Abstract
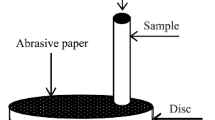
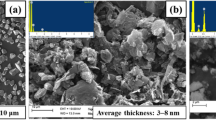
Dense Al5356/TiN composites with TiN particles uniformly dispersed in the matrix were produced by cold spraying (CS) using both the mechanically mixed (MM) and ball-milled (BM) powder blends with 50 wt.% TiN compared to that of CS pure Al5356 deposit. The microhardness of the composite deposited with the BM blend was three times higher than that of pure Al5356 coating. Compared to the coating deposited with the MM powder (MM composite), the hardness of the coating deposited with the BM powder (BM composite) was significantly increased owing to the increase of TiN volume fraction, which is comparable to that of the MM composite deposited with the 75 wt.% TiN feedstock. The adhesive strength of the composites was remarkably improved in comparison with the pure Al5356 coating because of the pinning effect of TiN particles. The coefficient of frication (COF) and wear rate (WR) were measured using a ball-on-disc tribometer. It was found that the COFs and WRs of the composites were much lower than those of pure Al5356 coating. Especially, the WRs of the MM and BM composites were, respectively, decreased by about 14 and 50 times than that of pure Al5356 deposit. This phenomenon could be ascribed that TiN particles contribute to a third-body abrasion in the following sliding process, which benefits the decrease of COF by rolling action partially instead of sliding action. For the BM composite, more and finer TiN particles present in the worn surface compared to the MM composite, which will be helpful to the further decrease of the COF and WR.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.T. Yu, J.Z. Cui, L. Wang, Metal Matrix Composites, Metallurgical Industry Press, Beijing, 1995. (in Chinese)
A.M. Davidson, D. Regener, A Comparison of Aluminium-based Metal-matrix Composites Reinforced with Coated and Uncoated Particulate Silicon Carbide, Compos. Sci. Technol., 2000, 60(6), p 865-869
D.P. Mondal, S. Das, High Stress Abrasive Wear Behaviour of Aluminium Hard Particle Composites: Effect of Experimental Parameters, Particle Size and Volume Fraction, Tribol. Int., 2006, 39(6), p 470-478
Y. Yalcin, H. Akbulut, Dry Wear Properties of A356-SiC Particle Reinforced MMCs Produced by Two Melting Routes, Mater. Design, 2006, 27(10), p 872-881
Y.L. Shen, J.J. Williams, G. Piotrowski, N. Chawla, Y.L. Guo, Correlation Between Tensile and Indentation Behavior of Particle-reinforced Metal Matrix Composites: an Experimental and Numerical Study, Acta Mater., 2001, 49(16), p 3219-3229
A. Slipenyuk, V. Kuprin, Y. Milman, V. Goncharuk, J. Eckert, Properties of P/M Processed Particle Reinforced Metal Matrix Composites Specified by Reinforcement Concentration and Matrix-to-Reinforcement Particle Size Ratio, Acta Mater. 2006, 54(1), p 157-166
J.N. Hall, J.W. Jones, A.K. Sachdev, Particle Size, Volume Fraction and Matrix Strength Effects on Fatigue Behavior and Particle Fracture in 2124 Aluminum-SiCp Composites, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 1994, 183(1-2), p 69-80
A.K. Ray, K. Venkateswarlu, S.K. Chaudhury, S.K. Das, B.R. Kumar, L. C. Pathak, Fabrication of TiN Reinforced Aluminium Metal Matrix Composites Through a Powder Metallurgical Route, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2002, 338(102), p 160-165
Fr.-W. Bach, L. Engl, and L.A. Josefiak, Development of Light Metal Matrix Composite Coatings Using High Velocity Thermal Spray Processes, Thermal Spray 2003: Advancing the Science and Applying the Technology, C. Moreau and B. Marple, Eds., May 5-8, 2003 (Orlando, FL, USA), ASM International, OH, 2003, p 769-777
A. Papyrin, Cold Spray Technology, Advanced Materials & Processes, Adv. Mater. Process., 2001, 159(9), p 49-51
T. Stoltenhoff, H. Kreye, H.J. Richter, An Analysis of the Cold Spray Process and Its Coating, J. Therm. Spray Technol., 2002, 11(4), 542-550
W.-Y. Li, C. Zhang, H.T. Wang, C.-J. Li, Significant Influences of Metal Reactivity and Oxide Films at Particle Surfaces on Coating Microstructure in Cold Spraying, Appl. Surf. Sci., 2007, 253(7), p 3557-3562
W.-Y. Li, X.P. Guo, C. Verdy, L. Dembinski, H.L. Liao, C. Coddet, Improvement of Microstructure and Property of Cold-sprayed Cu-4 at.% Cr-2 at.% Nb Alloy by Heat Treatment, Scripta Mater., 2006, 55(4), p 327-330
D.T. Morelli, A.A. Elmoursi, T.H. Van Steenkiste, D.W. Gorkiewicz, and B. Gillispie, Kinetic Spray of Aluminum Metal Matrix Composites for Thermal Management Applications, Thermal Spray 2003: Advancing the Science and Applying the Technology, B.R. Marple and C. Moreau, Eds., ASM International, OH, 2003, p 85-90
G.L. Eesley, A.N. Elmoursi Patel, Thermal Properties of Kinetic Spray Al-SiC Metal Matrix Composite, J. Mater. Res., 2003, 18(4), p 855-860
F. Gärtner, T. Stoltenhoff, T. Schmidt, and H. Kreye, The Cold Spray Process and Its Potential for Industrial Applications, Thermal Spray Connects: Explore Its Surfacing Potential, E. Lugscheider, Ed., DVS, Düsseldorf, 2005 (in CD-ROM)
T.H. Van Steenkiste, A. Elmoursi, D. Gorkiewicz, B. Gillispie, Fracture Study of Aluminum Composite Coatings Produced by the Kinetic Spray Method, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2005, 194(1), p 103-110
H. Weinert, E. Maeva and V. Leshchynsky, Low Pressure Gas Dynamic Spray Forming Near-net Shape Parts, Thermal Spray 2006: Building on 100 Years of Success, B.R. Marple, M.M. Hyland, Y.C. Lau, R.S. Lima, and J. Voyer, Eds., May 15-18, 2006 (Seattle, WA), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2006
J. Haynes, A. Pandey, J. Karthikeyan, and A. Kay, Cold Sprayed Discontinuously Reinforced Aluminum, Thermal Spray 2006: Building on 100 Years of Success, B.R. Marple, M.M. Hyland, Y.C. Lau, R.S. Lima, and J. Voyer, Eds., May 15-18, 2006 (Seattle, WA), ASM International, Materials Park, OH, 2006
H.K. Kang, S.B. Kang, Tungsten/Copper Composite Deposits Produced by a Cold Spray, Scripta Mater., 2003, 49(12), p 1169-1174
T. Novoselova, P. Fox, R. Morgan, W. O’Neill, Experimental Study of Titanium/aluminium Deposits Produced by Cold Gas Dynamic Spray, Surf. Coat. Technol., 2006, 200(8) p 2775-2783
S. Marx, A. Paul, A. Köhler, and G. Hüttl, Cold Spraying—Innovative Layers for New Applications, Thermal Spray connects: Explore Its Surfacing Potential, E. Lugscheider, Ed., May 2-4, 2005 (Basel, Switzerland), DVS, 2005, p 209-215
L. Ajdelsztajn, B. Jodoin, G.E. Kim, J.M. Schoenung, Cold Spray Deposition of Nanocrystaline Aluminum Alloys, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2005, 36(3), p 657-666
H.J. Kim, C.H. Lee, S.Y. Hwang, Superhard Nano WC-12%Co Coating by Cold Spray Deposition, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2005, 391(1-2), 243-248
MatWeb, http://www.matweb.com. Accessed 10 April 2007
R.S. Guo, S. Cai, H.M. Ji, H.Z. Wu, Engineering Structural Ceramics, Tianjing University Press, Tianjin, China, 2002. (in Chinese)
W.-Y. Li, G. Zhang, X.P. Guo, H.L. Liao, C. Coddet, Characterizations of Cold-sprayed TiN Particle-Reinforced Al Alloy-Based Composites—From Structures to Tribological Behaviour, Adv. Eng. Mater., 2007, 9, 577-583
J. Liu, Material Wear Principle and Wear Resistance, Tsinghua University Press, Beijing, 1993. (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Franche-Comte Regional Council of France. The authors would like to thank Lucas Dembinski of LERMPS for the supply of Al5356 powder.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, WY., Zhang, G., Zhang, C. et al. Effect of Ball Milling of Feedstock Powder on Microstructure and Properties of TiN Particle-Reinforced Al Alloy-Based Composites Fabricated by Cold Spraying. J Therm Spray Tech 17, 316–322 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-008-9182-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-008-9182-4