Abstract
Objective
To investigate the current status and further development of Panax genus and 6 important individual species including P. notoginseng, P. quinquefolium, P. vietnamensis, P. japonicus, P. stipuleanatus and P. zingiberensis.
Methods
The bibliometric analysis was based on the Web of Science core database platform from Thomson Reuters. Totally, 7,574 records of scientific research of Panax species published from 1900–2019 were analyzed. The statistical and visualization analysis was performed by CiteSpace and HistCite software.
Results
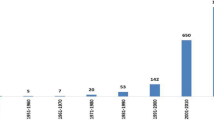
The academic research of Panax species increase promptly. Plant science is the main research field while research and experimental medicine and agricultural engineering will be the further development tendency. Particularly, the discrimination research of P. notoginseng will be the research tendency among Panax species, especially diversity research. In addition, P. vietnamensis deserves more attention in the genus Panax.
Conclusion
This research provides a reference for further research of the genus and individual species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang YP, Choi HK, Brinckmann JA, Jiang X, Huang LF. Chemical analysis of Panax quinquefolius (North American ginseng): a review. J Chromatogr A 2015;1426:1–15.
Sticher O. HPLC separation and quantitative determination of ginsenosides from Panax ginseng, Panax quinquefolium and from Ginseng drug preparations. Planta Medica (Chin) 1980;39:348–357.
Shergis JL, Zhang AL, Zhou WY, Xue CC. Panax ginseng in randomised controlled trials: a systematic review. Phytother Res 2013;27:949–965.
Pan YZ, Gong X, Yang Y. Phylogenetic position of the genus Dobinea: evidence from nucleotide sequences of the chloroplast gene rbcL and the nuclear ribosomal ITS region. J Syst Evol 2008;46:586–594.
Wen J, Zimmer EA. Phylogeny and biogeography of Panax L. (the ginseng genus, araliaceae): inferences from ITS sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Mole Phylogen Evolut 1996;6:167–177.
Xia PG, Guo HB, Zhang Y, Deyholos MK, Peng L, Jia YY, et al. Wild Panax vietnamensis and Panax stipuleanatus markedly increase the genetic diversity of Panax notoginseng (Araliaceae) revealed by start codon targeted (SCoT) markers and ITS DNA barcode. Biochem Syst Ecol 2016;66:37–42.
Du ZX, Wu J, Meng XX, Li JH, Huang LF. Predicting the global potential distribution of four endangered Panax species in middle-and low-latitude regions of China by the geographic information system for global medicinal plants (GMPGIS). Molecules Oct 2017;22:14.
Hai RS, Kim JY, Yun TK, Vainio MH. The cancer-preventive potential of Panax ginseng: a review of human and experimental evidence. Cancer Causes Control 2000;11:565–576.
Wang T, Guo RX, Zhou GH, Zhou XD, Kou ZZ, Sui F, et al. Traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology and toxicology of Panax notoginseng (Burk.) FH Chen: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 2016;188:234–258.
Sun S, Wang CZ, Tong R, Li XL, Fishbein A, Wang Q, et al. Effects of steaming the root of Panax notoginseng on chemical composition and anticancer activities. Food Chem 2010;118:307–314.
Dong TTX, Cui XM, Song ZH, Zhao KJ, Ji ZN, Lo CK, et al. Chemical assessment of roots of Panax notoginseng in China: regional and seasonal variations in its active constituents. J. Agric Food Chem 2003;51:4617–4623.
Choi HK, Wen J. A phylogenetic analysis of Panax (Araliaceae): integrating cpDNA restriction site and nuclear rDNA ITS sequence data. Plant System Evolution 2000;224:109–120.
Sun I. About the real ginseng root (Panax Ginseng, Songsan). naunyn-Schmiedeberg Archive Exper Pathol pharm 1933;170:443–457.
Yataganbaba A, Ozkahraman B, Kurtbas I. Worldwide trends on encapsulation of phase change materials: abibliometric analysis (1990–2015). Appl Energy 2017;185:720–731.
Wang YR, Wang QJ, Wei XZ, Shao J, Zhao J, Zhang ZC, et al. Global scientific trends on exosome research during 2007–2016: a bibliometric analysis. Oncotarget 2017;8:48460–48470.
Xu WQ, Zou ZM, Pei J, Huang LF. Longitudinal trend of global artemisinin research in chemistry subject areas (1983–2017). Bioorg Med Chem 2018;26:5379–5387.
Cao Y, Xu XW, Liu SJ, Huang LF, Gu J. Ganoderma: a cancer immunotherapy review. Front Pharmacol 2018;9:14.
Duong A, Kay J, Khan M, Simunovic N, Ayeni OR. Authorship in the field of femoroacetabular impingement: an analysis of journal publications. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2017;25:94–100.
Laengle S, Merigo JM, Miranda J, Slowinski R, Bomz I, Borgonovo E, et al. Forty years of the European Journal of Operational Research: a bibliometric overview. Eur J Oper Res 2017;262:803–816.
Xu WQ, Choi HK, Huang LF. State of Panax ginseng research: a global analysis. Molecules 2017;22:13.
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. Faseb J Feb 2008;22:338–342.
Redondo M, Leon L, Povedano FJ, Abasolo L, Perez-Nieto MA, Lopez-Munoz F. A bibliometric study of the scientific publications on patient-reported outcomes in rheumatology. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;46:828–833.
Khan MS, Ullah W, Bin Riaz I. Top 100 cited articles in cardiovascular magnetic resonance: a bibliometric analysis. J Cardiov Magn Reson 2016;18:6.
Zhou J, Wu M, Taniyasu S, Besso H, Tanaka O, Saruwatari Y, et al. Dammarane-Saponins of Sanchi-Ginseng, roots of Panax notoginseng (BURK.) F.H. Chen (Araliaceae): structures of new saponins, notoginsenosides-R1 and -R2, and identification of Ginsenosides-Rg2 and -Rh1. Chem Pharmaceu Bull 1981;29:2844–2850.
Kuong DD, Dovgiǐ AI, Adrianov NV, Varenitsa AI, Archakov AI. Induction of cytochrome P-450 by triterpensaponins in Vietnamese ginseng. Biokhimiia 1991;56:707–713.
Yahara S, Kasai R, Tanaka O. New dammarane type saponins of leaves of Panax japonicus C.A. Meyer (1). Chikusetsusaponins L5, L9(a) and L10. Chem Pharmaceu Bull 2008;25:2041–2047.
Hideo H, Satoshi M, Masamori U, Tomonori K, Yoshio I, Ryoji K. Inhibitory effect of some triterpenoid saponins on glucose transport in tumor cells and its application to in vitro cytotoxic and antiviral activities. Planta Med 1994;60:240–243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Zeng TX drafted the original manuscript; Pei J and Zhao L contributed to supervision and investigation. Miao YJ performed data curation and formal analysis; Zheng Y and Gu SJ wrote and edited this paper; Huang LF contributed to review writing, editing and supervision.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Supported by Beijing Natural Scientific Foundation (No. 7202135), National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1812403-1-1, No. 81473315), National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (No. 2018FY100701), the Open Research Fund of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine Key Laboratory of Systematic Research of Distinctive Chinese Medicine Resources in Southwest China (No.SCMR20210, 2021GZ2011003)
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeng, Tx., Pei, J., Miao, Yj. et al. Current Status and Research Trends of Panax Between 1900–2019: A Bibliometric Analysis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 28, 547–553 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3315-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-021-3315-8