution and reliability in peach. Tree Genet Genomes 10:1271–1279
Cipriani G, Lot G, HuangWG Peterlunger E, Testolin R (1999) AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]: isolation, characterization and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 99:65–72
Decroocq V, Favé MG, Hagen L, Bordenave L, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape EST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dettori MT, Micali S, Giovinazzi J, Scalabrin S, Verde I, Cipriani G (2015) Mining microsatellites in the peach genome: development of new long-core SSR marker for genetic analyses in five Prunus species. Springerplus 4:337
Ding MM, Wang K, Wang WT, Chen MJ, Wu DJ, Xu CJ, Chen KS (2017) Development of high quality EST-SSR markers without stutter bands in peach and their application in cultivar discrimination and hybrid authentication. Hortic Sci 52:24–30
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana MJ, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Aru´s P, Laigret F (2002) Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry. Theor Appl Genet 105:127–138
Du QZ, Zhang DQ, Li BL (2012) Development of 15 novel microsatellite markers from cellulose synthase genes in Populus tomentosa (Salicaceae). Am J Bot 99:46–48
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin ver. 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Fathi A, Ghareyazi B, Haghnazari A, Ghaffari MR, Pirseyedi SM, Kadkhodaei S, Naghavi MR, Mardi M (2008) Assessment of the genetic diversity of almond (Prunus dulcis) using microsatellite markers and morphological traits. Iran J Biotechnol 6(2):98–106
Fu N, Wang PY, Liu XD, Shen HL (2014) Use of EST-SSR markers for evaluating genetic diversity and fingerprinting Celery (Apium graveolens L.) cultivars. Molecules 19:1939–1955
Guichoux E, Lagache L, Wagner S, Chaumeil P, Leger P, Lepais O, Lepoittevin C, Malausa T, Revardel E, Salin F, Petit RJ (2011) Current trends in microsatellite genotyping. Mol Ecol Resour 11:591–611
Hagen LS, Chaib J, Fad B, Decrocq V, Bouchet JP, Lambert P, Audergon JM (2004) Genomic and cDNA microsatellites from apricot (Prunus armeniaca L). Mol Ecol Notes 4:742–745
Hu J, Wang LY, Li J (2011) Comparison of genomic SSR and EST-SSR markers for estimating genetic diversity in cucumber. Biol Plant 55:577–580
Huang XQ, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud des Sci Nat 44:223–270
Kantety RV, La Rota M, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, rice, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Kumar H, Kaur G, Banga S (2012) Molecular characterization and assessment of genetic diversity in sesame (Sesamum indicum L.) germplasm collection using ISSR markers. J Crop Improv 26:540–557
Lamboy WF, Alpha CG (1998) Using simple sequence repeats (SSRs) for fingerprinting germplasm accessions of grape (Vitis L.) species. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 123:182–188
Li G, Ra WH, Park JW, Kwon SW, Lee JH, Park CB, Park YJ (2011) Developing EST-SSR markers to study molecular diversity in Liriope and Ophiopogon. Biochem Syst Ecol 39:241–252
Li XY, Shangguan LF, Song CN, Wang C, Gao ZH, Yu HP, Fang JG (2014) Analysis of expressed sequence tags from Prunus mume flower and fruit and development of simple sequence repeat markers. BMC Genet 11:66
Ma RC, Xie H, Xu Y, Ma Y, Jiang YQ, Cao MQ (2003) Molecular analysis of almond germplasm in China. Options Mediterr 63:281–290
Martínez-Gómez P, Arulsekar S, Potter D, Gradziel TM (2003) An extended interspecific gene pool available to peach and almond breeding as characterized using simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers. Euphytica 131:313–322
Morgante M, Hanafey M, Powell W (2002) Microsatellites are preferentially associated with nonrepetitive DNA in plant genomes. Nat Genet 30:194–200
Mujaju C, Sehic J, Nybom H (2013) Assessment of EST-SSR markers for evaluating genetic diversity in Watermelon accessions from Zimbabwe. Am J Plant Sci 4:1448–1456
Murray HC, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl. Acids Res. 8:4321–4325
Nagaraj SH, Gasser RB, Ranganathan S (2007) A hitchhiker’s guide to expressed sequence tag (EST) analysis. Brief Bioinform 8:6–21
Parsons JB, Newbury HT, Jackson MT, Ford-Lloyd BV (1997) Contrasting genetic diversity relationships are revealed in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using different marker types. Mole Breed 3:115–125
Pertea G, Huang X, Liang F, Antonescu V, Sultana R, Karamycheva S, Lee Y, White J, Cheung F, Parvizi B, Tsai J, Quackenbush J (2003) TIGR gene indices clustering tools (TGICL): a software system for fast clustering of large EST datasets. Bioinformatics 19:651–652
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Rao NK (2004) Plant genetic resources: advancing conservation and use through biotechnology. Afr J Biotechnol 3:136–145
Rohlf FJ (2002) NTSYS-pc: numerical taxonomy system ver.2.1. Exeter Publishing Ltd., New York
Shiran B, Amirbakhtiar N, Kiani S, Mohammadi S, Sayed-Tabatabaei BE, Moradi H (2007) Molecular characterization and genetic relationship among almond cultivars assessed by RAPD and SSR markers. Sci Hortic 111:280–292
Sorkheh K, Shiran B, Gradziel TM, Epperson BK, Martinez-Gomez P, Asadi E (2007) Amplified fragment length polymorphism as a tool for molecular characterization of almond germplasm: genetic diversity among cultivated genotypes and related wild species of almond, and its relationships with agronomic traits. Euphytica 156:327–344
Sorkheh K, Prudencio AS, Ghebinejad A, Kohei Dehkordi M, Erogul D, Rubio M, Martínez-Gómez P (2016) In silico search, characterization and validation of new EST-SSR markers in the genus Prunus. BMC Res Notes 9:336
Sosinski B, Gannavarapu M, Hager LD, Beck LE, King GJ, Ryder CD, Rajapakse S, Baird WV, Ballard RE, Abbott AG (2000) Characterization of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunuspersica (L.) Batsch]. Theor Appl Genet 101:421–428
Testolin R, Marrazzo T, Cipriani G (2000) Microsatellite DNA in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 43:512–520
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotech 23:48–55
Vendramin E, Dettori MT, Giovinazzi J, Micali R, Quarta R, Verde I (2007) A set of EST-SSRs isolated from peach fruit transcriptome and their transportability across Prunus species. Mol Ecol Notes 7:307–310
Wang Y, Georgi LL, Zhebentyayeva TN, Reighard GL, Scorza R, Abbott AG (2002) High throughput targeted SSR marker development in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch]. Genome 45:319–328
Wang YJ, Li XY, Han J, Fang WM, Li XD, Wang SS, Fang JG (2014) Analysis of genetic relationships and identification of flowering-mei cultivars using EST-SSR markers developed from apricot and fruiting-mei. Scientia Hortic 132:12–17
Weising K, Nybon H, Wolff K, Meyer W (1995) DNA fingerprinting in plants and fungi. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Whitfield CW, Band MR, Bonaldo MF, Kumar CG, Liu L, Pardinas JR, Robertson HM, Soares MB, Robinson GE (2001) Annotated expressed sequence tags and cDNA microarrays for studies of brain and behavior in the honey bee. Genome Res 12:555–566
Xie H, Sui Y, Chang FQ, Xu Y, Ma RC (2006) SSR allelic variation in almond (Prunus dulcis Mill). Theor Appl Genet 112:366–372
Xu Y, Ma RC, Xie H, Liu JT, Cao MQ (2004) Development of SSR markers for the phylogenetic analysis of almond trees from China and the Mediterranean region. Genome 47:1091–1104
Yamamoto T, Mochida K, Imai T, Shi IZ, Ogiwara I, Hayashi T (2002) Microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] derived from an enriched genomic and cDNA libraries. Mol Ecol Notes 2:298–302
Yeh FC, Yang R, Boyle TJ, Ye Z, Xiyan JM (2000) PopGene32, Microsoft Windows based Freeware for Population Genetic Analysis, Version 1.32. Molecular Biology and Biotechnology Centre, University of Alberta, Edmonton
Zeinalabedini M, Majourhat K, Khayam-Nekoui M, Grigorian V, Torchi M, Dicenta F, Martinez-Gomez P (2007) Molecular characterization of almond cultivars and related wild species using nuclear and chloroplast DNA markers. J Food Agric Environ 5(3–4):242–247
Zhang GW, Xu SC, Mao WH, Hu QZ, Gong YM (2013) Determination of the genetic diversity of vegetable soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] using EST-SSR markers. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 14:279–288
Zhebentyayeva T, Reighard G, Gorina V, Abbott A (2003) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) analysis for assessment of genetic variability in apricot germplasm. Theor Appl Genet 106:435–444
Zhen YQ, Li ZZ, Huang HW, Wang Y (2004) Molecular characterization of kiwifruit (Actinidia) cultivars and selections using SSR markers. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 129:374–382
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Project funding: The work was supported by Payme-Noor University of Tehran, Iran and Shahid Chamran University of Ahvaz (AG1396-Grant_Faculty of Agriculture).
The online version is available at http://www.springerlink.com
Corresponding editor: Tao Xu.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koohi Dehkordi, M., Beigzadeh, T. & Sorkheh, K. Novel in silico EST-SSR markers and bioinformatic approaches to detect genetic variation among peach (Prunus persica L.) germplasm. J. For. Res. 31, 1359–1370 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-00922-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-00922-z