Abstract
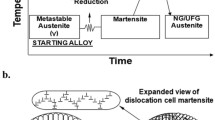
We recently described the reversal of strain-induced martensite to the parent austenite phase in the attempt to produce nanograins/ultrafine grains via controlled annealing of heavily cold-worked metastable austenite. The phase-reversion-induced microstructure consisted of nanocrystalline (d < 100 nm), ultrafine (d ≈ 100 to 500 nm), and submicron (d ≈ 500 to 1000 nm) grains and was characterized by high strength (800 to 1000 MPa)–high ductility (30 to 40 pct) combination, which was a function of cold deformation and temperature-time annealing sequence.[1] In this article, we demonstrate that the success of the approach in obtaining nanograined/ultrafine-grained (NG/UFG) structure depends on the predominance of dislocation-cell–type structure in the severely deformed martensite. Electron microscopy and selected area electron diffraction analysis indicated that with an increase in the degree of cold deformation there is transformation of lath martensite to dislocation-cell–type martensite, which is a necessary prerequisite to obtain phase-reversion-induced NG/UFG austenite. The transformation of lath-type to dislocation-cell–type martensite involves refinement of packet and lath size and break up of lath structure. Based on detailed and systematic electron microscopy study of cold-deformed metastable austenite (~45 to 80 pct deformation) and constant temperature-time annealing sequence, when the phase reversion kinetics is rapid, our hypothesis is that the maximization of dislocation-cell–type structure in lieu of lath-type facilitates NG/UFG structure with a high strength–high ductility combination. Interestingly, the yield strength follows the Hall–Petch relation in the NG/UFG regime for the investigated austenitic stainless steel.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D.K. Misra, S. Nayak, S. Mali, M.C. Somani, and L.P. Karjalainen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40A, pp. 2498–2509.
R.D.K. Misra, B. Ravi Kumar, M. Somani, and P. Karjalainen: Scripta Mater., 2008, vol. 59, pp. 79–82.
P. Juntunen, M.C. Somani, L.P. Karjalainen, R.D.K. Misra, and A. Kyrolainen: Proc. Int. Symp. on Advanced Stainless Steel (ISAS 2007), Chennai, Apr. 9–11, 2007.
M.C. Somani, P. Juntunen, L.P. Karjalainen, and R.D.K. Misra: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2009, vol. 40, pp. 729–44.
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, and Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, pp. 1431–37.
K. Tomimura, S. Takaki, S. Tanimoto, and Y. Tokunaga: ISIJ Int., 1991, vol. 31, pp. 721–27.
S. Takaki, K. Tomimura, and S. Ueda: ISIJ Int., 1994, vol. 34, pp. 522–27.
M. Tokizane, N. Natsumura, K. Tsuzaki, T. Maki, and I. Tamuri: Metall. Trans. A, 1982, vol. 13A, pp. 1379–96.
S. Rajasekhara, P.J. Ferreira, L.P. Karjalainen, and A. Kyröläinen: Metall. Mater. Trans. A, 2007, vol. 38A, pp. 1202–10.
The authors (RDKM, SAM, JSS) acknowledge support from Materials Processing program of National Science Foundation through Grant No. CMMI 0757799 (Program Manager—Dr. Joycelyn Harrison) and Center for Structural and Functional Materials (CSFM), University of Louisiana at Lafayette. The author SN is grateful for support from CSFM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Manuscript submitted July 27, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Misra, R., Nayak, S., Mali, S. et al. On the Significance of Nature of Strain-Induced Martensite on Phase-Reversion-Induced Nanograined/Ultrafine-Grained Austenitic Stainless Steel. Metall Mater Trans A 41, 3–12 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0072-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-009-0072-2