Abstract
Objective
To investigate a Met-controlled allosteric module (AM) of neural generation as a potential therapeutic target for brain ischemia.
Methods
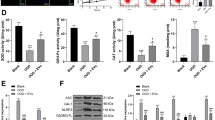
We selected Markov clustering algorithm (MCL) to mine functional modules in the related target networks. According to the topological similarity, one functional module was predicted in the modules of baicalin (BA), jasminoidin (JA), cholic acid (CA), compared with I/R model modules. This functional module included three genes: Inppl1, Met and Dapk3 (IMD). By gene ontology enrichment analysis, biological process related to this functional module was obtained. This functional module participated in generation of neurons. Western blotting was applied to present the compound-dependent regulation of IMD. Co-immunoprecipitation was used to reveal the relationship among the three members. We used IF to determine the number of newborn neurons between compound treatment group and ischemia/reperfusion group. The expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) were supposed to show the changing circumstances for neural generation under cerebral ischemia.
Results
Significant reduction in infarction volume and pathological changes were shown in the compound treatment groups compared with the I/R model group (P<0.05). Three nodes in one novel module of IMD were found to exert diverse compound-dependent ischemic-specific excitatory regulatory activities. An anti-ischemic excitatory allosteric module (AME) of generation of neurons (AME-GN) was validated successfully in vivo. Newborn neurons increased in BJC treatment group (P<0.05). The expression of VEGF and MMP-9 decreased in the compound treatment groups compared with the I/R model group (P<0.05).
Conclusions
AME demonstrates effectiveness of our pioneering approach to the discovery of therapeutic target. The novel approach for AM discovery in an effort to identify therapeutic targets holds the promise of accelerating elucidation of underlying pharmacological mechanisms in cerebral ischemia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang Z, Liu J, Yu YN, Chen YY, Wang YY. Modular pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Expert Opin Drug Discov 2012;7:667–677.
Cohen MR, Kohn A. Measuring and interpreting neuronal correlations. Nat Neurosci 2011;14:811–819.
Miri A, Daie K, Arrenberg AB, Baier H, Aksay E, Tank DW. Spatial gradients and multidimensional dynamics in a neural integrator circuit. Nat Neurosci 2011;14:1150–1159.
Talpalar AE, Endo T, Low P, Borgius L, Hagglund M, Dougherty KJ, et al. Identification of minimal neuronal networks involved in flexor-extensor alternation in the mammalian spinal cord. Neuron 2011;71:1071–1084.
Mizuseki K, Diba K, Pastalkova E, Buzsaki G. Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers. Nat Neurosci 2011;14:1174–1181.
Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, Harper JW. Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature 2010;466:68–76.
Hernandez CC, Zaika O, Tolstykh GP, Shapiro MS. Regulation of neural KCNQ channels: signaling pathways, structural motifs and functional implications. J Physiol 2008;586:1811–1821.
Schadt EE, Lum PY. Thematic review series: systems biology approaches to metabolic and cardiovascular disorders. Reverse engineering gene networks to identify key drivers of complex disease phenotypes. J Lipid Res 2006;47:2601–2613.
Lusis AJ, Weiss JN. Cardiovascular networks: systems-based approaches to cardiovascular disease. Circulation 2010;121:157–170.
Girirajan S, Truong HT, Blanchard CL, Elsea SH. A functional network module for Smith-Magenis syndrome. Clin Genet 2009;75:364–374.
Baranzini SE, Galwey NW, Wang J, Khankhanian P, Lindberg R, Pelletier D, et al. Pathway and network-based analysis of genome-wide association studies in multiple sclerosis. Hum Mol Genet 2009;18:2078–2090.
Piechota M, Korostynski M, Solecki W, Gieryk A, Slezak M, Bilecki W, et al. The dissection of transcriptional modules regulated by various drugs of abuse in the mouse striatum. Genome Biol 2010;11:R48.
Thiagalingam S. A cascade of modules of a network defines cancer progression. Cancer Res 2006;66:7379–7385.
Sameith K, Antczak P, Marston E, Turan N, Maier D, Stankovic T, et al. Functional modules integrating essential cellular functions are predictive of the response of leukaemia cells to DNA damage. Bioinformatics 2008;24:2602–2607.
Wong DJ, Nuyten DS, Regev A, Lin M, Adler AS, Segal E, et al. Revealing targeted therapy for human cancer by gene module maps. Cancer Res 2008;68:369–378.
Lunghi P, Giuliani N, Mazzera L, Lombardi G, Ricca M, Corradi A, et al. Targeting MEK/MAPK signal transduction module potentiates ATO-induced apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells through multiple signaling pathways. Blood 2008;112:2450–2462.
Rotem E, Loinger A, Ronin I, Levin-Reisman I, Gabay C, Shoresh N, et al. Regulation of phenotypic variability by a threshold-based mechanism underlies bacterial persistence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:12541–12546.
Hofer SB, Ko H, Pichler B, Vogelstein J, Ros H, Zeng H, et al. Differential connectivity and response dynamics of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in visual cortex. Nat Neurosci 2011;14:1045–1052.
Yan SK, Xin WF, Luo GA, Wang YM, Cheng YY. Simultaneous determination of major bioactive components in Qingkailing injection by high-performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 2005;53:1392–1395.
Zhang ZJ, Wang Z, Zhang XY, Ying K, Liu JX, Wang YY. Gene expression profile induced by oral administration of baicalin and gardenin after focal brain ischemia in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2005;26:307–314.
Zhang ZJ, Li P, Wang Z, Li PT, Zhang WS, Sun ZH, et al. A comparative study on the individual and combined effects of baicalin and jasminoidin on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Brain Res 2006;1123:188–195.
Liu J, Zhang ZJ, Zhou CX, Wang Y, Cheng YY, Duan DY, et al. Outcome-dependent global similarity analysis of imbalanced core signaling pathways in ischemic mouse hippocampus. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 2012;11:1070–1082.
Yu Y, Zhang X, Li B, Zhang Y, Liu J, Li H, et al. Entropy-based divergent and convergent modular pattern reveals additive and synergistic anticerebral ischemia mechanisms. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2016;241:2063–2074.
Chen YY, Yu YN, Zhang YY, Li B, Liu J, Li DF, et al. Quantitative determination of flexible pharmacological mechanisms based on topological variation in mice anti-ischemic modular networks. PLoS One 2016;11:e0158379.
Li B, Liu J, Zhang YY, Wang PQ, Yu YN, Kang RX, et al. Quantitative identification of compound-dependent on-modules and differential allosteric modules from homologous ischemic networks. CPT Pharmacometr Syst Pharmacol 2016;5:575–584.
Zhang ZJ, Wang LY, Wang Z, Li PT, Wang YY. Pharmacological evaluation of baicalin and jasminoidin and their combination on focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin J Chin Mater Med (Chin) 2006;31:907–910.
Jing ZW, Yan ZL, Zhou CX, Wang LY, Liu J, Wu HL, et al. Comparison of the network structural characteristics of calcium signaling pathway in cerebral ischemia after intervention by different components of Chinese medicine. J Tradit Chin Med 2011;31:251–255.
Wang Z, Jing ZW, Zhou CX, Zhang L, Cheng J, Zhang ZJ, et al. Fusion of core pathways reveals a horizontal synergistic mechanism underlying combination therapy. Eur J Pharmacol 2011;667:278–286.
Riccio A. Dynamic epigenetic regulation in neurons: enzymes, stimuli and signaling pathways. Nat Neurosci 2010;13:1330–1337.
Sales-Pardo M, Guimera R, Moreira AA, Amaral LA. Extracting the hierarchical organization of complex systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:15224–15229.
Meshi O, Shlomi T, Ruppin E. Evolutionary conservation and over-representation of functionally enriched network patterns in the yeast regulatory network. BMC Syst Biol 2007;1:1–7.
Chen Y, Wang Z, Wang Y. Spatiotemporal positioning of multipotent modules in diverse biological networks. Cell Mol Life Sci 2014;71:2605–2624.
Parkkinen JA, Kaski S. Searching for functional gene modules with interaction component models. BMC Syst Biol 2010;4:4–14.
Schaaf CP, Benzing J, Schmitt T, Erz DH, Tewes M, Bartram CR, et al. Novel interaction partners of the TPR/MET tyrosine kinase. FASEB J 2005;19:267–269.
Koch A, Mancini A, El BO, Tamura T. The SH2-domian-containing inositol 5-phosphatase (SHIP)-2 binds to c-Met directly via tyrosine residue 1356 and involves hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)-induced lamellipodium formation, cell scattering and cell spreading. Oncogene 2005;24:3436–3447.
Schoch HJ, Fischer S, Marti HH. Hypoxia-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression causes vascular leakage in the brain. Brain 2002;125:2549–2557.
Zhou QQ, Liu CE, Wang J, Wang YL, Zhou B. Correlation of vascular endothelial growth factor to permeability of blood-brain barrier and brain edema during high-altitude exposure. Neur Regener Res 2009;10:775–779.
Wang L, Li Z, Zhang X, Wang S, Zhu C, Miao J, et al. Protective effect of shikonin in experimental ischemic stroke: attenuated TLR4, p-p38MAPK, NF-kappaB, TNF-alpha and MMP-9 expression, up-regulated claudin-5 expression, ameliorated BBB permeability. Neurochem Res 2014;39:97–106.
Ernst A, Alkass K, Bernard S, Salehpour M, Perl S, Tisdale J, et al. Neurogenesis in the striatum of the adult human brain. Cell 2014;156:1072–1083.
Macas J, Nern C, Plate KH, Momma S. Increased generation of neuronal progenitors after ischemic injury in the aged adult human forebrain. J Neurosci 2006;26:13114–13119.
Hou SW, Wang YQ, Xu M, Shen DH, Wang JJ, Huang F, et al. Functional integration of newly generated neurons into striatum after cerebral ischemia in the adult rat brain. Stroke 2008;39:2837–2844.
Acknowledgement
Special thanks to Hang XY and Fang WB for their technical assistances in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Li KN and Wang Z designed the research. Li KN, Zhang YY, and Yu YN performed the research and analyzed data. Wu HL performed the text mining. Li KN drafted the manuscript. All authors gave final approval of the version to be published, and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Additional information
Conflict of Interest
All authors have no conflict of interest regarding this paper.
Supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (No. 7174298), Miaopu Project of Beijing Tiantan Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University (No. 2014MP04) and the 51th lot General Financial Grant from the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 2012M510723)
Electronic Supplementary Material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Kn., Zhang, Yy., Yu, Yn. et al. Met-Controlled Allosteric Module of Neural Generation as A New Therapeutic Target in Rodent Brain Ischemia. Chin. J. Integr. Med. 27, 896–904 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3182-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11655-019-3182-8