Abstract
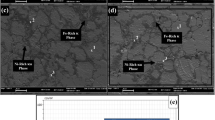
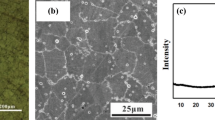
In the present study, the wear properties of 205 manganese steels produced by a casting process with different boron contents (0.0023-0.0182 wt.%) were investigated, using a pin-on-disc tribometer under dry sliding conditions. The friction coefficient of 205 manganese steel by boron addition (at 0.0076 wt.%) reduced from 0.28 to 0.18. The addition of boron to 205 manganese steel led to a decrease in the friction coefficient due to the lubricating effect of boron. X-ray diffraction showed that the boron addition to 205 manganese steel increased lattice parameters of the samples. The wear test results at 5 and 10 N loads showed that the wear amount of 205 manganese steels decreased with boron addition. Thus, the wear results showed that the wear resistance of 205 manganese steel is increased with the addition of small amounts of boron. Furthermore, scanning electron microscopy images indicated that the characteristic wear mechanisms for the boron-doped samples on the worn surfaces were abrasive, and it was plastic deformation, mild abrasive, and adhesive wear mechanism in the undoped 205 manganese steel.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Marinelli, M. Sade, and A.F. Guillermet, On the Structural Changes Accompanying the fcc/hcp Martensitic Transformation in Fe–Mn–Co Alloys, Script. Mater., 2002, 46(11), p 805–810
S.S.M. Tavares, S. Miragliab, and D. Fruchart, Hydrogen Induced Martensite in a Fe–17Mn–1.9Al–0.1C steel, J. Alloys Compds., 2003, 356–357, p 340–342
G.B. Olson and M. Cohen, A General Mechanism of Martensitic Nucleation: Part II. FCC → BCC and Other Martensitic Transformations, Met. Trans. A, 1976, 7(12), p 1905–1914
I. Meszarosa and J. Prohaszka, Magnetic Investigation of the Effect of α′-Martensite on the Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel, J. Mater. Proces. Technol., 2005, 161(1–2), p 162–168
A.A. Gulyaev, Some Features of γ-ε Martensitic Transformation and Shape Memory Effect in Fe-Mn-Si Based alloys, J. Phys. IV France, 1995, 5(C8), p C8-469–C8-474
D. Schryvers, L. Toth, J. Van Humbeeck, and J. Beyer, Ni2Al Versus Ni5Al3 Ordering in Ni65Al35 Austenite and Martensite, J. Phys. IV France, 1995, 5(C8), p C8-1029–C8-1033
M. Eskil and E. Kanca, Phase Evolution in Fe Mn Si Shape Memory Alloys Due to Forging Speed, Int. J. Mod. Phys. B, 2013, 27(32), p 1350182
G. Kniaginin, Austenitic Manganese Cast Steel, PWN, Krakow, 1968 ((in Polish))
W. Sakwa, S. Jura, and J. Sakwa, Wear Resistance Iron Alloys, STOP, Krakow, 1980 ((in Polish))
S. Hofer, M. Harti, G. Schestak, R. Schneider, E. Arenholz, and L. Samek, Comparison of Austenite High Mn-Steels with Different Mn and C Contents Regarding Their Processing Properties, BHM, 2011, 156(3), p 99–104
G. Tecza and S. Sobula, Effect of Heat Treatment on Change Microstructure of Cast High-Manganese Hadfield Steel with Elevated Chromium Content, Arch. Foundry Eng., 2014, 14(2), p 5–8
J. Glownia, G. Tecza, M. Aslanowicz, and A. Oscilowski, Tools Cast from the Steel of Composite Structure, Arch. Metall. Mater., 2013, 58(3), p 803–808
D.J. Mun, E.J. Shin, K.C. Cho, J.S. Lee, and Y.M. Koo, Cooling Rate Dependence of Boron Distribution in Low Carbon Steel, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2012, 43(5), p 1639–1648
B.M. Kapadia, R.M. Brown, and W.J. Murphy, The Influence of Nitrogen, Titanium and Zirconium on the Boron Hardenability Effect in Constructional Alloy Steels, Trans. AIME, 1968, 242, p 1689–1694
L. Karlsson, H. Norden, and H. Odelius, Non-equilibrium Grain Boundary Segregation of Boron in Austenitic Stainless Steel—I. Large Scale Segregation Behaviour, Acta Metall., 1988, 36(1), p 1–12
G.F. Melloy, P.R. Slimon, and P.P. Podgursky, Optimizing the Boron Effect, Metall. Mater. Trans. B, 1973, 4(10), p 2279–2289
P. Maitrepierre, J. Rofes-Vernis, and D. Thivellier, Boron in Steel, S.K. Banerjii and J.E. Morral, Ed., Warrendale, AIME, 1979,
D.J. Mun, E.J. Shin, Y.W. Choi, J.S. Lee, and Y.M. Koo, Effects of Cooling Rate, Austenitizing Temperature and Austenite Deformation on the Transformation Behavior of High-Strength Boron Steel, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 545, p 214–224
H.Z. Cui and W.Q. Chen, Effect of Boron on Morphology of Inclusions in Tire Cord Steel, J. Iron. Steel Res. Int., 2012, 19(4), p 22–27
M. Ueno and T. Inoue, Trans. ISIJ, 1973, 13, p 210
J.E. Morral and T.B. Cameron, A Model for Ferrite Nucleation Applied to Boron Hardenability, Metall. Trans. A, 1977, 8(11), p 1817–1819
J. Morral and T. Cameron, Boron in Steel, S.K. Banerjii and J.E. Morral, Ed., Warrendale, AIME, 1979,
G. Shigesato, T. Fujishiro, and T. Hara, Boron Segregation To Austenite Grain Boundary In Low Alloy Steel Measured by Aberration Corrected STEM–EELS, Mater. Sci. Eng. A, 2012, 556, p 358–365
P. Maitrepierre, D. Thivellier, and R. Tricot, Influence of Boron on the Decomposition of Austenite in Low Carbon Alloyed Steels, Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 1975, 6(2), p 287
B. Shen and F. Sun, Friction Behaviors of the Hot Filament Chemical Vapor Deposition Diamond Film under Ambient Air and Water Lubricating Conditions, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2009, 22(5), p 658–664
X. Wang, L. Wang, B. Shen, and F. Sun, Friction and Wear Performance of Boron Doped, Undoped Microcrystalline and Fine-Grained Composite Diamond Films, Chin. J. Mech. Eng., 2015, 28(1), p 155–163
G.F. Melloy, P.P. Slimmon, and P.P. Podgursky, Optimizing the Boron Effect, Metall. Mater. Trans., 1973, 4(10), p 2279–2289
I. Gunes, Investigation of Tribological Properties and Characterization of Borided AISI, 420 and AISI, 5120 Steels, T. Indian I. Metals, 2014, 67(3), p 359–365
M. Ulutan, O.N. Celik, H. Gasan, and U. Er, Effect of Different Surface Treatment Methods on the Friction and Wear Behavior of AISI, 4140 Steel, J. Mater. Sci. Technol., 2010, 26(3), p 251–257
M. Tabur, M. Izciler, F. Gul, and I. Karacan, Abrasive Wear Behavior of Boronized AISI, 8620 Steel, Wear, 2009, 266, p 1106–1112
L. Taekyung, M. Eshaan, R. Santhosh, and S.L. Chong, Tribological and Corrosion Behaviors of Warm- and Hot-Rolled Ti-13Nb-13Zr Alloys in Simulated Body Fluid Conditions, Int. J. Nanomed., 2015, 10, p 207–212
B. Aktas, V. Balak, and C. Carboga, Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Boron-Doped AISI, 1020 Steels, Acta Phys. Pol. A, 2017, 132(3), p 455–457
B. Aktas and H. Tekin, Effects of Co3O4 Addition on Friction and Dry Sliding Wear Characteristics of 8 mol% Yttria-Stabilized Cubic Zirconia, J. Mater. Eng. Perform., 2019, 28(1), p 549–556
Acknowledgments
Authors thank Harran University, Sanliurfa, Turkey, for allowing the use of their laboratory facilities and also thank Murat Eskil and Serkan Dal for their support in the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carboga, C., Aktas, B. & Kurt, B. Dry Sliding Wear Behavior of Boron-Doped 205 Manganese Steels. J. of Materi Eng and Perform 29, 3120–3126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04796-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11665-020-04796-9