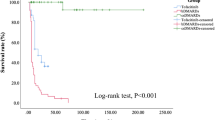
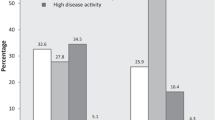
Abstract
Pre-rheumatoid arthritis is the inevitable phase before the actual onset of rheumatoid arthritis and has the crucial clinical significance of early controlling and preventing disease progression. Full understanding, from both Western medicine (WM) and Chinese medicine (CM), could offer new ideas for decision making in clinical and mechanism research. This paper reviews the novel studies of WM and CM to discuss the advantages and potential mechanisms working behind.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerlag DM, Raza K, Van Baarsen LGM, Brouwer E, Buckley CD, Burmester GR, et al. EULAR recommendations for terminology and research in individuals at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: Report from the Study Group for Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:638–641.
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO, et al. 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 2010;62:2569–2581.
Bizzaro N, Bartoloni E, Morozzi G, Manganelli S, Riccieri V, Sabatini P, et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titer predicts time to rheumatoid arthritis onset in patients with undifferentiated arthritis: results from a 2-year prospective study. Arthritis Res Ther. 2013;15(R16):1–9.
Rakieh C, L Nam J, Hunt L, Hensor EMA, Das S, Bissell LA, et al. Predicting the development of clinical arthritis in anti-CCP positive individuals with non-specific musculoskeletal symptoms: a prospective observational cohort study. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:1659–1666.
Macías-Segura N, Castañeda-Delgado JE, Bastian Y, Santiago-Algarra D, Castillo-Ortiz JD, Alemán-Navarro AL, et al. Transcriptional signature associated with early rheumatoid arthritis and healthy individuals at high risk to develop the disease. PLoS One 2018;13:1–19.
Okamoto Y, Parish M, Kongpachith S, Lauren J, Kinslow J. IgA Plasmablasts are elevated in subjects at risk for future rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2016;68:2372–2383.
Manley G, Conn JR, Catchpoole EM, Runnegar N, Mapp SJ, Markey KA. Peptidylarginine deiminase from Porphyromonas gingivalis citrullinates human fibrinogen and α-enolase: implications for autoimmunity in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 2017;32:736–740.
Alpizar-Rodriguez D, Lesker TR, Gronow A, Gilbert B, Raemy E, Lamacchia C, et al. Prevotella copri in individuals at risk for rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:590–593.
Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 2017;76:960–977.
Machold KP, Landewé R, Smolen JS, Stamm TA, Van Der Heijde DM, Verpoort KN, et al. The Stop Arthritis Very Early (SAVE) trial, an international multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial on glucocorticoids in very early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:495–502.
Eriko KT, Takashi S, Takuro N, Satoru T, Maiko Y, Akane W, et al. Early therapeutic intervention with methotrexate prevents the development of rheumatoid arthritis in patients with recent-onset undifferentiated arthritis: a prospective cohort study. Mod Rheumatol 2015;25:831–836.
Van Aken J, Heimans L, Gillet-Van Dongen H, Visser K, Karel Ronday H, Speyer I, et al. Five-year outcomes of probable rheumatoid arthritis treated with methotrexate or placebo during the first year (the PROMPT study). Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:396–400.
Wevers-De Boer K, Visser K, Heimans L, Ronday HK, Molenaar E, Groenendael JHLM, et al. Extended report: Remission induction therapy with methotrexate and prednisone in patients with early rheumatoid and undifferentiated arthritis (the IMPROVED study). Ann Rheum Dis 2012;71:1472–1477.
Weinblatt ME, McInnes IB, Kremer JM, Miranda P, Vencovsky J, Guo X, et al. A randomized phase II b study of mavrilimumab and golimumab in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 2018;70:49–59.
Luo Q, Jiangqing Y, Lulu Z, Zhongqin L, Zhen D, Xue L, et al. Elevated expression of PD-1 on T cells correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Med Rep 2018;17:3297–3305.
Gerlag DM, Safy M, Maijer KI, Tang MW, Tas SW, Starmans-Kool MJF, et al. Effects of B-cell directed therapy on the preclinical stage of rheumatoid arthritis: The PRAIRI study. Ann Rheum Dis 2019;78:179–185.
Emery P, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Combe BG, Furst DE, Barré E, et al. Evaluating drug-free remission with abatacept in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from the phase 3b, multicentre, randomised, active-controlled AVERT study of 24 months, with a 12-month, double-blind treatment period. Ann Rheum Dis 2015;74:19–26.
Smolen JS, Wollenhaupt J, Gomez-Reino JJ, Grassi W, Gaillez C, Poncet C, et al. Attainment and characteristics of clinical remission according to the new ACR-EULAR criteria in abatacept-treated patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: new analyses from the Abatacept study to Gauge Remission and joint damage progression in methotrexate. Arthritis Res Ther 2015;17:1–12.
Heimans L, Wevers-de Boer KVC, Visser K, Goekoop RJ, Van Oosterhout M, Harbers JB, et al. A two-step treatment strategy trial in patients with early arthritis aimed at achieving remission: the improved study. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1356–1361.
Saleem B, Mackie S, Quinn M, Nizam S, Hensor E, Jarrett S, et al. Does the use of tumour necrosis factor antagonist therapy in poor prognosis, undifferentiated arthritis prevent progression to rheumatoid arthritis? Ann Rheum Dis 2008;67:1178–1180.
Xie ZJ, Wen CP, Wang XC, Cao LY, Fan YS. The clinical research of the Jiedu Tongluo Qushi principle on treating the rheumatoid arthritis in active stage. Chin J Basic Med Tradit Chin Med (Chin) 2008;14:865–867.
Hunt L, Emery P. Defining populations at risk of rheumatoid arthritis: the first steps to prevention. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2014;10:521–530.
Daily JW, Zhang T, Cao S, Park S. Efficacy and safety of Guizhi-Shaoyao-Zhimu Decoction for treating rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Altern Complement Med 2017;10:756–770.
Huang L, Lv Q, Xie D, Shi T, Wen C. Deciphering the potential pharmaceutical mechanism of Chinese traditional medicine (Gui-Zhi-Shao-Yao-Zhi-Mu) on rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep 2016;6:22602.
Wen CP, Jin CY, Xu ZL, Cao LY. Clinical observation of Jiedu Tongluo Lishi Decoction on treating reactive rheumatoid arthritis. China J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2007;13;1306–1310.
Lv QW, Zhang W, Shi Q, Zheng WJ, Li X, Chen H, et al. Comparison of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F with methotrexate in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis (TRIFRA): a randomised, controlled clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis 2015; 74:1078–1086.
Luo J, Jin DE, Yang GY, Zhang YZ, Wang JM, Kong WP, et al. Total glucosides of paeony for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Complement Ther Med 2017;34:46–56.
Liu WW, Qian X, Ji W, Lu Y, Wei G, Wang Y. Effects and safety of sinomenine in treatment of rheumatoid arthritis contrast to methotrexate: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. J Tradit Chin Med 2016;36:564–577.
Huang L, Xie D, Yu Y, Liu H, Shi Y, Shi T. TCMID 2.0: a comprehensive resource for TCM. Nucleic Acids Res 2018;46:D1117–D1120.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (No. 2018YFC1705500)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, Xy., Wen, Cp. On Research Progress of Western and Chinese Medicine Treatment on Pre-Rheumatoid Arthritis. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 25, 643–647 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3223-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3223-3